PEST analysis is a framework that analyzes an organization’s external and internal environments. PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological. By understanding an external environment and an internal environment, an organization can determine what factors will determine its success or failure and strategize on how to become more competitive.
The external environment refers to macro-environmental factors outside the company, such as government regulations, the economy or financial state of the region, new entrants, substitute goods or services, etc. Understanding these factors helps an organization adapt its management style, organizational structure, and culture and adopt other strategic planning processes to give the organization an advantage over its competitors. PEST analysis is thus a vital management tool in business for both short-term and long-term goals.
Organizations will conduct it by evaluating the viability and effectiveness of business strategies by examining the associated political, economic, social, and technological opportunities and threats. There are variations of this analysis, including PESTLE/PESTEL, STEEP, STEEPLE, and STEER analyses that evaluate other external environmental factors specific to the industry or market.
EXAMPLE
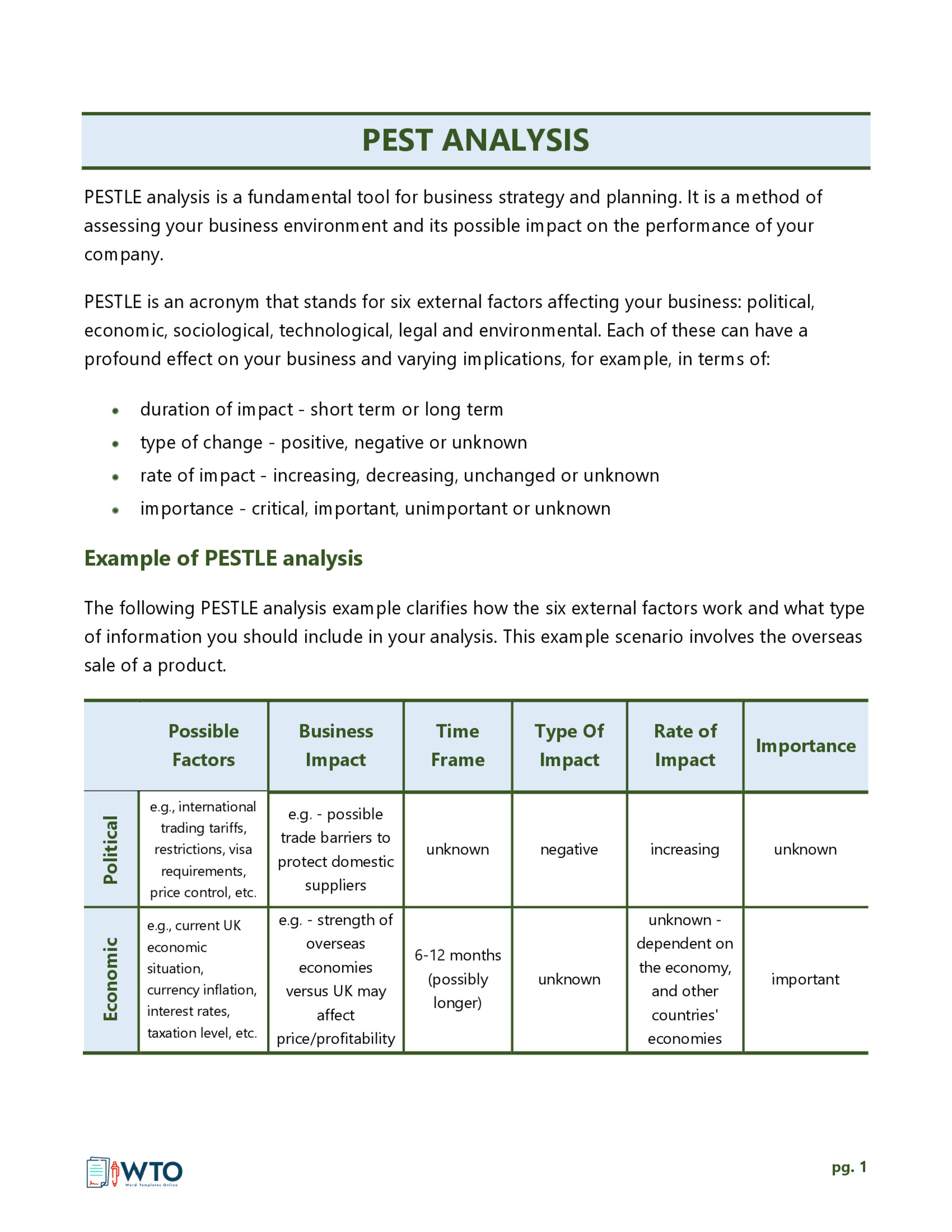
PESTLE includes legal and environmental factors too.
Additionally, this analysis also precedes other management processes such as SWOT analysis, risk analysis, and SOAR analysis. This informative article about PEST analysis aims to equip the reader with adequate information on what it entails and how it is utilized in business.
Key points
- PEST analysis assesses external macro factors that affect an organization’s short- and long-term operations.
- The analysis derives its name from the factors it evaluates: political, economic, social, and technological factors.
- PEST analysis is not just limited to a specific industry but can be adapted for any industry or organization.
- The underlying idea is that external factors contribute to the success or failure of an organization.
- Once the impact of external factors on the industry or market is determined, an organization can plan accordingly to ensure it has a strategic advantage over its competitors.
What is a PEST Analysis Template?
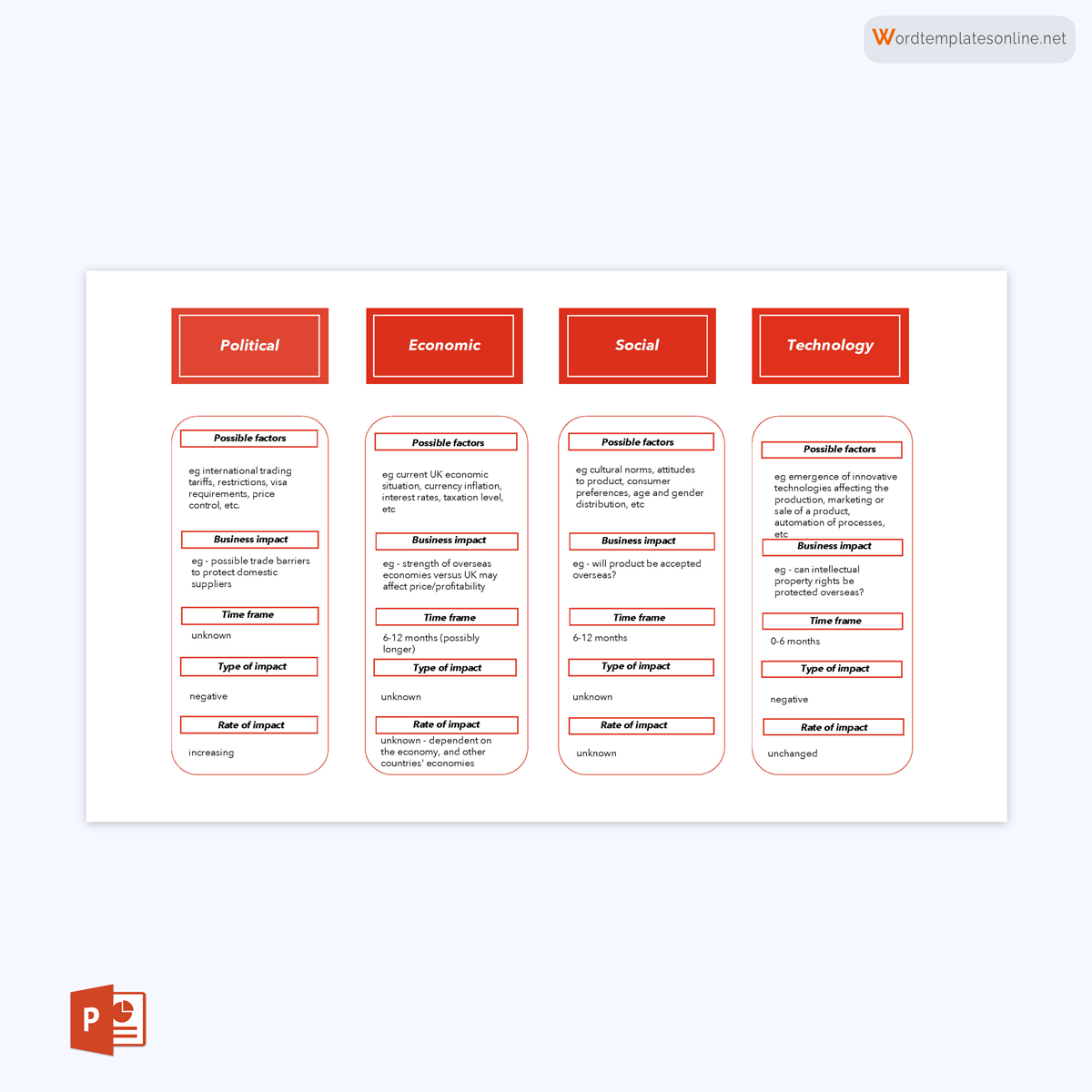
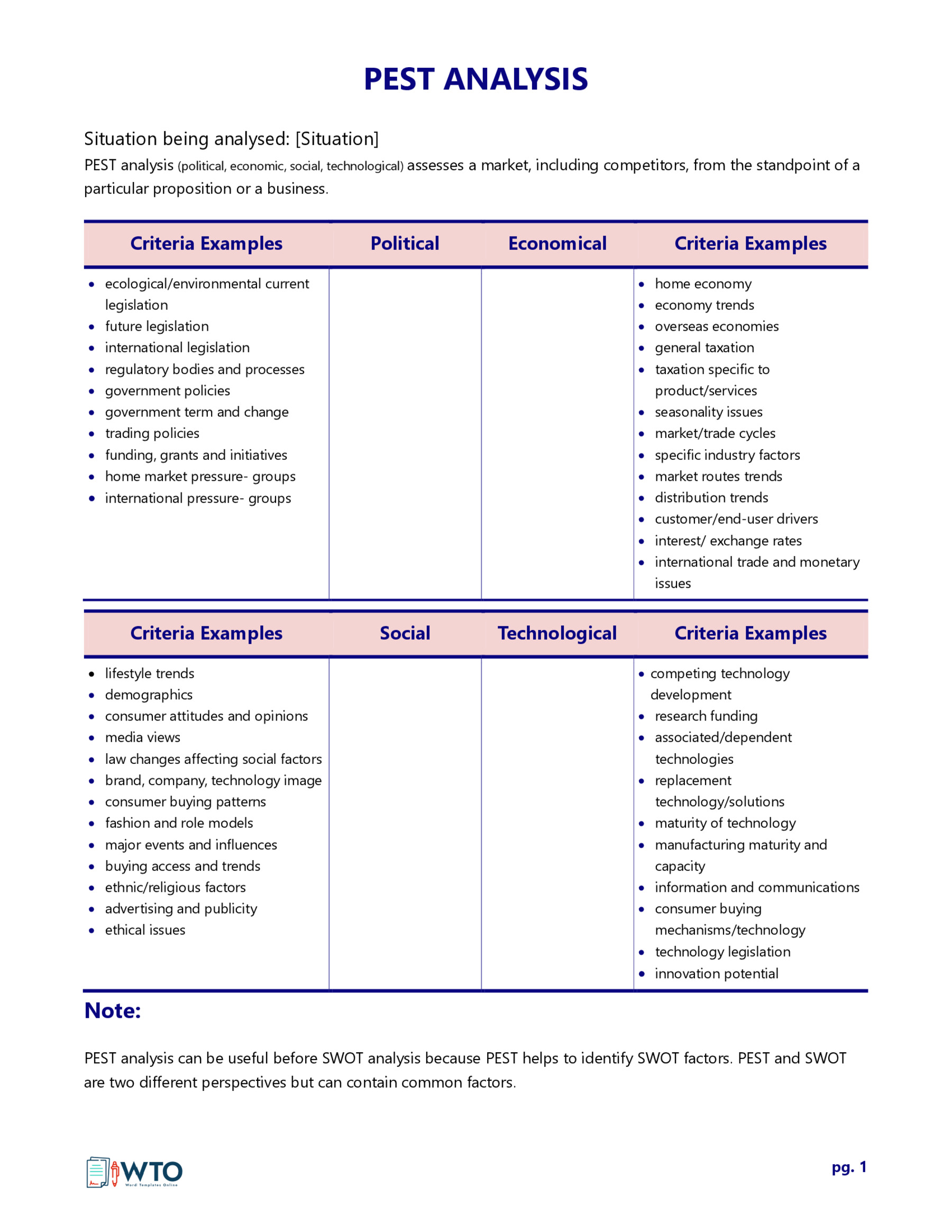
The PEST Analysis Template is a structured framework designed to facilitate the systematic evaluation of an organization’s external environment. This template serves as an organized matrix where each of the four key dimensions—political, economic, social, and technological—is distinctly categorized.
Within these categories, various sub-factors are listed to guide the analysis in a more granular manner. The template aims to enable organizations to distill complex external variables into a digestible and actionable format, thereby simplifying the process of strategic planning and decision-making.
Constituents of a template
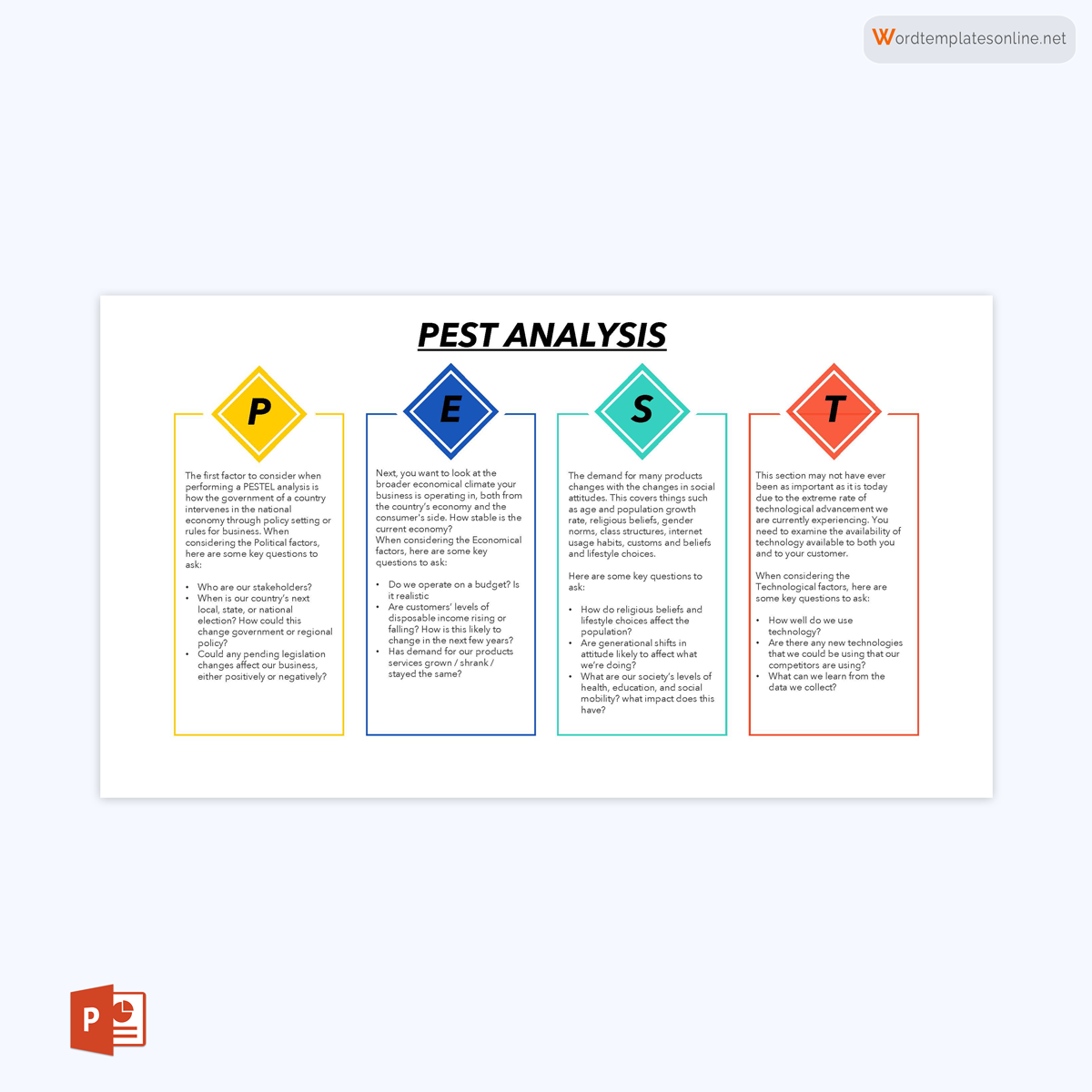
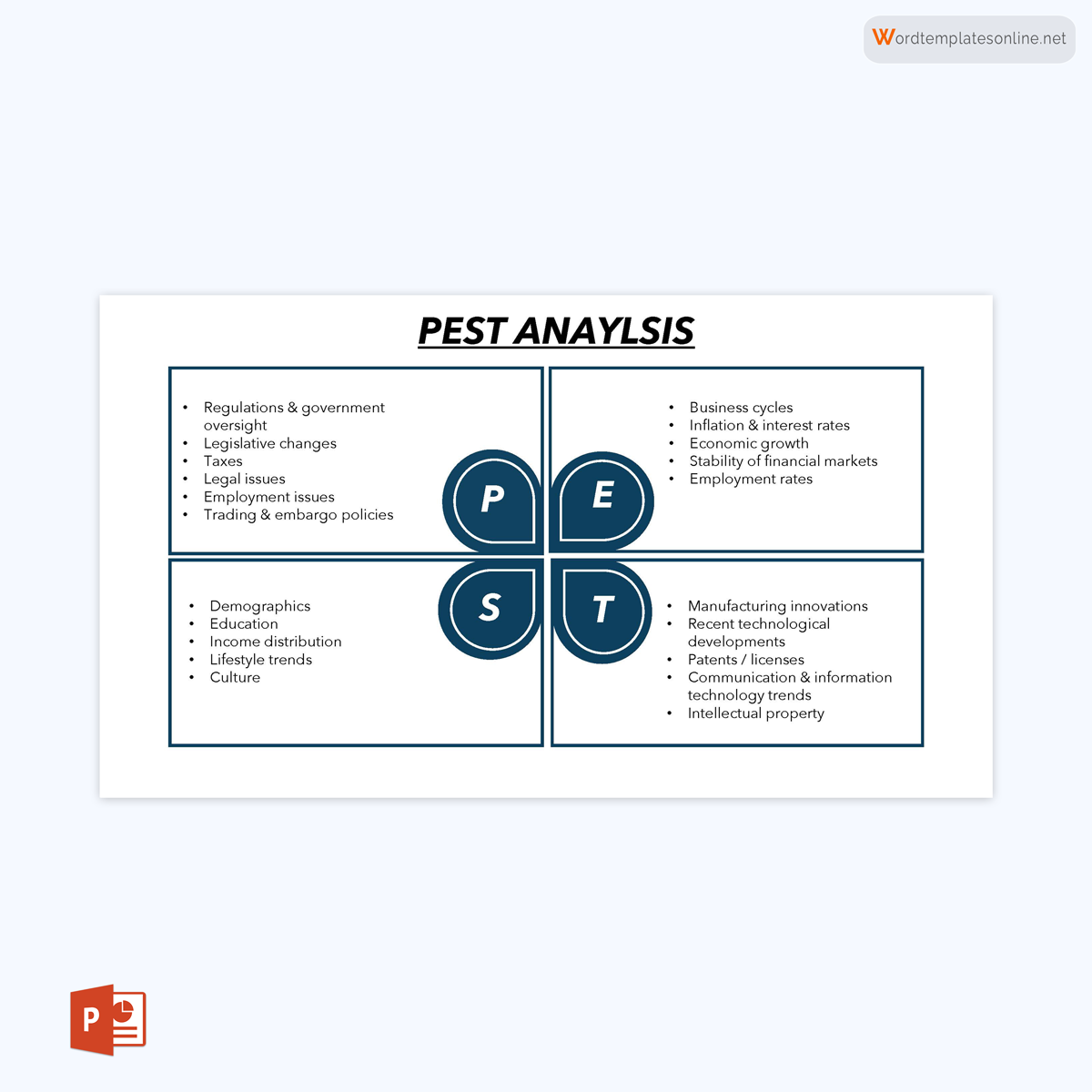
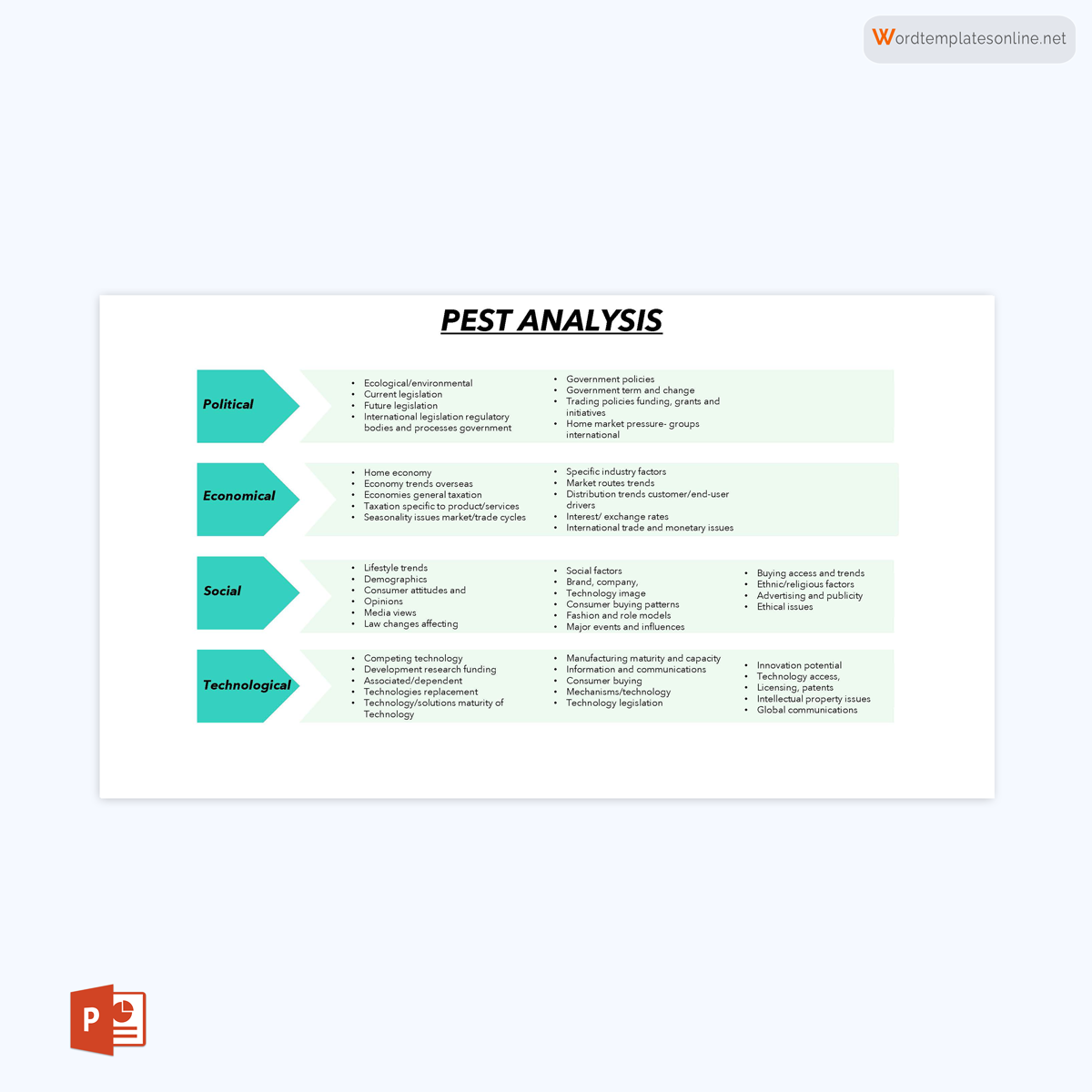
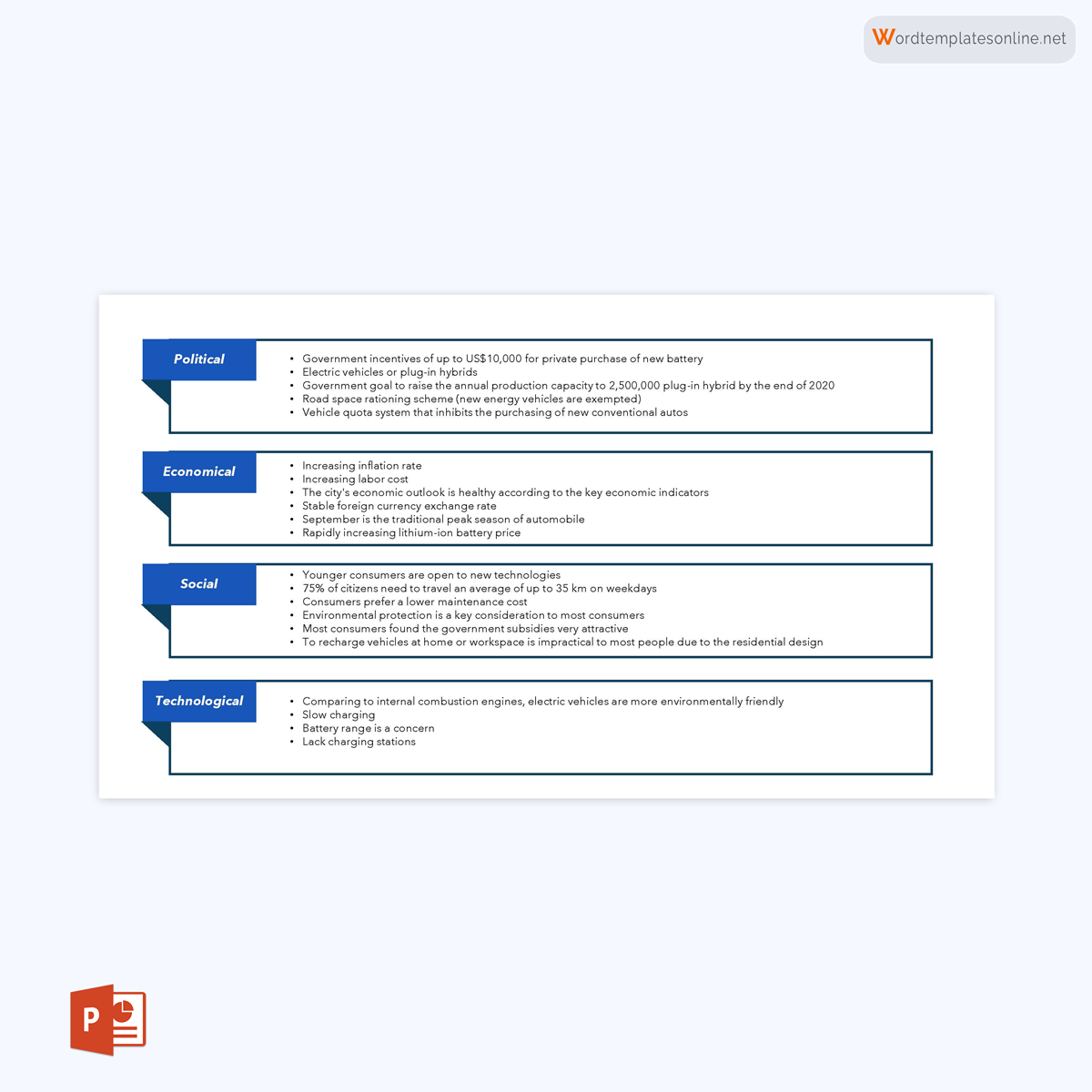
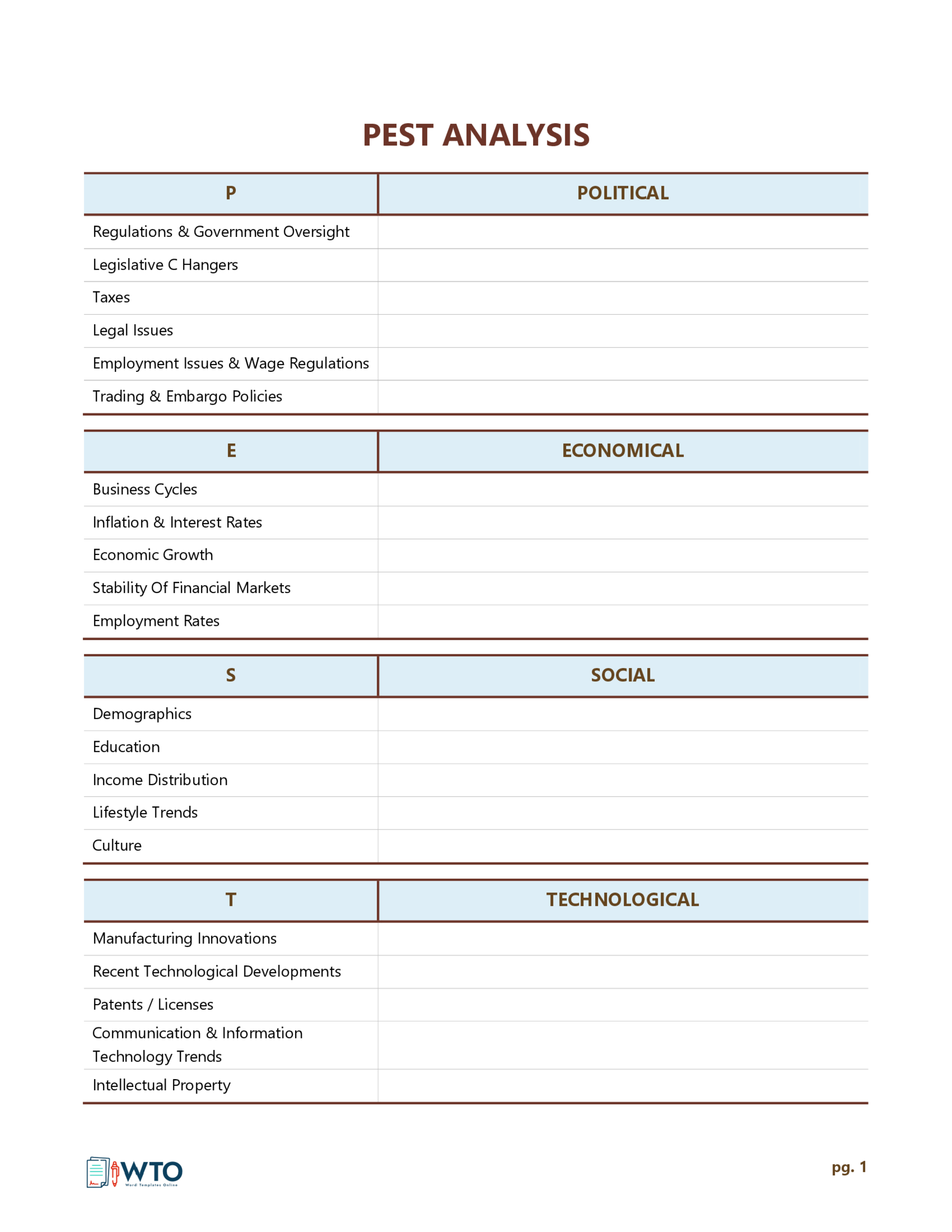
- Political Factors: This section scrutinizes the influence of government policies, regulations, and political stability on the organization. It may include aspects like taxation policies, trade tariffs, and geopolitical issues.
- Economic Factors: This quadrant delves into the economic conditions affecting the organization. Variables such as inflation rates, interest rates, and economic growth are considered here.
- Social Factors: This part analyzes the social and cultural aspects that can affect the demand for an organization’s products or services. Factors like demographics, lifestyle attitudes, and social norms fall under this category.
- Technological Factors: The focus here is on technological innovations, automation, and R&D activities that may offer opportunities or pose threats to the organization.
PEST Analysis Templates








Templates in word format


Who Needs PEST Analysis and Why?
PEST analysis is an excellent tool for helping both existing and new companies gain a strategic advantage in business. Its main purpose is to assess political, economic, social, and technological aspects (business environment) that may directly impact operations. As a result, the analysis is typically carried out by top-level management and C-level officers for strategic planning. Other parties known to partake in it are stakeholders, decision-makers, consultants, partners, external agencies, and bodies. PEST analyses are also used in project management and research.
Organizations will perform this analysis to identify threats and opportunities, changes in the business environment, and existing and potential risks in their business environment. Using the information obtained through the analysis, organizations can prepare accordingly, adapt their strategies to changes in the business environment, avoid the pitfalls of business ventures, and make informed decisions based on facts rather than assumptions.
Through it, companies can make better decisions and implement strategies that benefit the broader external environment, thus increasing their chances of success. Therefore, the analysis will be used for marketing, planning, business and product development, and structuring in organizations.
Areas assessed by PEST analysis
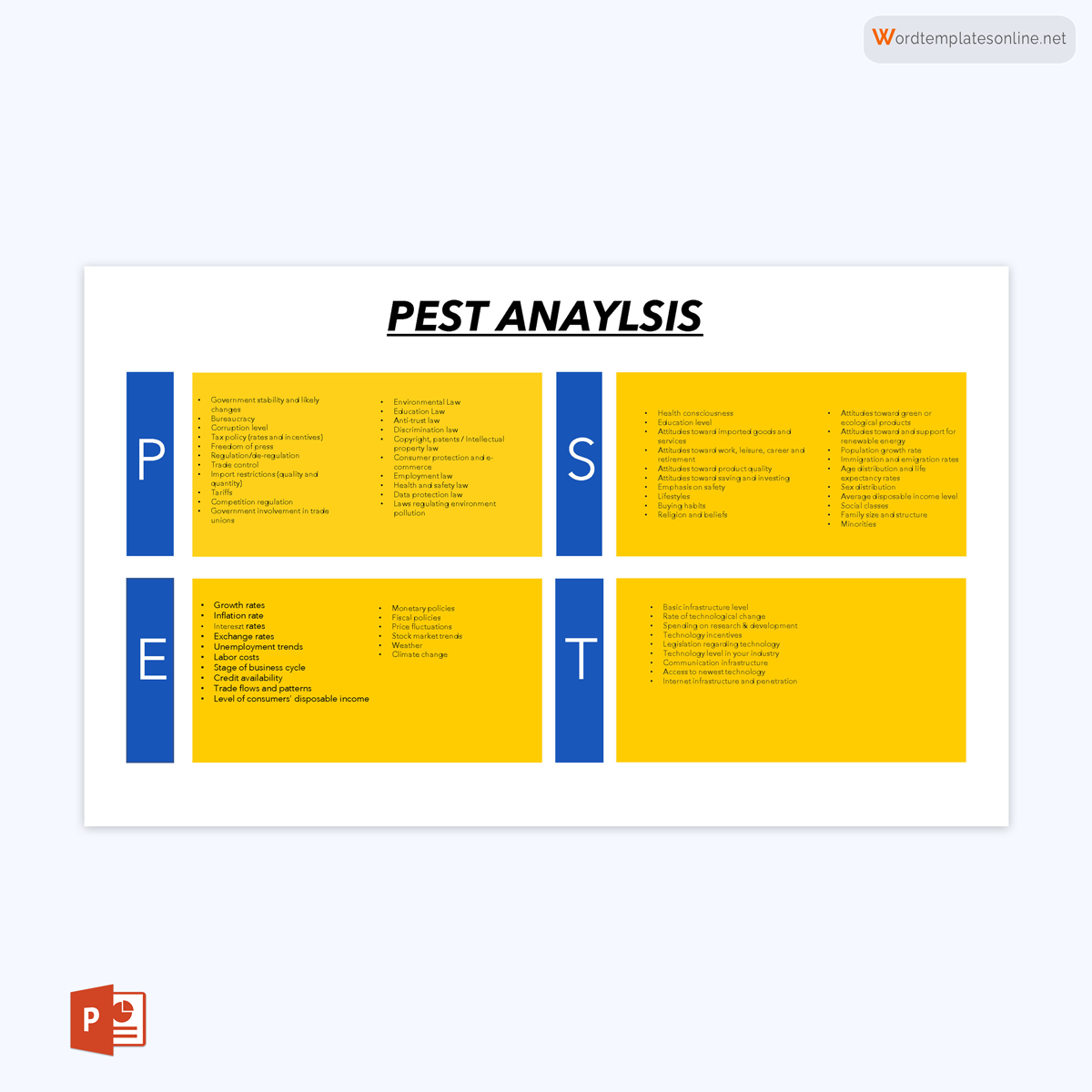
The PEST analysis looks into macro factors that affect the organization or business from external forces. These external forces include political, economic, social, and technological forces.
Each factor has its own significance in business:
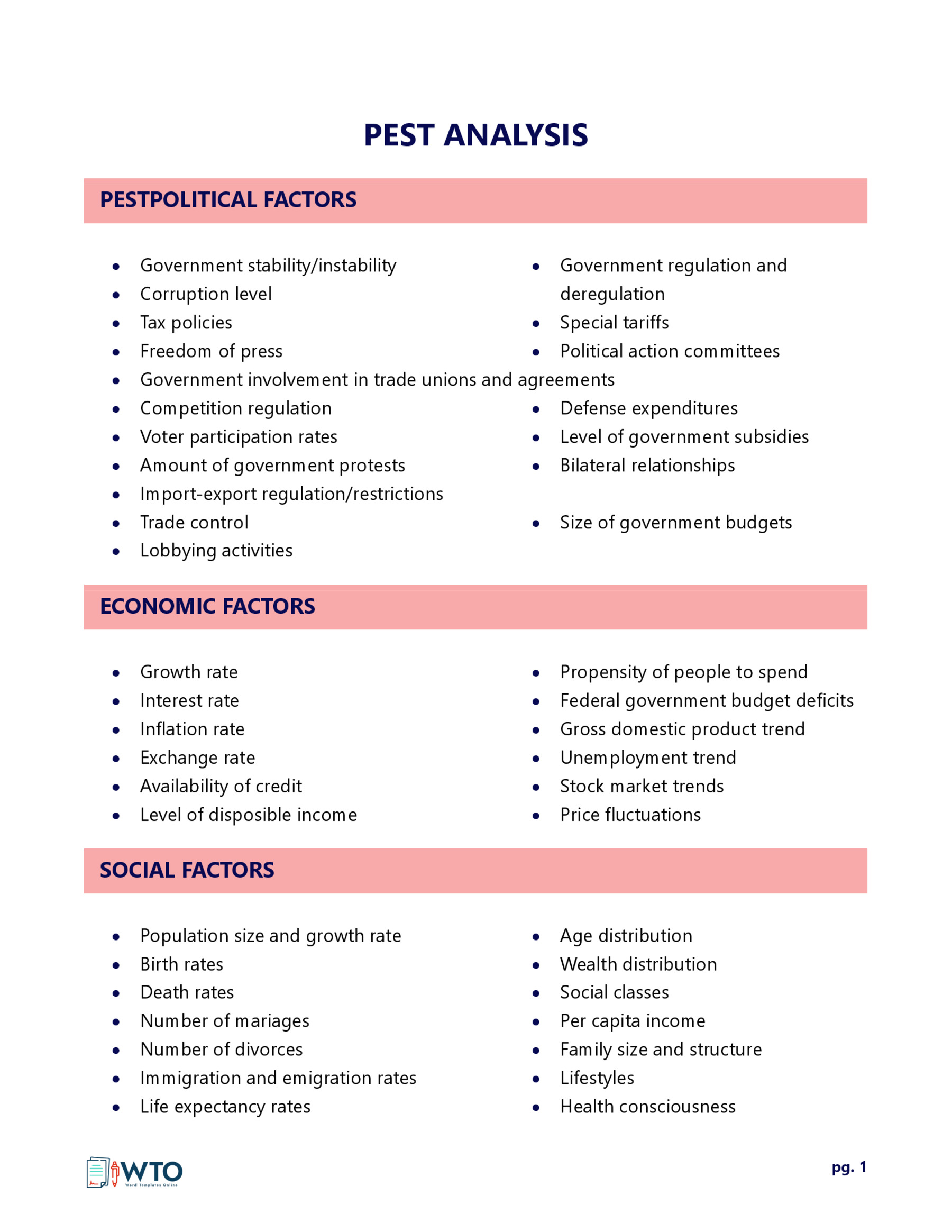
- Political: This aspect assesses how government policies and political status affect a particular industry or business. This analysis will look into multiple aspects such as taxes, legislation, laws, international relations, etc.
- Economic: This area focuses on macroeconomic indicators such as inflation, unemployment, exchange rates, supply and demand, recession, etc.
- Social: This looks into the demographic and socioeconomic status impacting an organization. This will include different social factors, including demographics and age distribution, cultural norms, lifestyle and workplace trends, etc.
- Technological: This area looks into emerging technologies that are likely to affect a business or industry. Other factors analyzed include government expenditure on technology research, trends, and changes in technology.
How to Use PEST Analysis
PEST analysis is a tool that can be used in various contexts and situations. It can be carried out at the beginning of a business venture to assess the factors that may affect business progression or for strategic planning for short-term goals.
In addition, it can be conducted after an organization has been in business for a significant time to identify a problem and find out its location and solution. When performing the PEST analysis, each component is assessed independently and jointly to determine its impact on the organization.
Below are the steps for carrying it out effectively:
Step 1: Brainstorm factors
The analysis initially begins with research to identify the various aspects of external factors that may impact an organization. This may include macroeconomic factors such as the effects of inflation and the effects of economic policies on a certain industry. In order to obtain comprehensive data on external factors, one needs to create a list of all possible external factors that could have an effect on the industry or organization and begin brainstorming by writing down any factor that might be relevant.
The main factors are as follows:
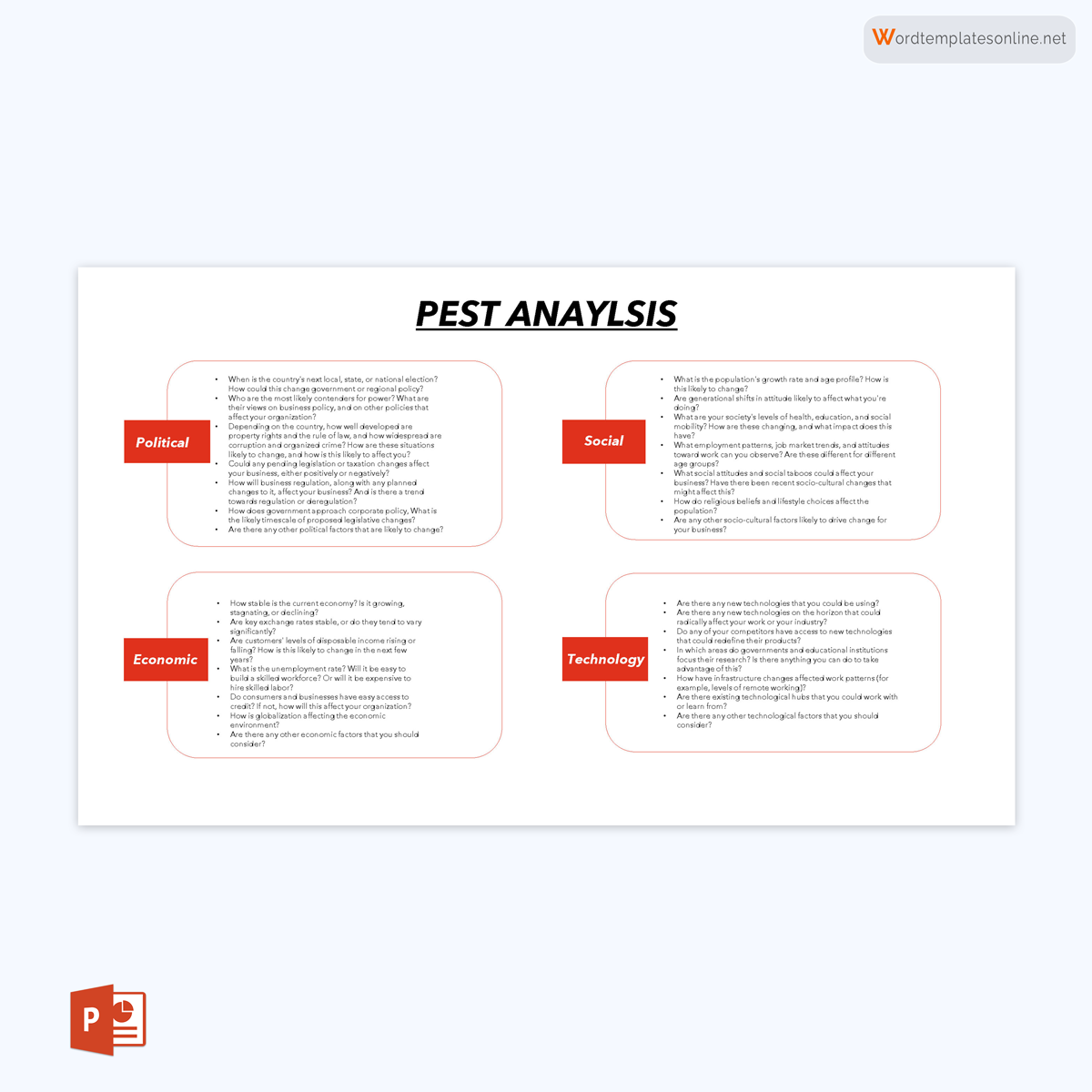
- Political factors to consider: Political factors are laws, governmental regulations, and influences regarding the production and distribution of goods and services. Government regulations and policies affect everything from taxes, investments, and loans to labor laws, competition and trade agreements. All governments generally apply laws but vary depending on factors such as country type (developing versus developed), size, or political view. As a result, political factors vary across different regions. Other factors include corruption rates, planned policy changes, national elections, etc.
- Economic factors to consider: The economy has a large impact on business operations. Companies will thus assess different aspects of the economy, such as the state of the economy (growth rates), exchange rates, customers’ disposable income, and purchasing power, access to credit and interest rates, inflation, unemployment rate, effects of globalization, and many other economic indicators. Economic conditions greatly influence the viability and sustainability of businesses.
- Socio-cultural factors to consider: Social factors are the societal influences that affect a business on a grand scale. They affect the way people live, how they act, what they think, and what they want. These factors include population growth rates, cultural aspects, age distribution, class structures, lifestyle choices, religious beliefs, health, education levels, employment patterns, career attitudes, demographic trends, social attitudes, behaviors, and trends.
- Technological factors to consider: The technological environment is constantly changing. New technological innovations occur at a rapid rate, requiring companies to update their strategies to be up-to-date now and then. Some technological factors include technological incentives, automation, R&D activity, and the rate of change in technology.
Step 2: Review responses and collate ideas
After brainstorming the factors, gather responses and ideas from participants and ask for their input. Collate ideas to capitalize on the available opportunities that exist with changes in the external environment. Review responses and collect ideas for each component.
Step 3: Rate the ideas
Next, rate the ideas based on how effectively they fit the current market, industry conditions, and organization goals. Consult the participants during this exercise. This will help determine if certain factors are more influential than others and which factors need to be focused on to manage the organization’s operations better. Factors are then prioritized based on potential effects, determining which factors should be given greater attention. Priorities will vary from one industry to another.
Step 4: Brainstorm threats
After prioritizing and ranking the factors that have a greater influence on the organization, one can then brainstorm possible threats to each factor. Threats may refer to changes in human behavior as well as changes in legislation, social attitudes, and cultural values. Assess factors that directly or indirectly impact organizational strategies and operations in order to identify any weaknesses that need to be addressed. This helps companies avoid problems entirely or mitigate the potential impacts.
Lastly, it may be necessary to document the outcomes regarding the potential opportunities and risks/threats. If a significant risk needs immediate attention, one can inform relevant parties or stakeholders and request that they participate in risk mitigation strategies. The report can then be used to monitor progress and for reference in the future.
Applications of PEST Analysis
Increasingly, PEST analysis is being used as a tool for strategic planning to help organizations better capitalize on opportunities by anticipating potential threats and designing responses, depending on the current external environment and their current and future plans and goals. The analysis is also used to evaluate internal forces in the same areas: internal politics, economic forces, social climate, and technology level. This is used to make improvements and changes in areas where the organization falls short.
Additionally, it is performed jointly with other strategic planning analyses, such as SWOT analysis, to formulate more comprehensive strategies. These two frameworks will examine consistent aspects of the business; the approach can help gain unique and distinct information that provides a better basis for decision-making.
PEST analysis is performed as part of a DCF valuation model. This is because political, economic, social, and technological factors greatly influence the opportunities and threats a business will face and, consequently, its potential profitability. This directly impacts a business’s valuation in the future. It ensures all these factors are considered during valuation as criteria for valuation.
Variations in PEST Analysis
There are several ways to conduct a PEST analysis. Although the basic one remains the same, the approach has several alterations, such as prioritizing factors. This leads to variations in the analysis.
Examples of these variations include:
PESTLE/PESTEL
This variation incorporates two additional components, which are legal and environmental factors on top of the political, economic, social-cultural, and technological factors. Legal factors can take priority over environmental factors or vice versa as applicable to the type of industry.
PESTLIED
The PESTLIED approach is a variation of the original analysis that includes legal, international, environmental, and demographic factors. The PEST base remains unchanged.
STEEPLE
The STEEPLE refers to social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical factors. The order of priority assigned to the factors is different from that of a standard PEST analysis.
SLEPT
This variation adds to the legal aspect of the business environment. However, this aspect is given a higher priority as the factors are assessed as follows: socio-cultural, legal, economic, political, and technological factors.
LONGPESTLE
Here as well, the base remains unchanged. This variation takes into account the local (LO), national (N), and global (G) factors of the PESTLE analysis. It is suited for multinational organizations.
Final Thoughts
PEST analysis is a powerful tool that can be used to assume and assess possible threats, opportunities, and their impacts on the viability and sustainability of any organization. This information is used to develop strategies that capitalize on the opportunities, thus giving the organization a competitive advantage over its competitors. The analysis focuses on external factors of the business environment in which the company is based. If properly carried out, the analysis can positively contribute to the organization’s success by helping management make better decisions.




