A “Carat” is a unit of weight used to measure diamonds and gemstones’ weight. It is represented by the letter “ct” in its abbreviation. The actual system of carat weights for diamonds is known as “points,” and it is different from the system used to measure gold alloys. In this article, we have provided the most precise and actual carat size charts. But first, let us get a basic know-how of the different terms used:
A diamond’s carat weight refers to its weight in pure diamonds and not the mass of any setting (e.g., gold, silver, platinum) or other metals that might include a diamond in a ring.
A “diamond carat weight chart” shows that one carat is equal to 0.2g, divided into 100 points. This implies that two diamonds of the same size and weight could differ in carat weight as much as 0.8g if one weighs 200 points and the other 168 points under similar conditions.
It is important to understand the difference between a diamond carat and a gold karat. A “karat” is a unit of measurement used to indicate the purity of gold alloys. Pure gold is 24 karats. For instance, 24-karat gold is 100% pure gold. The higher the karat number, the greater the percentage of gold in the alloy.
On the contrary, Carats in diamonds have nothing to do with its purity. It is simply a measure of weight. The higher the carat weight of a diamond, the rarer and more expensive it is.
What is a Diamond Carat Chart?
A diamond carat chart is a system of measuring the size of a diamond. It is the standard unit for measuring diamonds and calculates how much one stone weighs compared to another. One of the essential elements to consider when purchasing a diamond item is the diamond carat chart, one of diamonds 4c’s-carat, clarity, color, and cut.
The 4c’s of diamonds are the criteria by which diamonds are judged and are the most important factors in determining a diamond’s value. The diamond carat chart measures a diamond in milligrams and determines how much each diamond weighs. The size of the diamond is not solely dependent on its weight but also on its cut and clarity.
EXAMPLE
1-carat diamond may be smaller than a 0.90-carat diamond if it is lower quality. The size of a diamond is also determined by its setting. Diamonds with the same carat weight may vary in size if they are set in different types of rings or necklaces.
Actual Carat Size Charts
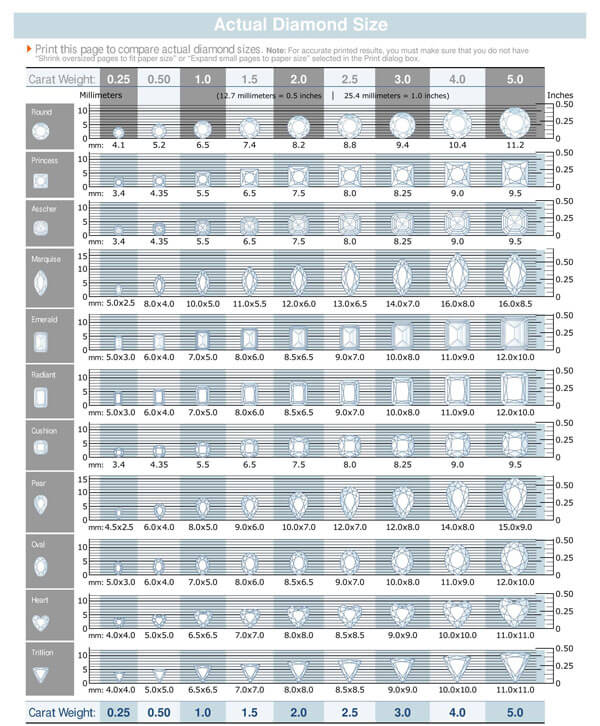
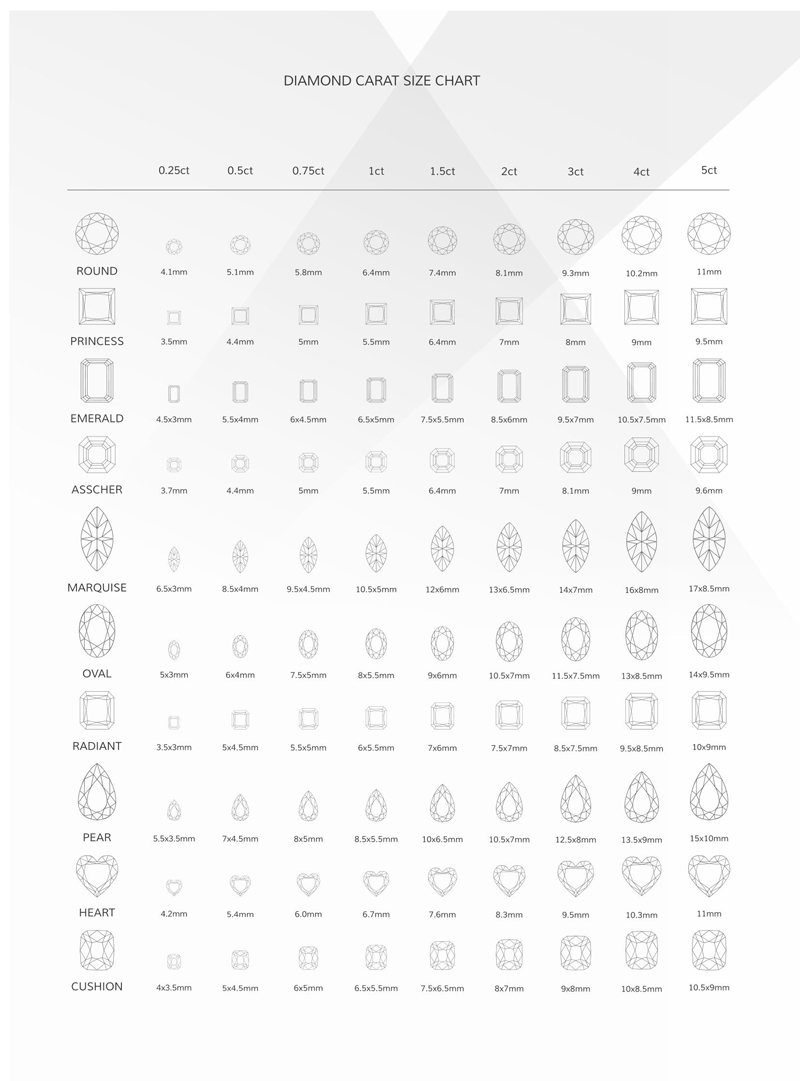


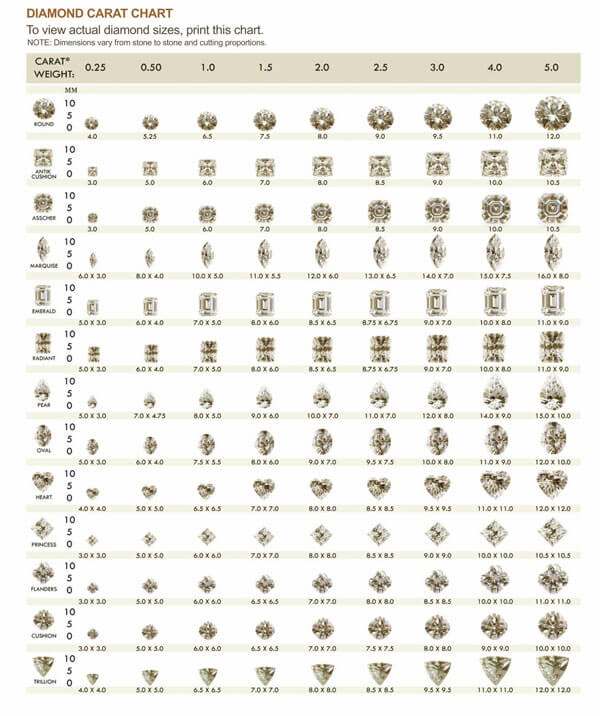
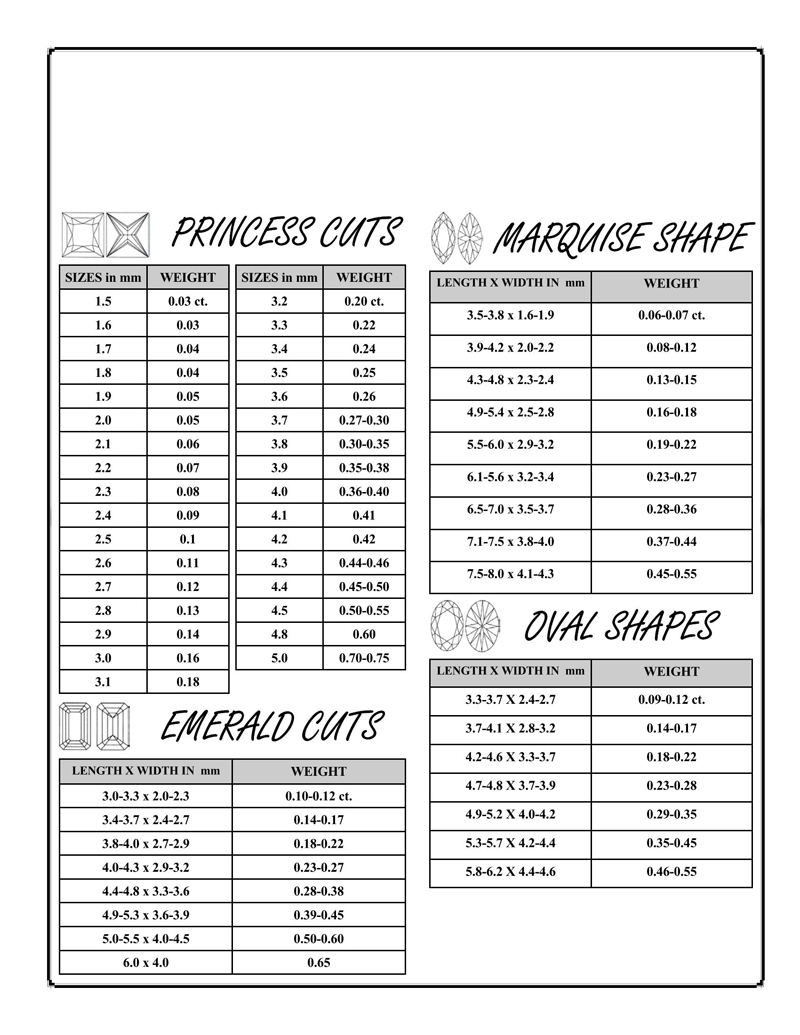
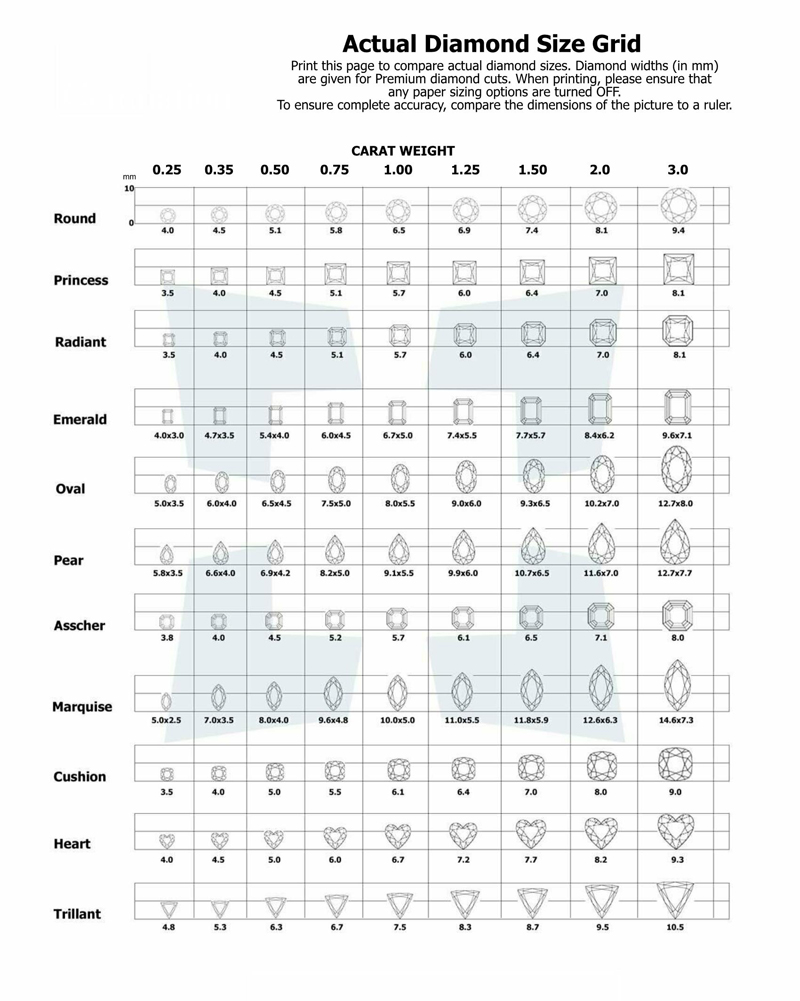
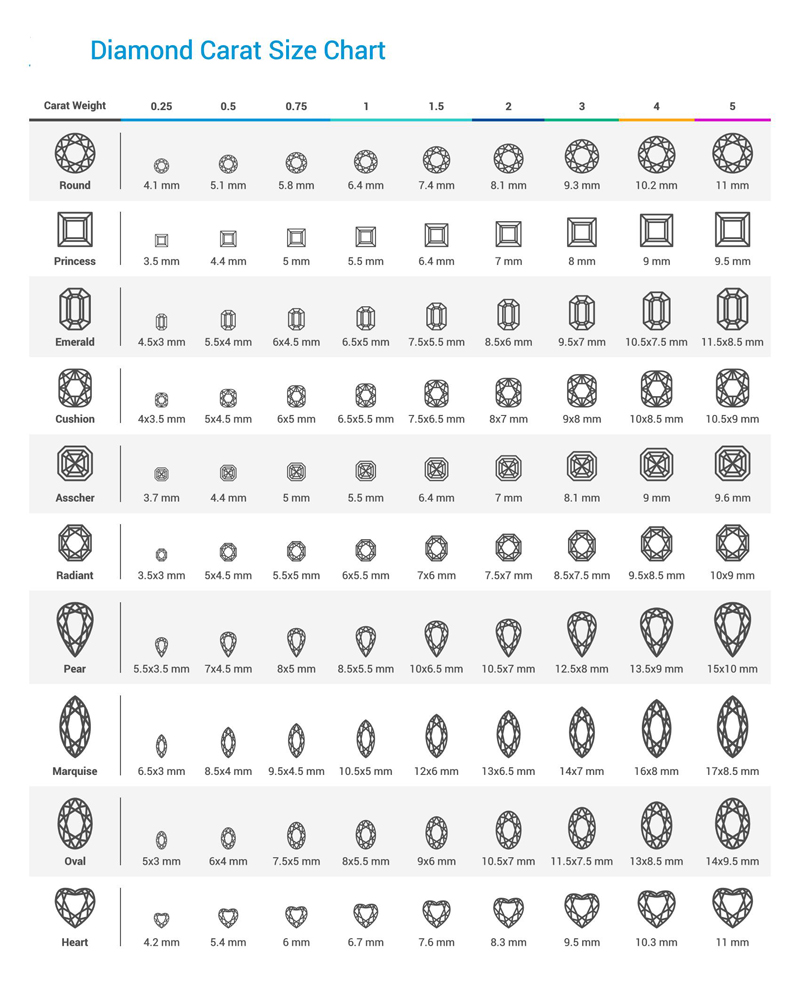
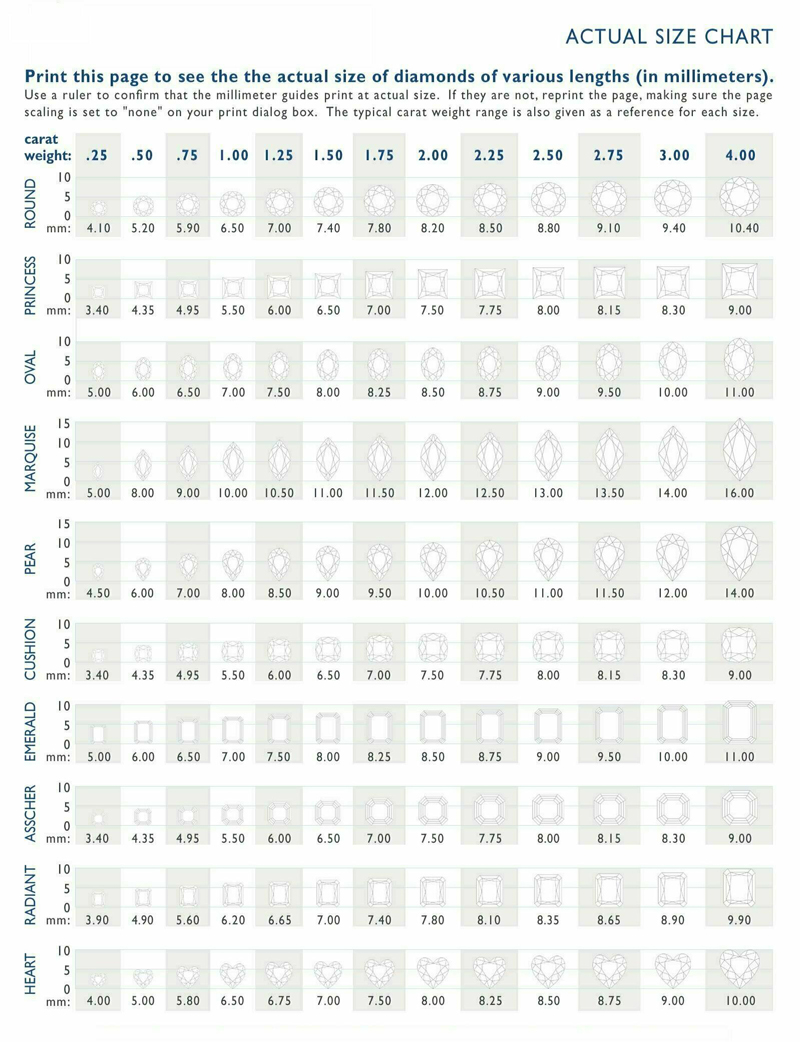

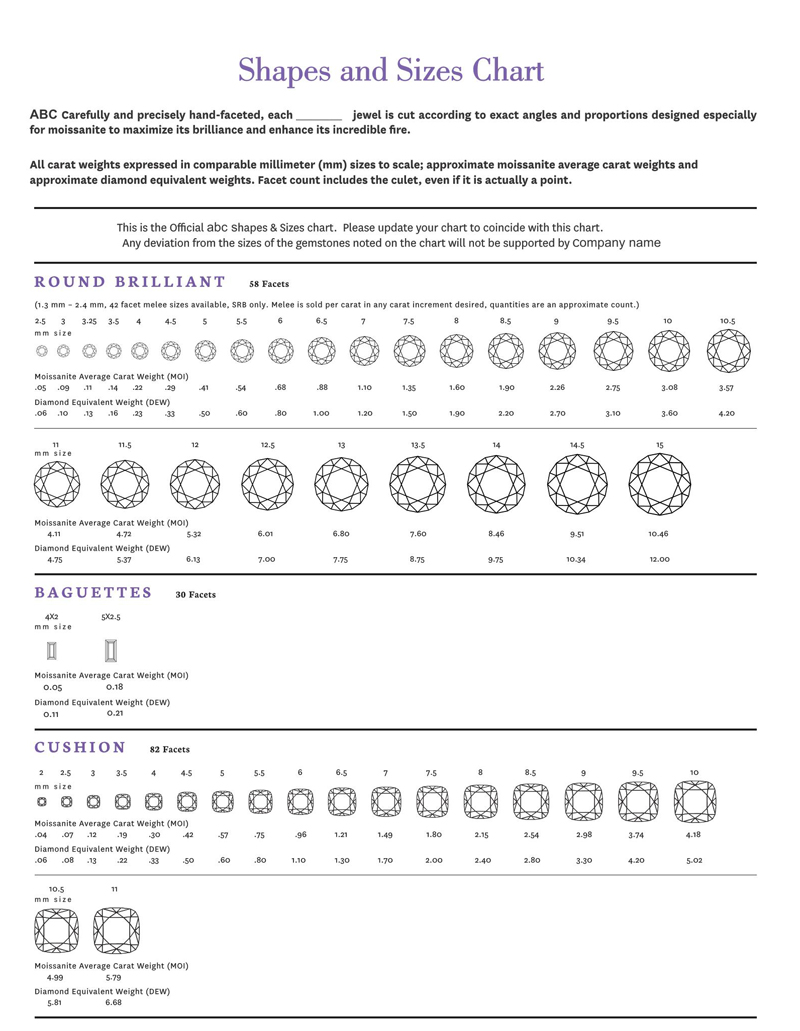
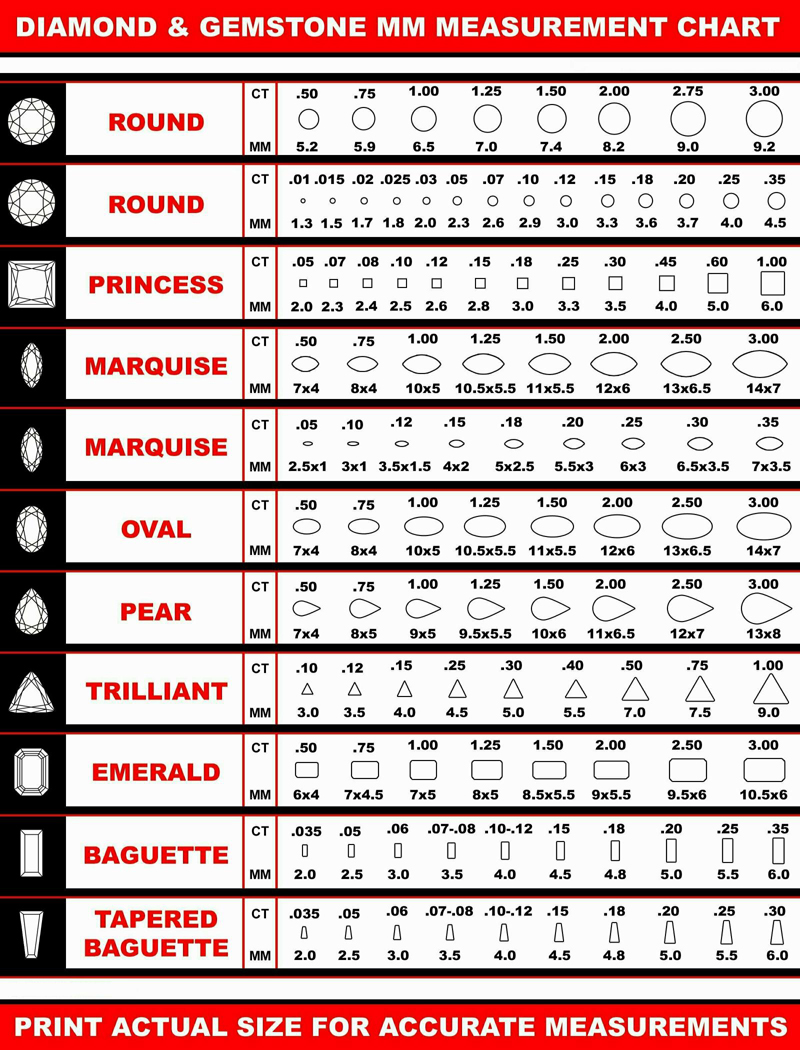
Important Factors Affecting Diamond Carat Size
Diamond carat weight is one of the most important factors when buying a diamond, as it will affect the price of the stone.
In addition, the following factors may also influence a diamond’s carat size:
Cut
A diamond’s cut describes how well the diamond reflects white light. This will affect how many the diamond sparkles and how it is shaped, which is the most important factor in determining its beauty. In most cases, the largest measuring stones are usually cut too shallowly, enabling light to pass through to the bottom, resulting in lost sparkle, also referred to as a fisheye.
The cut of a diamond usually has the biggest effect on its carat weight as it determines how much light is reflected from a stone. For this reason, diamonds with superior cut grades will have a greater weight than those with an inferior cut grade for the same shape and clarity grade. So, when buying a diamond, ensure that it has a superior cut grade and is as close to perfectly cut as possible.
note
When buying Diamond, make sure to look for diamonds with slight inclusions, clear colorless or white color, with no cracks or chips on the stone’s surface. Also, make sure that it weighs lighter than other stones of equal value.
Clarity
Diamonds have natural internal imperfections called inclusions. A diamond’s clarity indicates the number, size, and location of these imperfections. The fewer inclusions the diamond has, the better it will shine.
Diamonds are graded according to their clarity, and this also affects their carat weight size. The fewer inclusions a diamond has, the better its clarity is. Diamond carat weight can be reduced by half with inclusion in a diamond.
note
Diamonds with a higher clarity grade will usually come more expensive. When buying a diamond, make sure that the diamond you are buying has a clarity grade of VS1 or higher.
Color
The color of a diamond usually affects the value of a diamond. Diamonds are usually graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). If it’s any closer to red, diamonds may look like rubies instead of diamonds. The finest diamonds, according to experts, are those classified as D, F, G, H, I, and J.
Carat
Carats measure the weight of a diamond. Carats are divided into 100 points, so a .50 carat diamond is the same as 50 points.
note
When buying diamonds, make sure to take note of the 4 Cs: carat, clarity, color, and cut, so you can choose one according to your budget and preferences.
Shape
When buying a diamond, the shape is a significant factor in determining carat size.
EXAMPLE
An ‘ideal’ round diamond would be a 1ct stone, while a princess cut or emerald cut diamond could weigh up to 1ct because of its elongated shape.
note
When the further away a diamond’s shape is from an ideal cut, its carat weight will decrease while maintaining the same size. Also, a diamond’s carat weight can change by as much as 0.1ct from one shape to another, so if buying a princess cut, go for one slightly above 1ct and not exactly 1ct.
Size
The size of a diamond will ultimately affect its carat weight. With diamonds, size is significant as even a tiny increase or decrease from a “standard” size can hugely impact a diamond’s carat weight.
EXAMPLE 1
Buying a diamond over 1ct could increase the price by 50%. This makes it essential to choose a well-cut, perfectly sized diamond when looking for one to buy.
The size of the diamond will also affect its setting.
EXAMPLE 2
The smaller the diamond’s girdle (its middle), the more likely it will need to be set in fashion jewelry with prong settings instead of solitaires with claw settings.
Fancy-shaped diamonds usually appear more significant than their actual size. However, their value is low compared to round-cut diamonds. A 1-carat round diamond with an excellent cut usually has a 6.4-6.5 mm diameter and a crown of 33.2 mm2.
Related: Free Diamond Size Charts (MM)
Frequently Asked Questions
1 carat is equal to 0.2 grams. Therefore, the carat weight will influence the price of a diamond depends on its size. The larger the diamond, the more expensive it will be with each incremental increase in weight..
In general, carat weight of 1.0 or more is appropriate for a diamond seen from the side. If there are any questions regarding a certain size to be worn on a specific finger, consider consulting a jeweler.
No. Carat weight is the weight of a diamond, not its size. Carat weight is determined by measuring the mass of a diamond in carats; one carat is equal to 0.2 grams. While the size of a diamond is determined by its measurements, the larger the diamond, the more expensive it will be with each incremental increase in weight.
One carat (1ct) equals 0.2 grams (g). One carat diamond is approximately 6mm x 4mm or 2.3mm x 1.8mm in size, depending on the cut and shape of the stone. For example, a round brilliant cut diamond with a 1ct weight will typically be between 6-7mm in diameter (depending on its other measurements). A princess-cut diamond with a 1ct weight will also be about 6-6.5mm across.
Lab diamonds have the exact same mineral as natural Diamonds. However, it is normal for a lab-created diamond to vary slightly in weight from the “ideal” weight. For instance, a 1ct ideal round brilliant cut diamond will weigh within 0.02ct of 1ct (.18-.22). However, many labs can create diamonds that are very close approximations of natural diamonds in terms of weight. For this reason, you can expect lab-created diamonds to be near the same size as natural diamonds, if not necessarily the exact same size.




