Errors are inherent in any sector, and we often strive to compensate for them. Fortunately, a remediation plan template provides a structured framework to help recover from a major crisis. It allows us to develop a step-by-step action plan to remedy a blunder.
The template provides a streamlined, easy-to-use roadmap for resolving personal or organizational errors. It serves as a reference guide for identifying the root cause of the issue, drafting an action plan, and tracking the resolution process. Formulating a remediation strategy usually follows some form of evaluation or assessment.
This article will discuss the critical components of a remediation plan template, how to create it, and the stages of a remediation process. Free printable templates in PDF, Word, and Excel formats have been provided for your convenience.
What is Meant by a Remediation Plan?
A remediation plan is a systematic approach for addressing a problem or deficiency identified through an audit, risk assessment, or any other type of evaluation.
It is widely used in the education, engineering, security, health, IT, and commercial sectors to create a blueprint for addressing and mitigating identified risk factors.
The plan aims to identify the problem at hand, develop an action plan, implement resolution steps, and mitigate potential risks. It outlines procedures that must be performed to rectify the identified issues and improve the situation. An effective remediation plan can reduce the impact of an incident on an organization or project, ensure regulatory compliance, and improve overall performance.
Free Templates
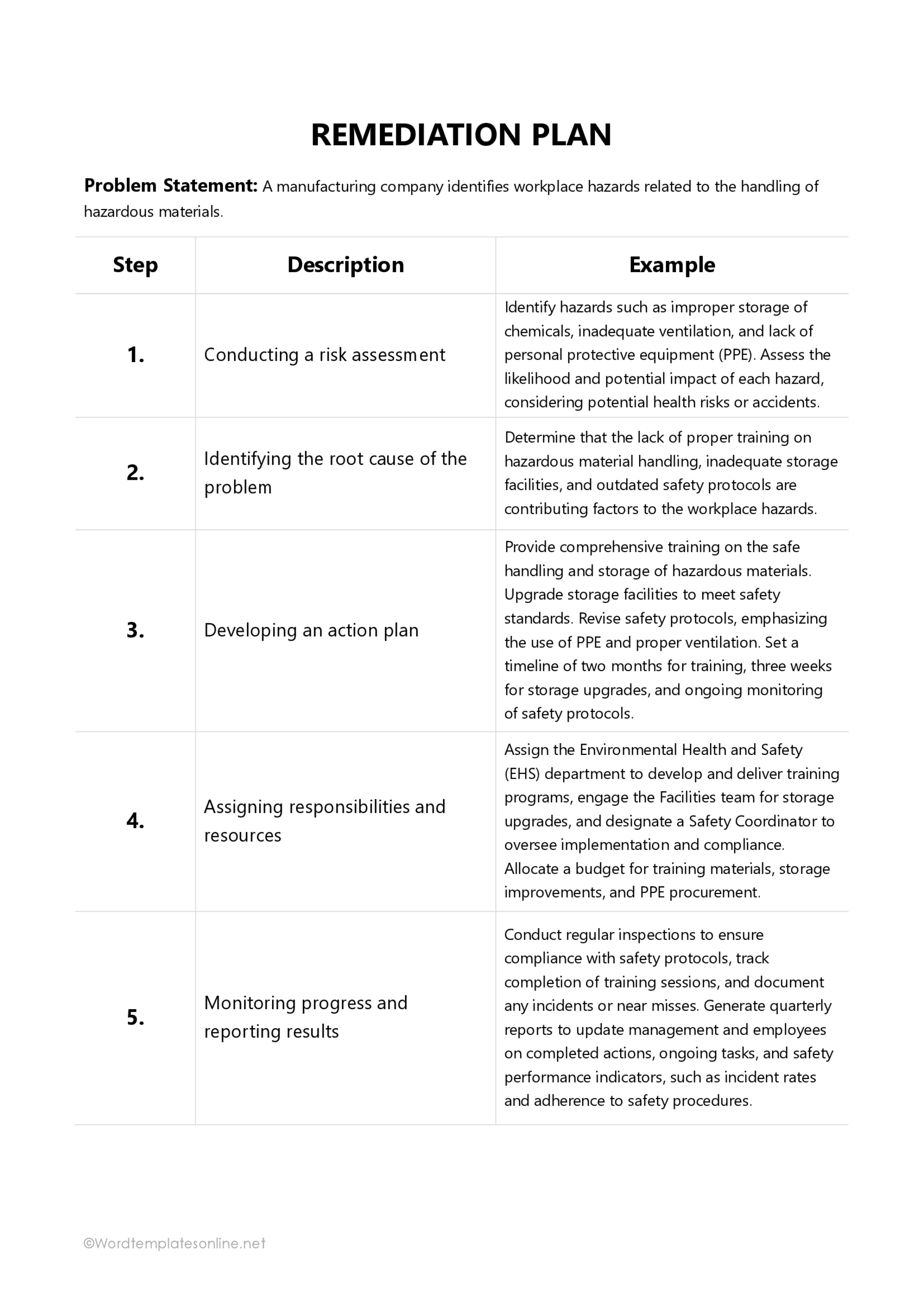
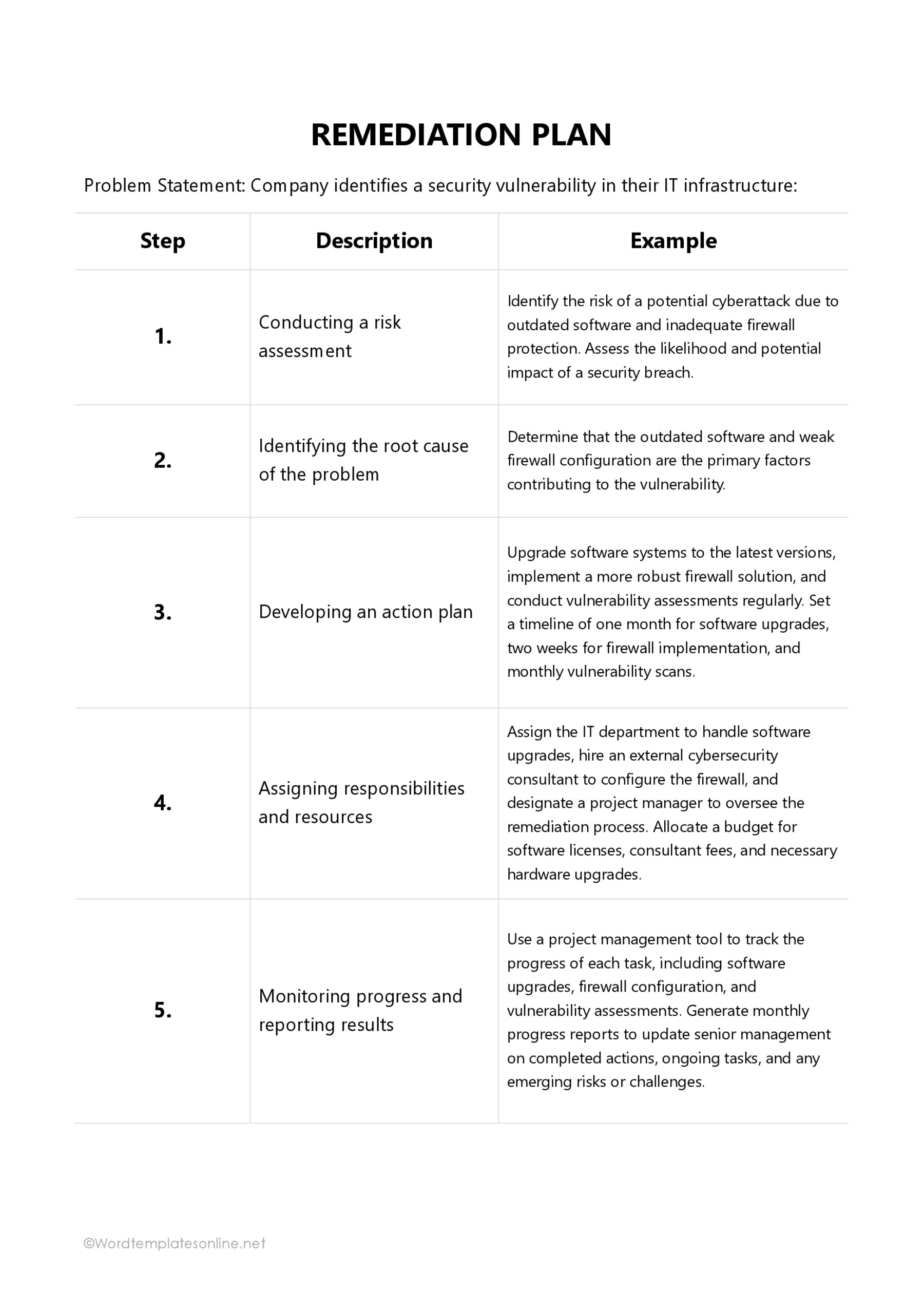
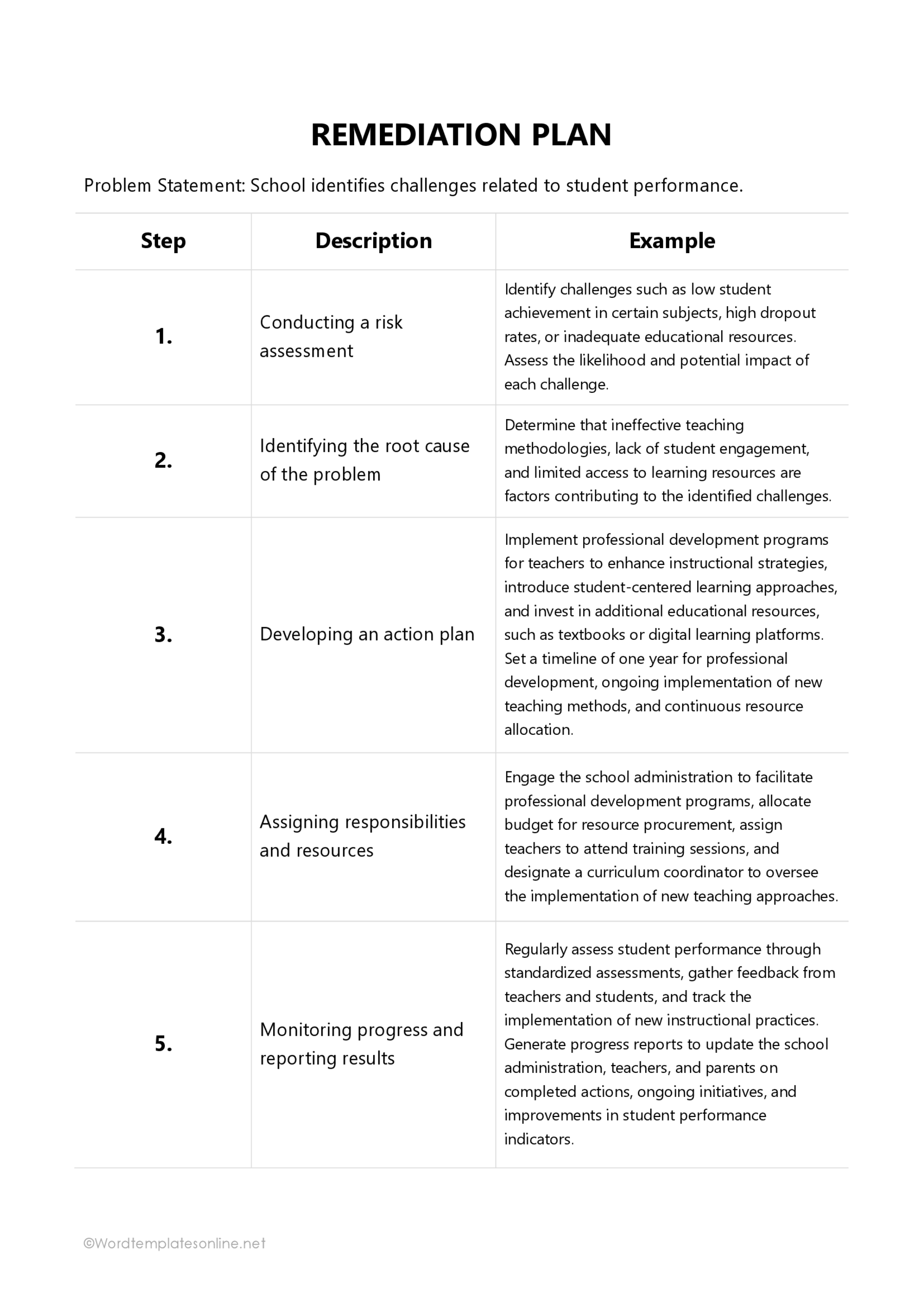
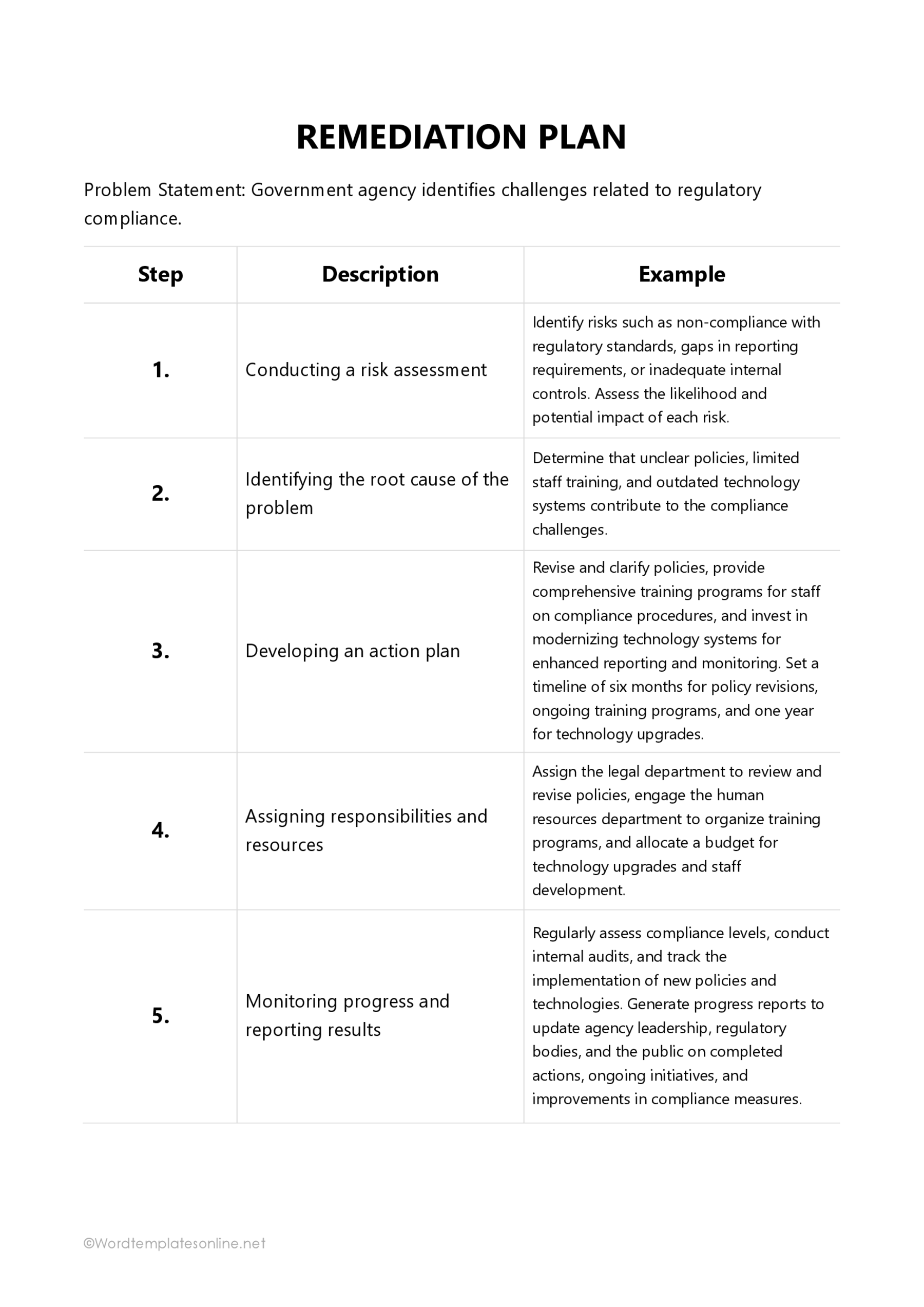
Key Components of a Remediation Plan Template
The components of a template for a remediation plan can differ based on the field in which it is used. However, certain key elements must be included when developing the template for the strategies outlined in the plan to be effective.
These components are discussed in this section:
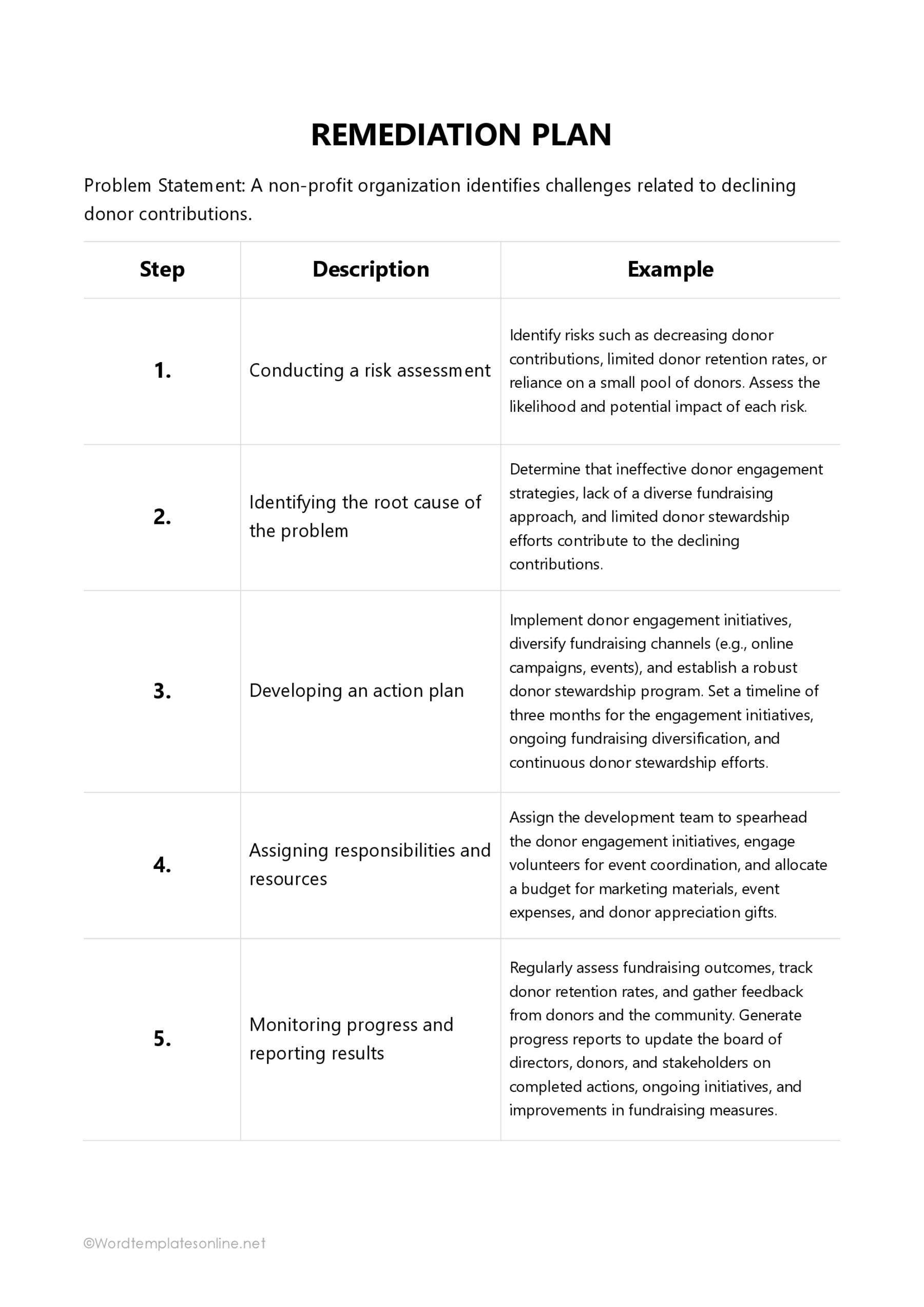
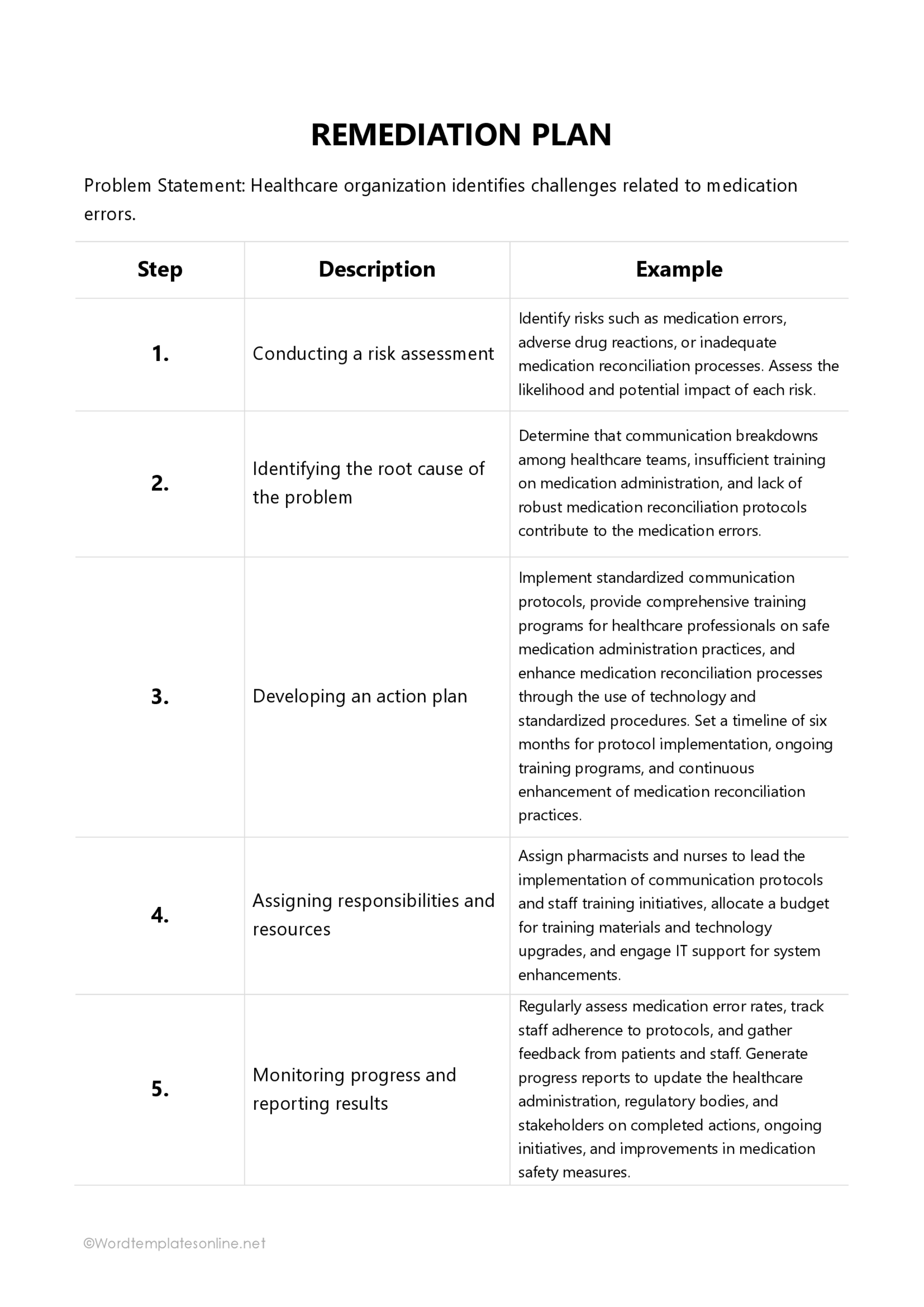
Problem statement
The first component of the template outlines the specific concerns and other problems that need to be addressed. This section should concisely describe the scope of the problem. It should also include pertinent details such as the organizational, project, or stakeholder impact and associated regulatory compliance issues. By including this section, you and other stakeholders can have a thorough understanding of the issue to develop appropriate strategies to resolve it.
Root cause analysis
A root cause analysis is an important component of the template since it helps you identify the factors that contributed to the problem at hand. It is generally an assessment or an audit and provides a detailed analysis of the relationship between the contributing factors and the problem. Understanding the underlying causes allows you to draft a targeted action plan that effectively remedies the source of the problem rather than just its symptoms.
Action plan
The action plan is the most important part of the template. After you have identified the root cause of the problem, take some time to brainstorm probable methods you may employ to correct and rectify it. You can then develop an effective action plan that outlines the exact procedures that must be implemented to address the identified problem. Specify the exact steps, timelines, and team members responsible for each task.
You should also specify potential risks and unintended consequences associated with its implementation, as well as contingency plans to rectify them. With a detailed plan, you can ensure that the necessary measures are completed in a timely manner.
Timeline
Like the action plan, the timeline is an essential component of the template. This section of the remediation plan specifies the time it will take to implement steps to address the issue. It should include dates and deadlines for each task. Some of these tasks may have interdependencies that should be accounted for to ensure the plan is executed sequentially. Make the timeline practical by assigning each task a reasonable completion time.
Resources
This section of the template outlines the resources allocated to the remediation process. These resources include funds, personnel, and materials needed to implement the remediation tasks effectively. These resources, which can be tangible or intangible, are essential in executing the action plan. To ensure the necessary resources are available during the implementation of the action plan, you should determine resource requirements in the planning process to allocate them accordingly.
Risk assessment
Risk assessment is an essential component of the template since it identifies potential challenges that might arise during the execution of the action plan. You can conduct a risk assessment to identify the likelihood and severity of potential risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them. This allows for a more fluid and successful action plan implementation, lowering the possibility of developing new risks.
Monitoring and reporting
Monitoring allows you to track the progress of implementation strategies and assess their efficiency. Reporting the remediation progress to relevant stakeholders demonstrates your accountability and provides a basis for decision-making. This may involve defining specific key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the objectives of the action plan and the generation of regular progress reports.
Best Practices for Creating an Effective Remediation Plan Template
Developing a template for a remediation plan requires you to adhere to certain practices to ensure its efficiency. Follow the tips below to develop a practical remediation plan that addresses the identified problem:
Involving relevant stakeholders
The remediation process is a collaborative effort involving various stakeholders from the organization or project as well as suppliers, clients, and experts, each with a unique part to play. Outline the primary stakeholders and establish clear communication channels in the planning stage of the action plan. This ensures the preferences and needs of each stakeholder are taken into account and that they are aware of each completed task.
Considering potential risks and unintended consequences
During the implementation of remediation strategies, you should be able to adapt to the obstacles that may arise during the remediation process. It is important to consider and outline potential risks and unintended consequences because, even with thorough planning, your action plan may encounter an unexpected hurdle. The main consideration is how quickly the risks will be identified and remedied. By noticing potential risks early enough, you can ensure you do not lose track of the core objective of the remedial effort.
Aligning with organizational goals and priorities
Ensure your remediation plan aligns with your organization’s goals and priorities. You can keep track of your plan’s progress by regularly referring to your organization’s mission, vision, and core values. This will allow you to pinpoint any critical milestones the remediation team missed and take corrective action immediately.
Regularly reviewing and updating the plan.
You can improve your remediation plan by reviewing and updating it regularly. This allows you to identify any deficiencies and areas for improvement in order to make the appropriate adjustments. This improves the plan’s effectiveness and increases the likelihood of successful remediation.
Seven Stages of the Remediation Process
A remediation plan provides an organized, straightforward framework for resolving problems that may impact the operations or performance of your organization or project. Depending on the specific issue, the stages of the remediation process may vary.
However, they all involve the following seven general stages:
Identify the issue
The first step of the remediation process is to identify the problem or issue that needs to be addressed. This can be achieved by assessing your organization’s processes, operations, and systems. You can also perform an audit or survey to determine the extent of the problem, its root causes, and potential impacts.
Conduct a risk assessment
Next, identify any potential risks the problem poses to your organization by conducting a thorough risk assessment. Whether they are operational, compliance, or financial risks, assess the possibility of each risk occurring and its potential impact. This helps you prioritize them based on significance and provides additional insight into where remediation efforts should be directed.
Develop a remediation plan
After conducting a risk assessment, develop a remediation plan that effectively addresses the identified problem. The plan should include an action plan, timelines, and resources needed to address the issue properly. You can focus your efforts and allocate resources more efficiently if you have a remediation plan with clear objectives. It ensures that your remediation strategies align with your organizational goals and priorities.
Implementation
After developing a remediation plan, implement it to correct the problem. This involves completing the tasks outlined in the plan promptly. This can involve assigning responsibilities to team members, allocating resources, monitoring and communicating progress to stakeholders, and adjusting the plan. These efforts should be aimed at correcting the identified problem.
Monitor Progress
Continually monitor the remediation plan during its implementation. Evaluate the progress of the remediation strategies, their effectiveness, and intended outcomes. This will help you ensure that the remediation steps are performed on time. It will also help you identify any deviations and areas that require adjustments.
Conduct Verification and Validation
Once the implementation of the plan is complete, it is critical to conduct verification and validation to verify the success of the remediation strategies. This phase involves evaluating whether the problem has been adequately addressed and if the desired outcomes have been realized. Depending on your industry, you can conduct tests or inspections to ensure that the problem has been resolved.
Report on Results
Once the remediation process has been deemed successful, the final stage entails reporting on the results. This involves reporting the results of the process to key stakeholders such as management, advisors, or suppliers. Depending on your field, it may also involve obtaining any certificates or approvals that verify the completion of the remediation process.
note
The infographic below outlines the do’s and don’ts when using a template to draft a remediation plan:
Who Can Benefit from Using a Remediation Plan Template?
Individuals and organizations across different sectors can benefit from using a template for a remediation plan to address problems that may impact their performance, project implementation, operations, and regulatory compliance.
They include:
Businesses
Any business experiencing significant operational, performance, or compliance issues can benefit from using a template for a remediation plan. These include businesses in the manufacturing, security, finance, and IT sectors. It provides a structured framework to identify and resolve issues leading to improved performance efficiently.
Government agencies
Government agencies at the local, state, and federal levels can use the template. They can experience issues that impact their projects, policies, or programs. Government agencies can use a template for a remediation plan to develop strategies to rectify issues within their jurisdiction.
Healthcare organizations
Patient safety is paramount in the healthcare sector. Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities experiencing significant issues can use a template to draft a remediation plan. They can address issues concerning patient safety, inefficient processes, and regulatory compliance. It enables them to address certain operational obstacles, streamline medical procedures, and improve the quality of patient care.
Educational institutions
The template can be utilized by high schools, colleges, and universities undergoing significant academic, student safety, or compliance issues. It gives teachers a professional approach to identifying the specific problem and other areas for improvement. This allows them to implement corrective actions that enhance the student’s learning experience.
Non-profit organizations
Non-profit organizations regularly work in challenging social and humanitarian environments. They also operate with very limited financial and personnel resources. The template provides an organized approach to identifying and effectively addressing these issues. It helps them determine the root causes of specific problems, develop targeted intervention strategies, and implement corrective actions to address these issues while allocating limited resources efficiently.
Final Words
As it happens, the world is far from perfect, and unmitigated problems can potentially escalate into larger issues that can cause unforeseen risks. With a remediation plan, you can ensure these problems do not impact your operations. This allows you to develop mitigation strategies that address them, guarantee regulatory compliance, and improve overall performance.
Developing a remediation plan from scratch can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with complicated issues. You can save time by downloading one of our free printable remediation plan templates in PDF, Word, and Excel formats. Using a template for your plan helps you spend more time on what matters – implementing the remediation strategies.




