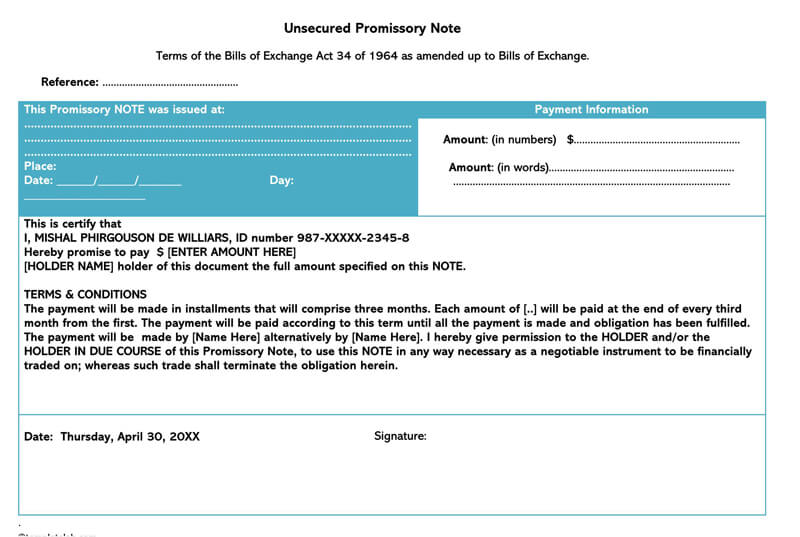
An unsecured promissory note is a financial instrument which showcases some written promise to repay a given amount of money in the future or on-demand.
It contains all the tiny details of the loan like how the borrower intends to repay the debt and the associated timeline.
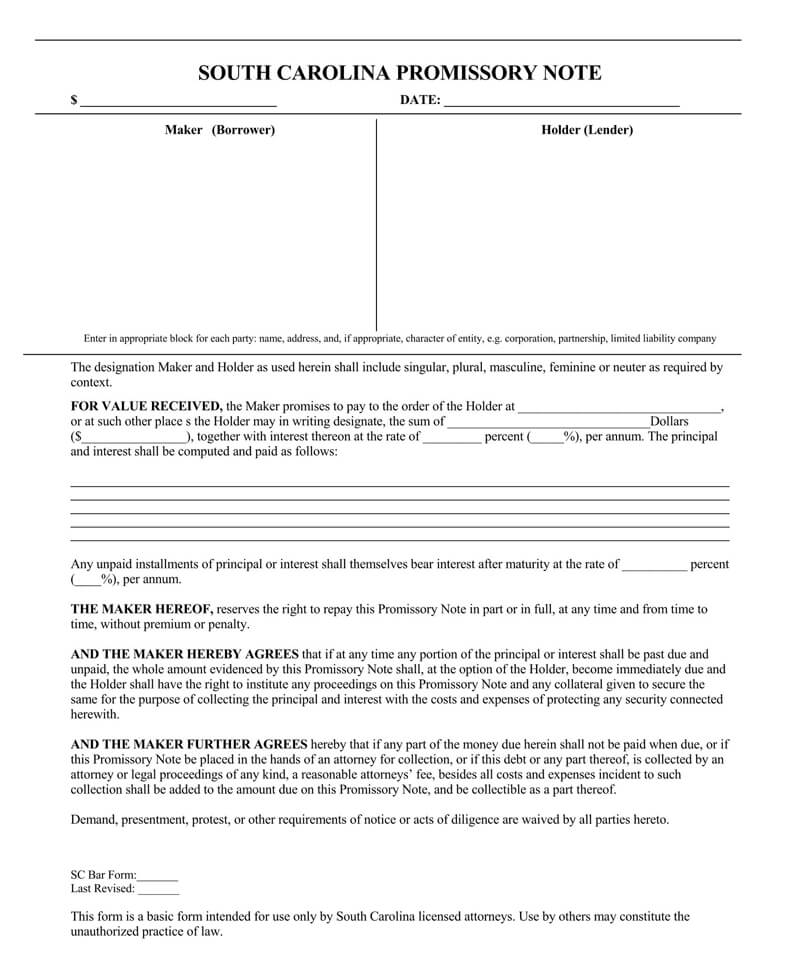
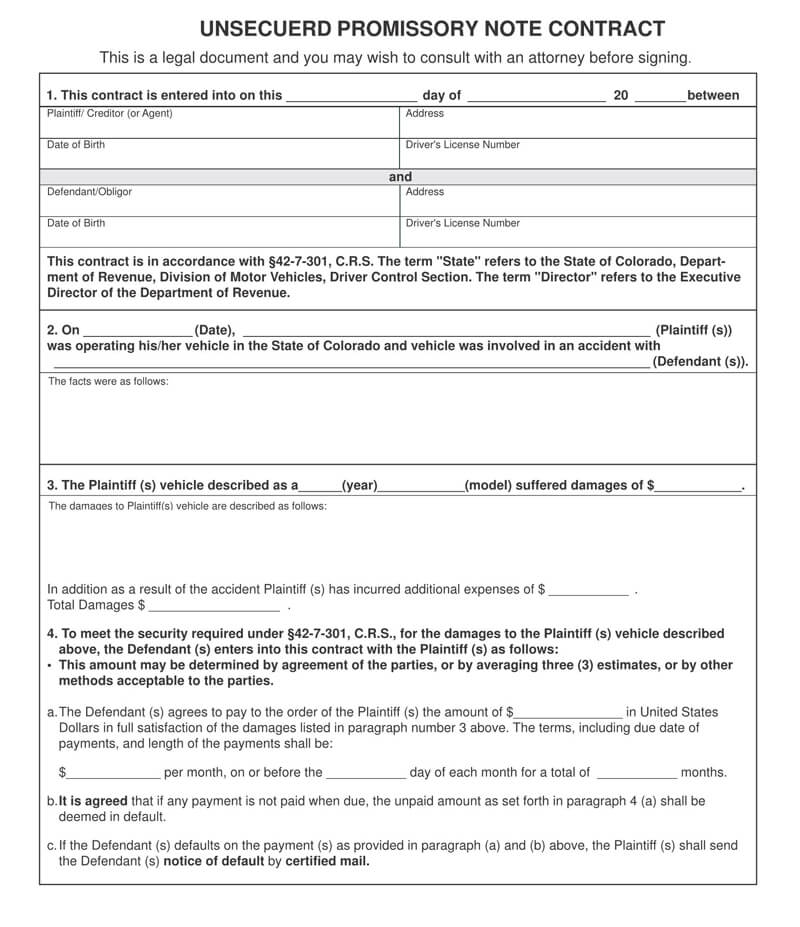
Free Unsecured Promissory Note Templates






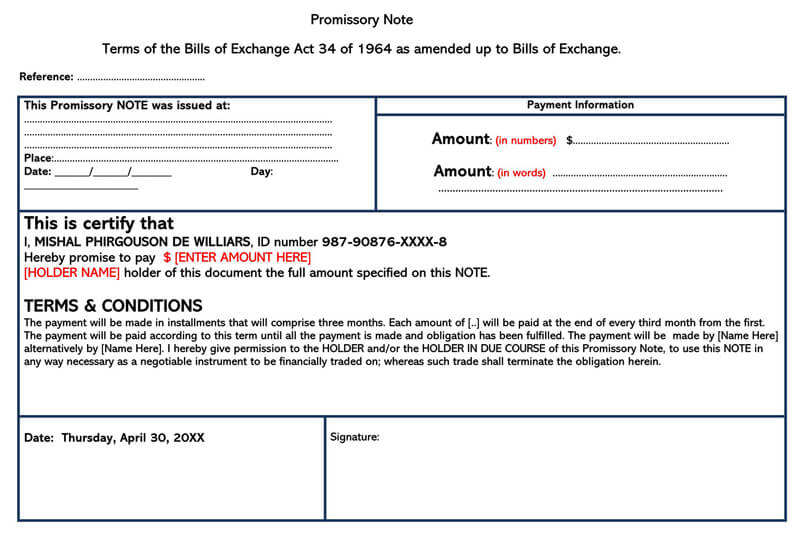








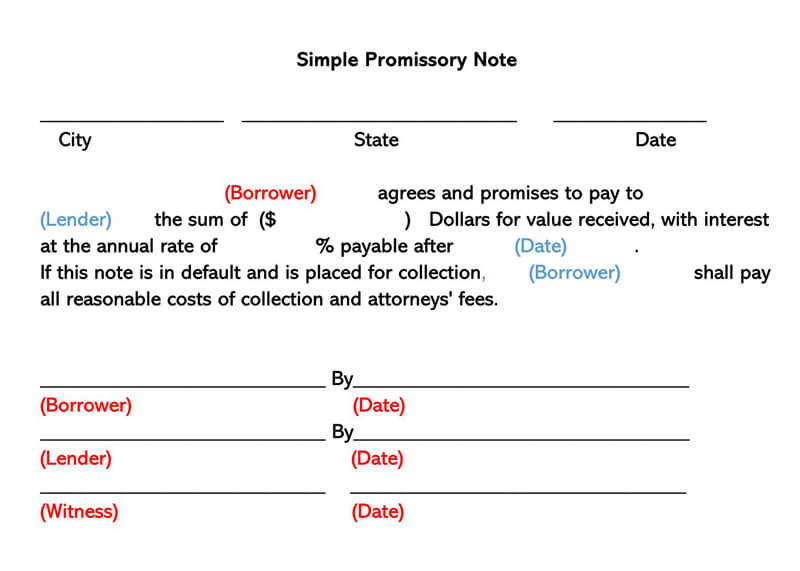




Unsecured Vs Secured Promissory Note
A secured promissory note is not so different from the unsecured counterpart. It, however, has the added benefit of attaching some collateral which may be withheld in the event that the borrower defaults on the loan repayment. This makes it safer and more reliable to make do with.
How to Write an Unsecured Promissory Note?
The promissory note has several parts and headings. The following are the major headings and what each stands for:
Borrower’s promise to pay
First and foremost, the borrower expresses the intent and willingness to repay the debt. He expressly states the amount of money he intends to borrow and the intention to repay it. Also included is the manner in which the debt is to be repaid.
Interest
Most lenders will give out their money at a fee. This is called interest. The note yet again spells out the interest levied on the principal amount. It also states exactly when the interest is payable and the manner in which it is to be remitted.
Payments
This forms the core of the note. It provides a breakdown of the payment of the amount borrowed. Specifically, it states the time and place of payments and the total amount of monthly payments.
Borrower’s right to repay
The borrower’s right to repay actually forms the core of this note. It is the one that categorically states that the borrower will actually pay back the loan taken. Further to that, it also spells out the manner in which the repayment is to take place.
Loan charges
Most lenders will give out the loans subject to some charges. Yet again, this note clearly states the interest chargeable on the loan. It also states how the interest is to be repaid and the total length of time that such repayment is to take.
Borrower’s failure to pay as required
Obviously, the possibility that a borrower may fail to pay back the debt as required is rife. It is only logical to appreciate this reality while drafting such a note. While at it, take care of the following issues:
- Surcharges for late receipts of payments and overdue – How much money shall the borrower have to part with in the form of a penalty? When shall such changes take effect? What is the full extent of the charges?
- Defaults – After how long shall the borrower deem to have defaulted? What happens at such a time?
- Notice of Default – In the unlikely event that the borrower is to default, he, as a matter of courtesy, has to inform the lender in advance. This is the role that the ‘notice of default’ dares to play. The note showcases how this notice is issued out if and when need be.
- Zero Waiver by Note Holder – A ‘notice of default’ is drafted from time to time and on a case-by-case basis. That means if the lender accepts a default at one time, the same might not automatically apply at another time of default. The permission will have to be sought afresh and separately.
- Remittances of the Note Holder’s Expenses and Costs – In case there are any costs involved in implementing the note, such are incurred by the borrower, rather than the lender (note holder). This information makes this plain.
Giving of notices
In the course of repaying the debt, it may not always be that you pay up the installments in time. Indeed, many are the times you will have to default. To avoid any penalties or unnecessary legal actions, you will have to notify your creditor in time. You have to specify this on your note.
Obligations of persons under this note
If the note is signed by more than one participant, each party is obligated to do his part insofar as enforcing the terms of the note are concerned. This requirement also gives the holder the leeway to enforce it against each signatory individually or jointly.
Notice of dishonor
Lastly, the note holder is also obliged to file a notice of dishonor in the event of a default. This simply notifies each party to the agreement of the failure to receive the amount due at the stated time.

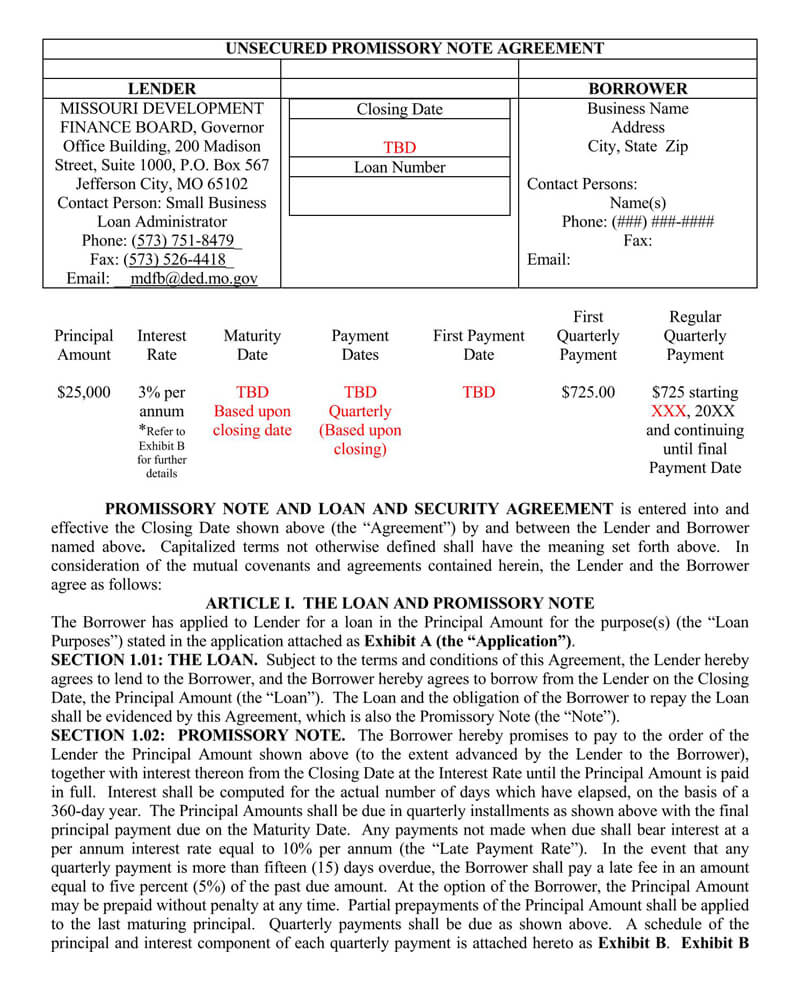


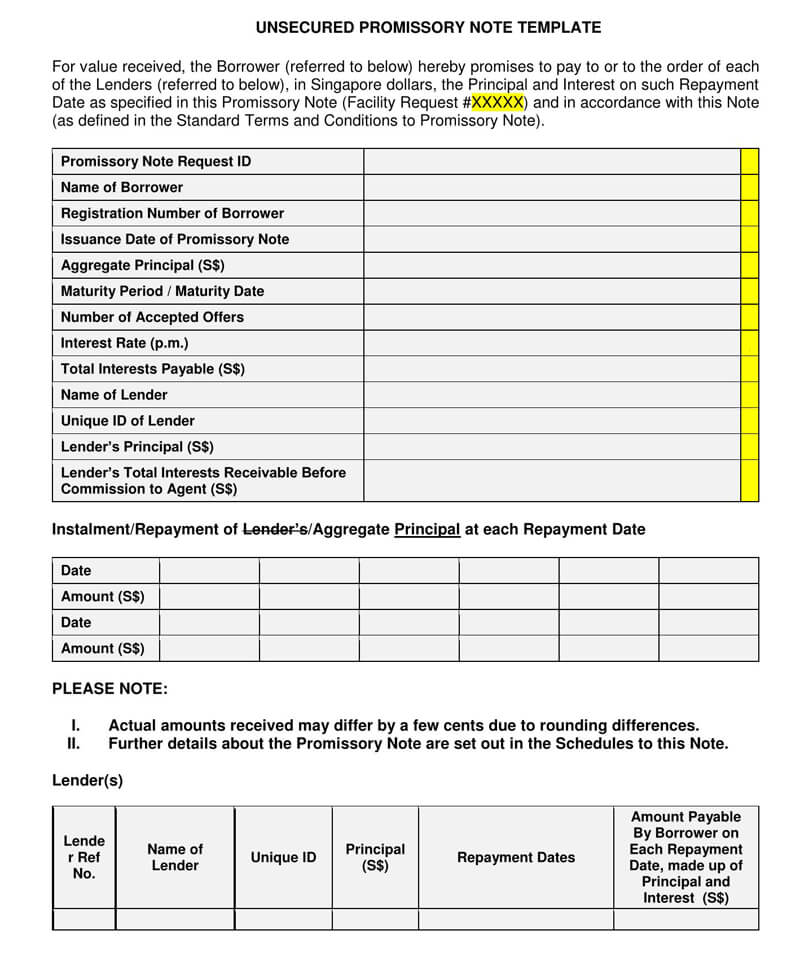












How Enforceable is an Unsecured Promissory Note?
Enforcing the note is quite tricky given the lack of collateral. However, all is not lost. There are subtle ways and means of enforcing this agreement. Below are the four main ways of enforcing it:
Issuing the threat of legal action
You may opt to issue a threat of legal action. Many people will usually get scared of this threat in and of itself. If they receive such a threat, they will often quickly resolve to repay the debt promptly.
Filing a petition
In case the borrower persists in his default even after issuing the threat above, you now move to the next step of filing a petition. You then hope that the court heeds your plea and rules in your favor.
Sell the promissory note to an independent entity
Sell the note, if you can, to an independent entity. They will pay you your money and then make arrangements thereafter to extract it from the borrower.
Enlist the services of a professional debt collection agency
As a final option, you may enlist the services of a professional debt collection agency. This is a good avenue to choose if the lender in question is a member of your family. You do not want to harm the bonds and relations that exist between you.
Frequently Asked Question
An unsecured promissory note, though legally recognized, is difficult in court. That is because no collateral is issued against the debt. If it is secured though, it is not only accepted but also easily enforced both in and out of the court.












