BMI is an abbreviation for Body Mass Index.
It is typically defined as;
A measure of weight that illustrates the relationship between weight and height.
It is used in the medical fraternity to determine if people have a normal weight or they are overweight, underweight, or obese.
EXAMPLE
Using BMI, the Centres for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that over a third (1/3) of the adult population in America is obese. The impact of this fact is that in 2008 obesity was estimated to cost the United States 147 billion dollars in healthcare. Obese persons were estimated to pay $1429 more than people with a normal weight that same year.
According to CDC, BMI should not be used to characterize body fat or diagnose health conditions as BMI has been linked to certain diseases, which is to some extent and not fully. However, people with a high or low BMI should consult their physician where they can undertake additional health screenings for conditions such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
The impacts of BMI can cross over to a person’s workplace as some companies can list you under a health group with a high risk which consequently would affect your insurance rate.
Download Free Charts
Importance of BMI
Even though BMI is not the only weight factor known to increase a person’s risk of health problems, it has been determined to be a contributing factor. Therefore, upholding a normal BMI should be a priority for adults. A high BMI has been related to an increased risk for diseases such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
According to a publication by The Lancet Public health in February 2019, data analysis has determined that a high BMI, which would indicate obesity, in young adults has been linked to influencing the prevalence of the following types of cancer:
- Colorectal
- Gallbladder
- Endometrial
- Multiple myeloma
- Kidney and
- Pancreatic cancer.
Obesity falls under 3 categories. Each category is characterized by a range of BMI values.
These categories include:
- Class I: A BMI is 30 to 34.9
- Class II: A BMI is 35 to 39.9
- Class III: A BMI is 40 and above
It also goes without saying that the higher the BMI, the more severe the obesity in an individual.
BMI Chart
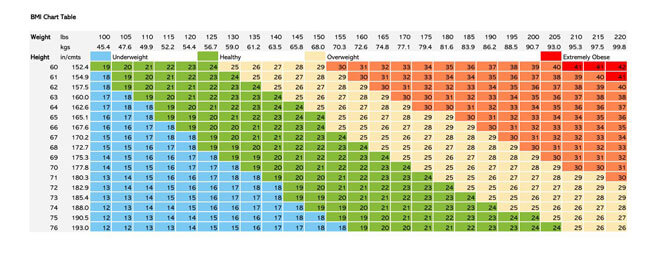
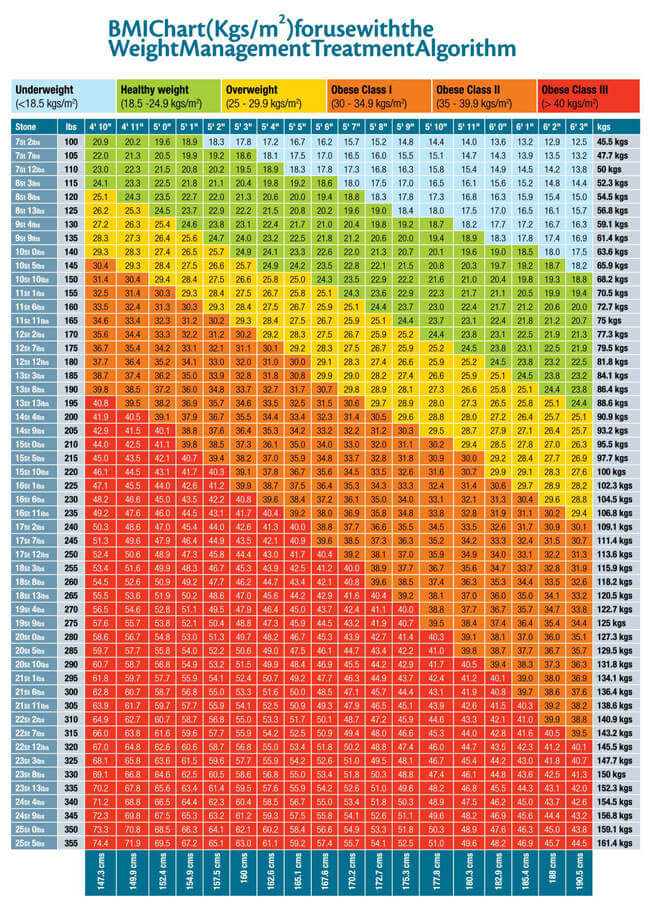
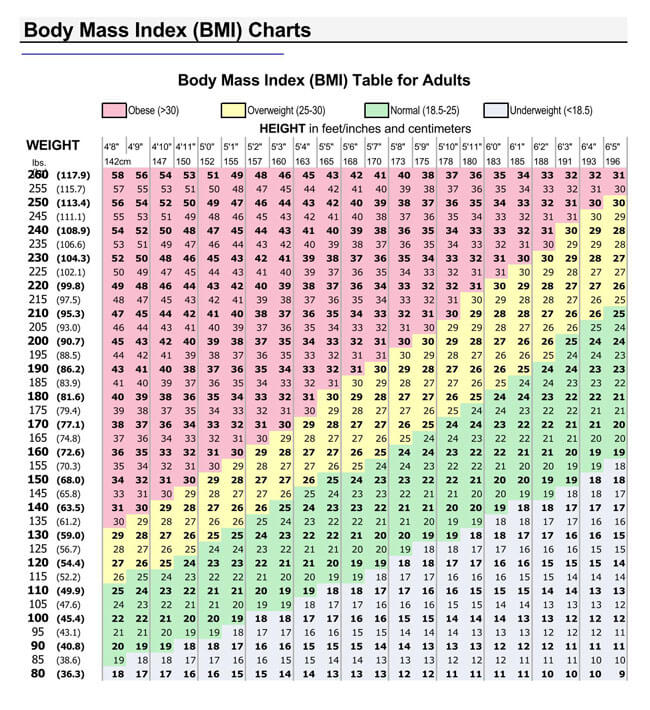
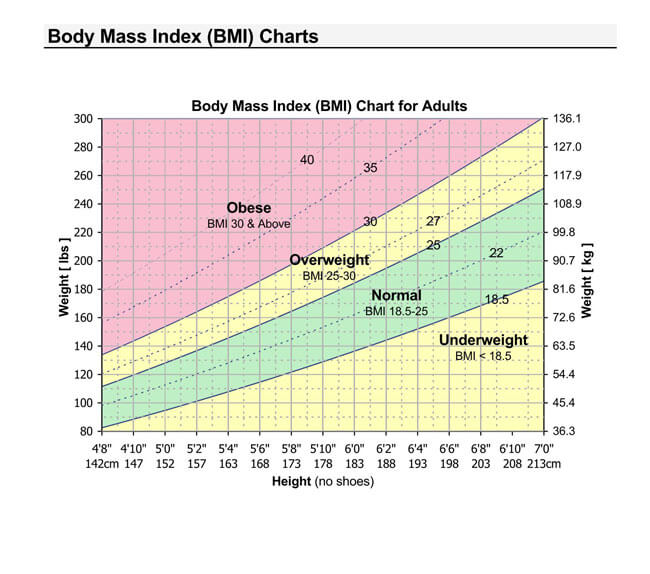
BMI values are represented in charts to make it easier for analysis and interpretation. Therefore, BMI charts are illustrations of how changes in height and weight vary a person’s BMI. There are two charts, one showing variations for weight between 95-245 pounds and the other from 250-400 pounds.
BMI chart for weight from 95 pounds to 245 pounds

BMI chart for weight between 250 pounds to 400 pounds

The first chart shows how BMI is used to classify a person as having an under healthy weight, healthy weight, overweight, and obesity. The second demonstrates the variations of BMI that bring about different categories of obesity.
The charts are adaptations of the Adult BMI chart developed by the University of Vermont, United States. Charts are only utilized as a guide and are not a clear indication of whether you have ideal body weight. The BMI chart’s primary purpose is to indicate if a person’s weight is increasing their risk for disease. This can be demonstrated through taking the example of a Boxing athlete with a high BMI; in such a case, the high BMI does not indicate they are overweight. Why? Because excess weight in this scenario could be due to increased muscle mass.
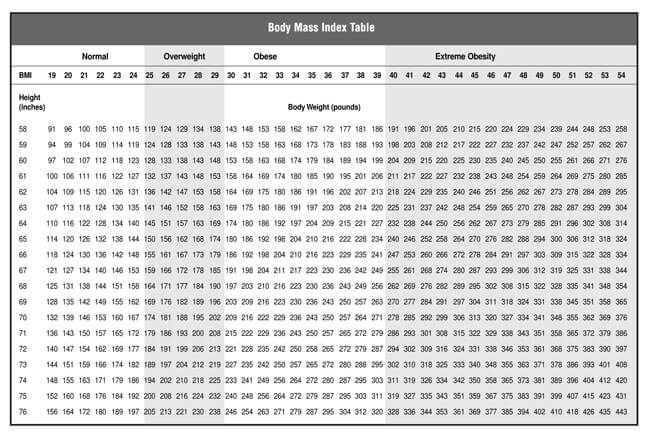
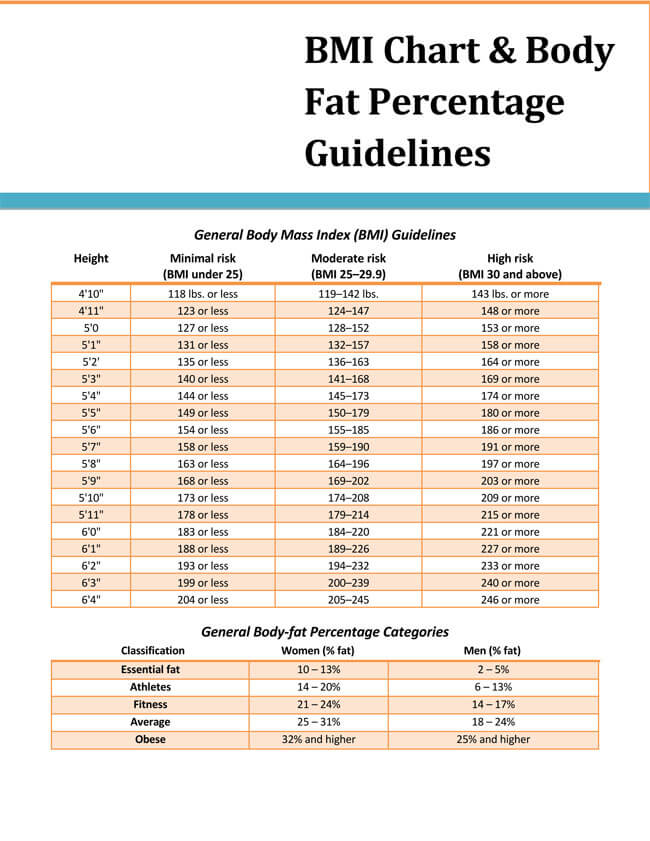
BMI Categories
BMI ranges can be categorized in such a way that values that fall under a certain range represents an almost equal health risk proneness to a given group of people.
These categories are as follows;
- BMI of less than 18.5- A person/individual with a BMI less than 18.5 can be termed to be underweight, and the recommendation would be to add on some weight. One can consult their doctor or dietician on how to go about it.
- BMI of 18.5–24.9- Healthy individuals have been established to have a BMI ranging from 18.5-24.9. This means their weight poses no health risk to people their height. You are recommended to maintain a healthy weight to reduce developing serious health problems.
- BMI of 25–29.9- A 25-29.9 BMI range indicates that one is slightly overweight. They are advised to consult their doctor or dietician on ways to go about losing some weight.
- BMI of over 30- BMI values above 30 indicate a person is heavily overweight. This can be a health risk factor to the individual, and they are advised to lose excess weight to improve their health. This is, of course, through the guidance of a doctor or a dietician
Calculating the BMI
We have already discussed what different BMI values imply and the factors, that is, weight and height, used to determine BMI. Now we shall go on to show you how to calculate your BMI. Calculating the BMI is different for adults and children.
For adults
You take your weight in kilograms (kg) and divide this by the square of your height in meters (m). This is for the metric system. However, if you are in the United States, where the imperial system is widely used, you can measure your height in inches, square it, then divide your weight in pounds by the product, and multiply the answer with 703.
Below is an example to demonstrate this:
EXAMPLE
BMI of over 30- BMI values above 30 indicate a person is heavily overweight. This can be a health risk factor to the individual, and they are advised to lose excess weight to improve their health. This is, of course, through the guidance of a doctor or a dietician
Alternatively, one can opt to use a digital BMI calculator such as the CDC’s BMI calculator.
For children
When it comes to measuring children’s BMI, the approach is different. For children between the ages of 2 and 3, a child’s paediatrician will often be the one to calculate their BMI. However, for older children, adolescents, and teenagers, doctors screen your child’s obesity using growth cart percentages that categorize using percentiles rather than use adult BMI charts.
Percentiles compare a child’s BMI to that of other US children of the same sex and age.
EXAMPLE
A child between the age of 2-18 will be deemed overweight if their BMI falls between the 85th and 94th percentile.
This approach helps your child’s doctor to understand weight-related risks your child could be facing during their growth and developmental stages.
BMI and Health Risks
The risks associated with BMI will vary depending on how high or low your BMI is. Below are some of the risk’s contingent on the value of one’s BMI.
High BMI risks
Through observations, it is an established fact that BMI is correlated to obesity-related conditions. However, there have been mixed results when assessing the relationship between a person’s BMI and their risk for disease or early death. High BMIs are linked to an increased risk of the following diseases and conditions;
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cancer
- Gallbladder disease
- Heart disease
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Depression
- Arthritis
- Sleep apnea
This relationship has been attributed to the fact that a higher-than-normal body weight will often be a result of excess fat in the body, which can cause malfunctioning of some body systems. Overproduction of fat cells causes excessive glucose production, plaque in arteries, hormones, and stress on bones and organs. This overwhelms the body, thus increasing the health risk of the individual.
Low BMI risks
On the other far end, low BMI has its own impacts on the health of the body. Low BMI, that is below 18.5, increases the risk of a person having to deal with:
- Malnutrition
- Anaemia
- Osteoporosis
- And other nutrient deficiencies
Being underweight can be a sign of digestive, hormonal, or other problems.
How to Lower BMI
Lowering your BMI needs an all-rounded approach as it means reducing your weight for your height is fixed; one can’t do much about that. As a consequence, it can be demanding to make lifestyle changes, rescheduling your daily routine, and putting in physical effort to achieve. But then again, it is so rewarding. A healthy weight can be priceless. Here are some a number of things you can do to lower your BMI.
- Consult family first- for people who live together, one member having a high BMI will often impact the whole unit. This is especially in cases where it is a child who has a high BMI. The family needs to come together and agree on what changes, in terms of lifestyle and diet, they need to adopt this can be for example enrolling in a gym, participating in a sport together, or having a modified weekly menu. Having the family involved can be very motivating for the child.
- Make smart food choices- Diet can go a long way to help you lower your BMI. There are various diets one can adopt. Generally, low-calorie, high fiber, beans, fruits, and whole grains diets have proven effective. The key is to have diets characterized by variety, limited added sugars, little unhealthy fat, and low sodium. A 10-10-2300 diet plan is recommended, that is, added sugars less than 10% of one’s total calorie intake, 10% or less saturated fat, and less than 2300 milligrams of sodium per day.
- Exercise regularly- according to the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week. This involves activities such as walking. Alternatively, one can do 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per week; this includes activities such as swimming, running, biking, etc. a person can choose to increase these times from 150 to 300 min and 75 minutes to 150 minutes for maximum benefits.
- Get adequate sleep- lack of enough sleep has been associated with increasing the risk of negative health outcomes such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity. Adults are recommended to have at least 7-9 hours of sleep. So kindly take a break from your busy schedule and get enough sleep; it is healthy.
- Manage stress well- Stress is part and parcel of our existence and cannot be avoided in totality. However, chronic stress is unhealthy and can put you at risk of having obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, depression, and HBP. Therefore, managing stress becomes an integral part of lowering one’s BMI. This can be done through regular exercise, yoga, meditation, etc. Family emotional support can be significant in managing stress.
- Eat out less and cook more at home– Try to adopt a habit of eating at home where you can implement recommended diet plans. This helps reduce your sugar, fat, and calorie intake. Home meals do not have to take too long to prepare; there are recipes that are simple and fast to prepare.
Frequently Asked Questions
The name BMI and its formula were invented by different people. The formula was developed by Adolphe Quetelet in 1830. Adolphe was a Belgian mathematician and social statistician. He used calculus and statistics to determine a relationship between weight and height which for 140 years was known as the Quetelet Index. The name came about later in 1972 when Ancel Keys, an American biologist, and physiologist, endorsed the index in a publication and popularized it as the BMI.
Yes. By the WHO (World Health Organization) and many other governments and medical agencies throughout the world.
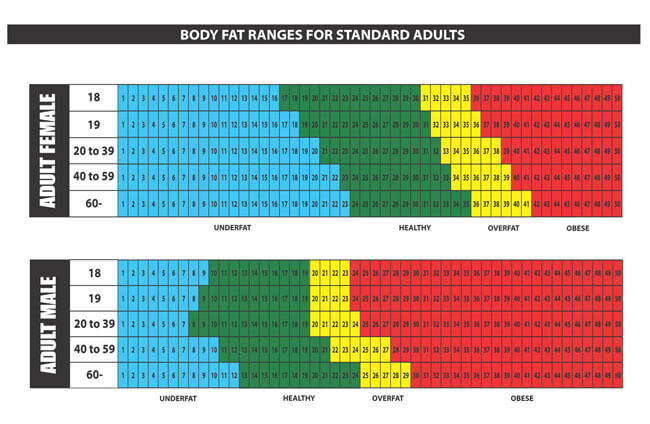
Yes. It has been recorded that women are more likely to carry higher levels of stored fat in their bodies than men. For example, for women, a fat 15%-20% of the bodyweight is healthy, where else the corresponding percentage for men is 10%-15%. However, for simplicity, WHO uses the same BMI categories.
Yes. It has been established body fat composition for individuals of the same BMI will differ across ethnic groups as it does with gender. However, for simplicity, WHO uses the same MI categories.
Yes. Once you have ascertained your BMI, you can consult your doctor or dietician on how much weight you are supposed to lose if your BMI is high or gain if it is low so as to achieve a healthy weight.
Final Words
BMI is a measure that is used to show the relationship between the weight and height of an individual. Even though BMI is not a direct cause of diseases, it has been observed to influence the proneness of people to certain diseases and conditions. The extreme ends of BMI values represent a person’s risk of having diseases such as anemia and high blood pressure, respectively.
People/individuals with a BMI less than 18.5 are considered underweight, and those with a BMI over 30 are said to overweight. BMI is simply a guide and not a definite method of diagnosis. Once you determine your BMI, consult a doctor or dietician to determine the way forward.




