An Audit Report is a written document that outlines an independent opinion or review and examination of a company’s financial statements, management accounts, management reports, and other related reports, such as compliant reports, conducted by an auditor to ascertain that they are compliant with the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Fundamentally, it is the auditor’s formal avenue of communication to an entity, stating informed conclusions about the audited financial statement.
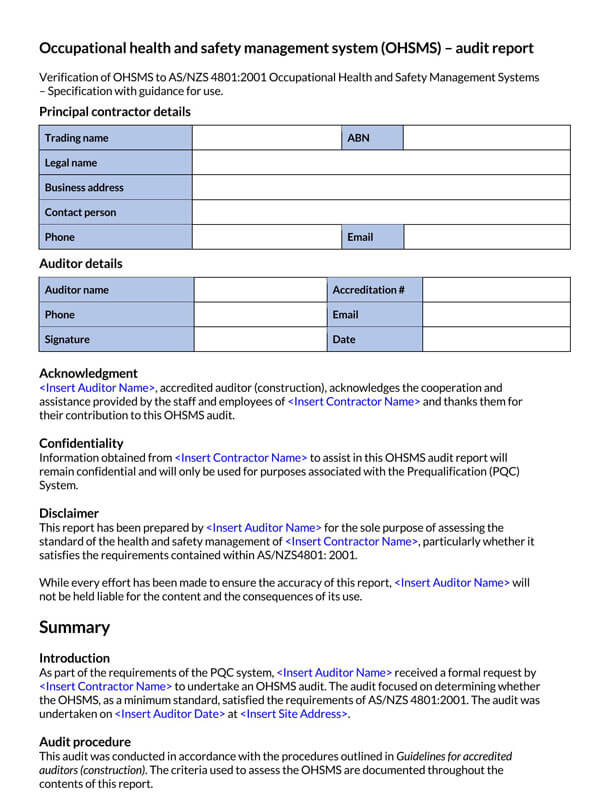
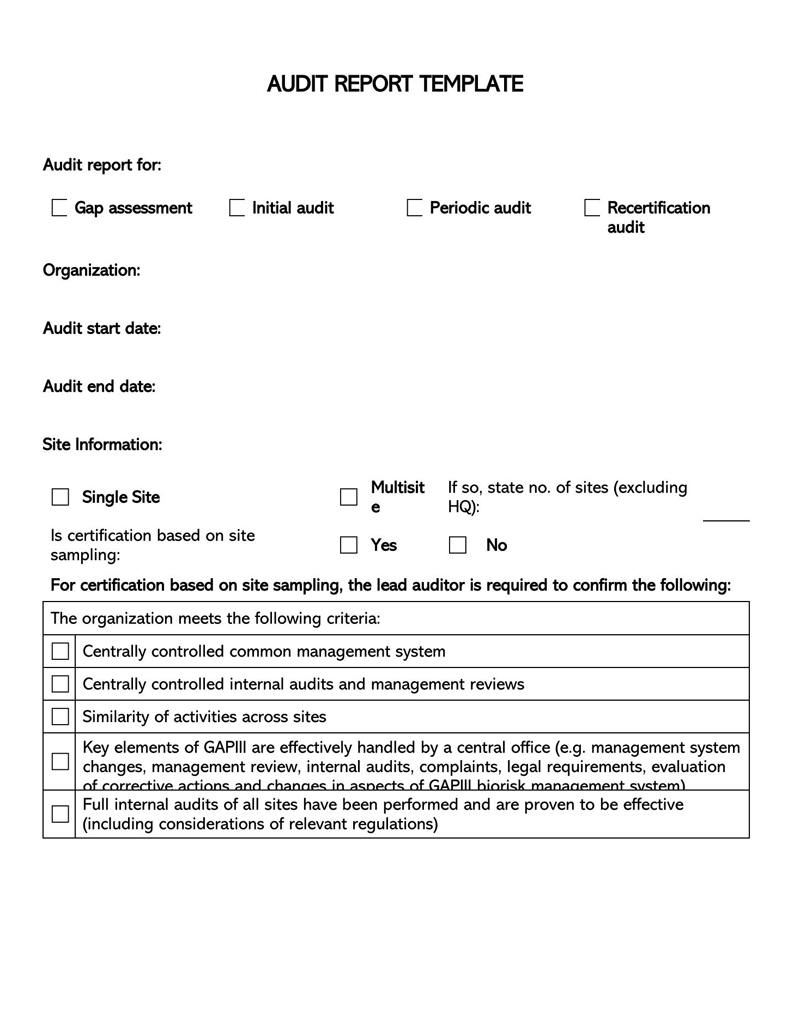
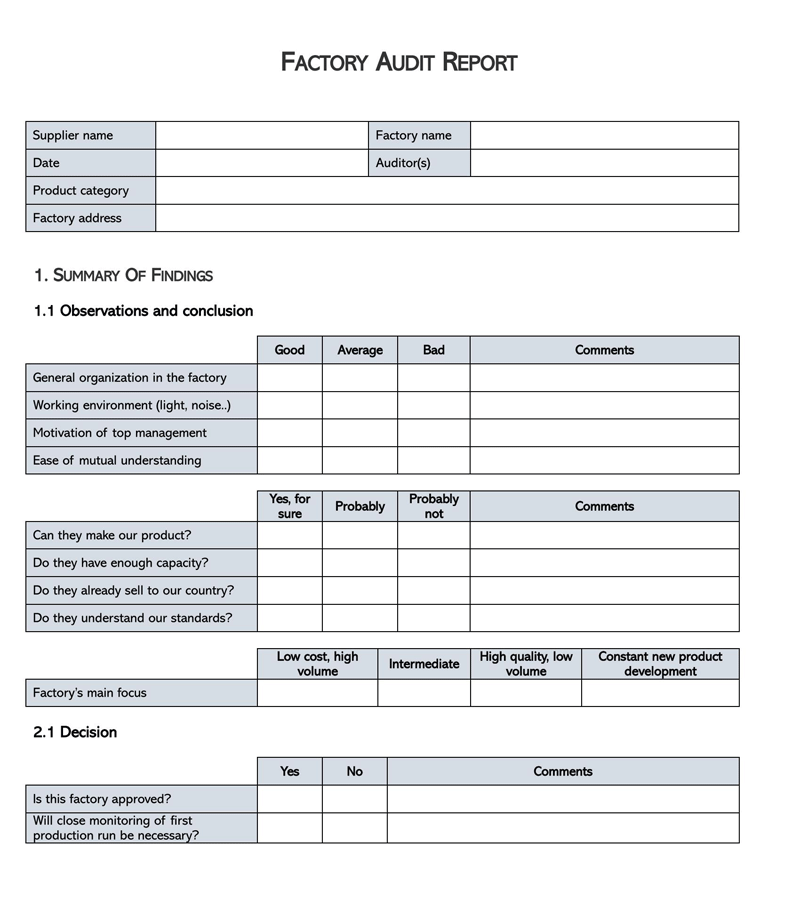
Free Audit Report Templates


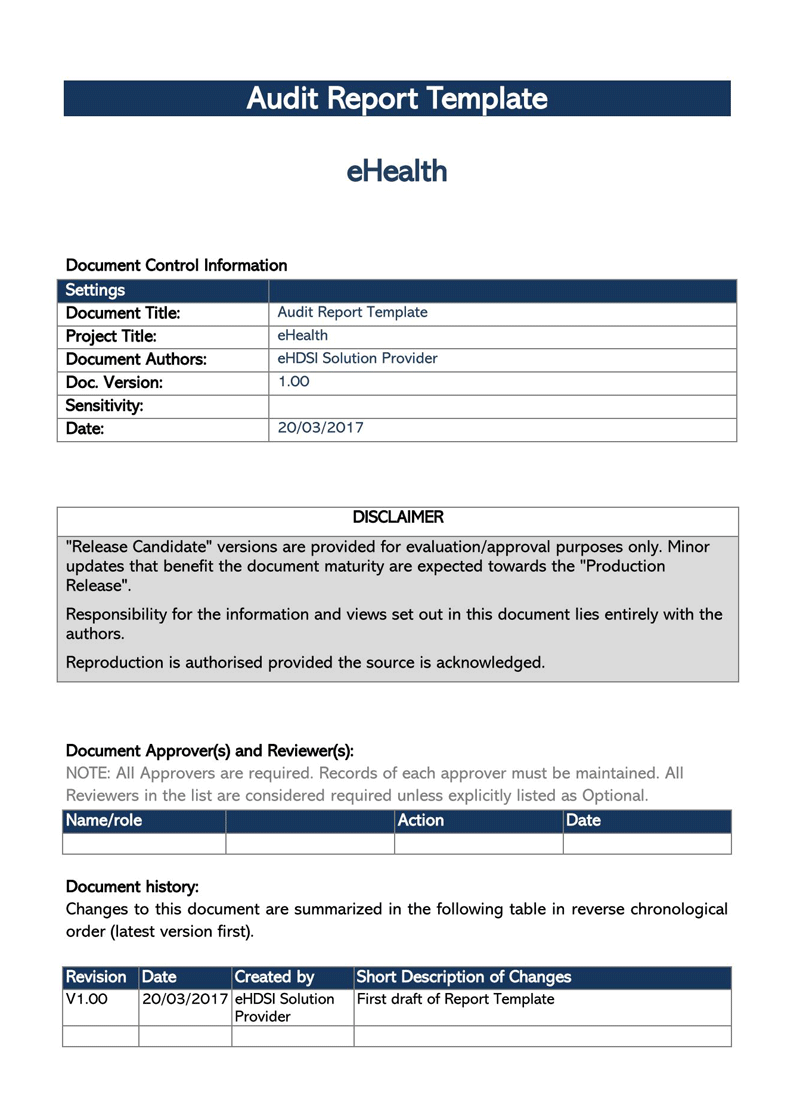
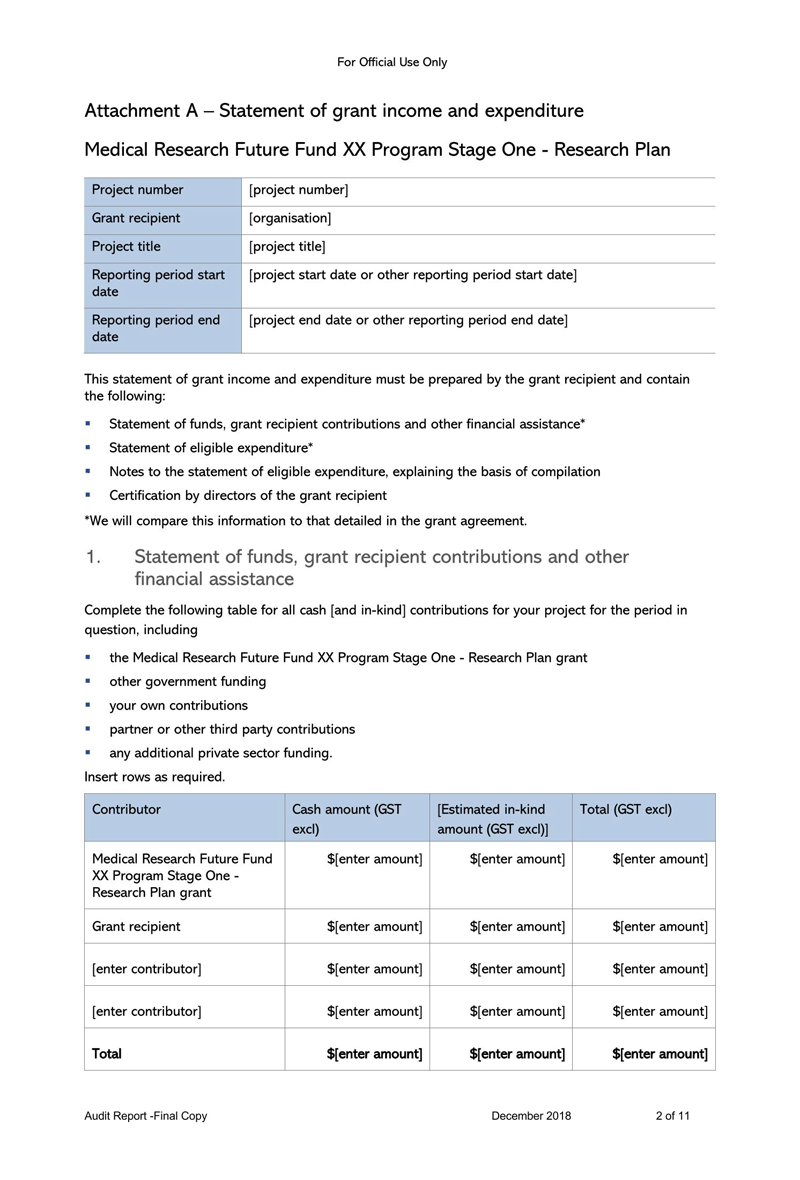



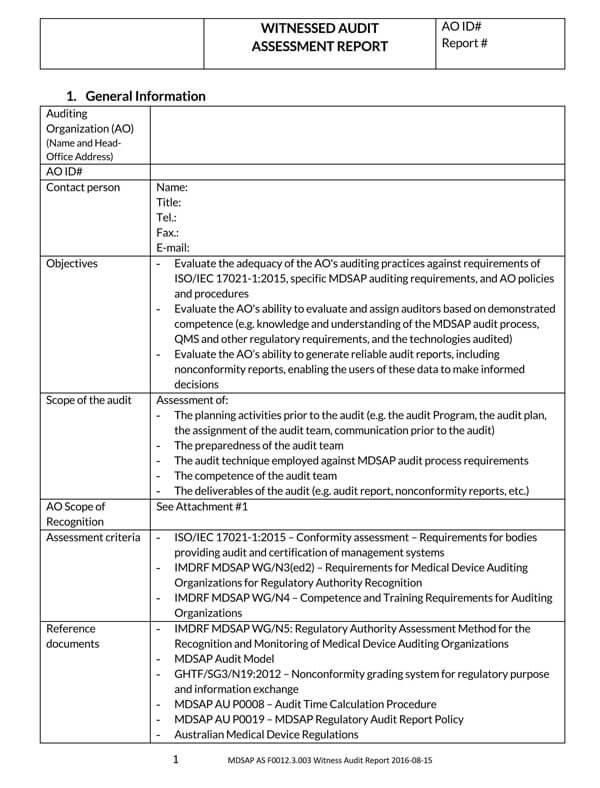

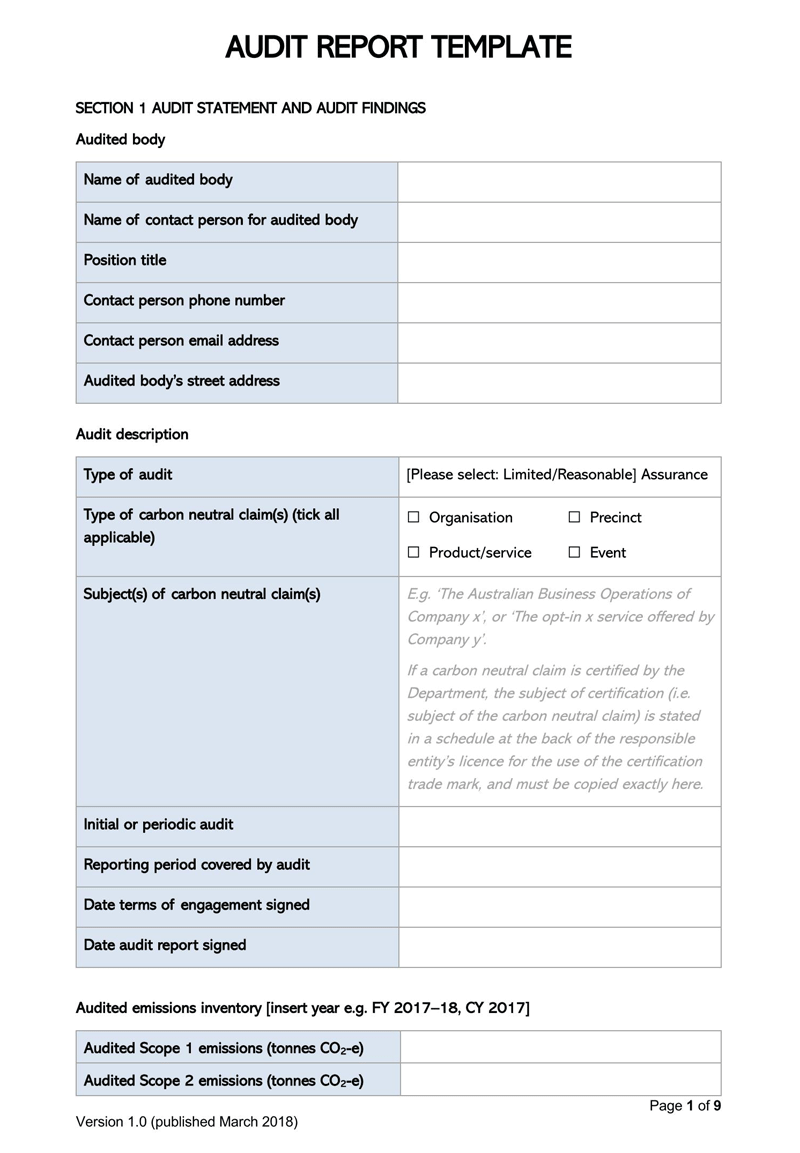
Variations Permitted by GAAS
The audit report is authored in a standard format stipulated by the Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS). However, GAAS allows certain variations of the report depending on the circumstances. These variations are clean opinion, qualified opinion, adverse opinion, and disclaimer opinion. The variations shall be discussed later in the article as “Types of audit reports.“
Uses of Audit Report
An audit report is used by different stakeholders in an entity, such as management, directors, investors, shareholders, banks, and government agencies. It communicates the financial position of an entity based on the assessment of a third-party professional auditor. Banks and lenders will require the report to be submitted before awarding a loan to an entity.
Government agencies such as the IRS and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) require that entities attach one when filing tax returns and financial statements, respectively.
Investors use the report to establish the reliability of the financial statements of a business currently and in the future before investing.
Shareholders and directors use the report to assess the integrity and competency of management. The audit report can also be used to illustrate the utilization of resources within a company.







How an Auditor’s Report Works
An auditor’s report is not an evaluation or measure of the profitability of an entity. Primarily, it represents an opinion on the company’s compliance with standard accounting practices. As a result, it shows that the entity’s financial statements can be relied on to define its financial position. Additionally, it represents the opinion of a third party, free of bias, on the integrity of the company’s financial records. As a result, the SEC can determine if they rely on the financial statements when public companies report their earnings.
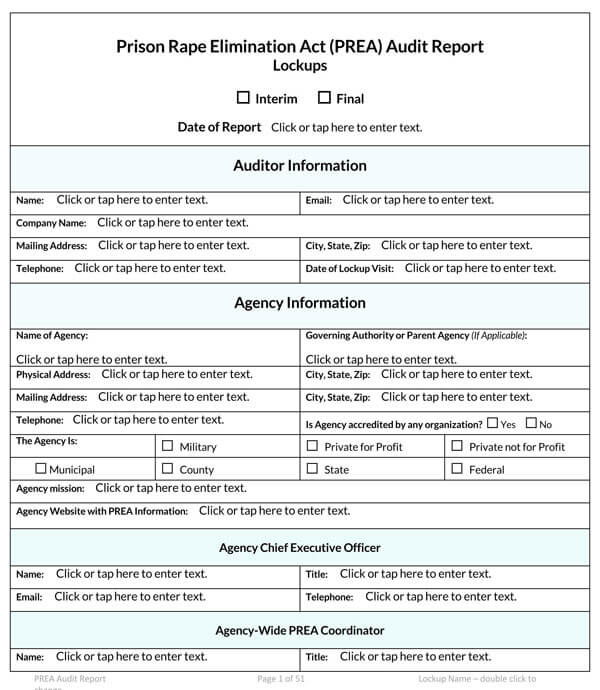
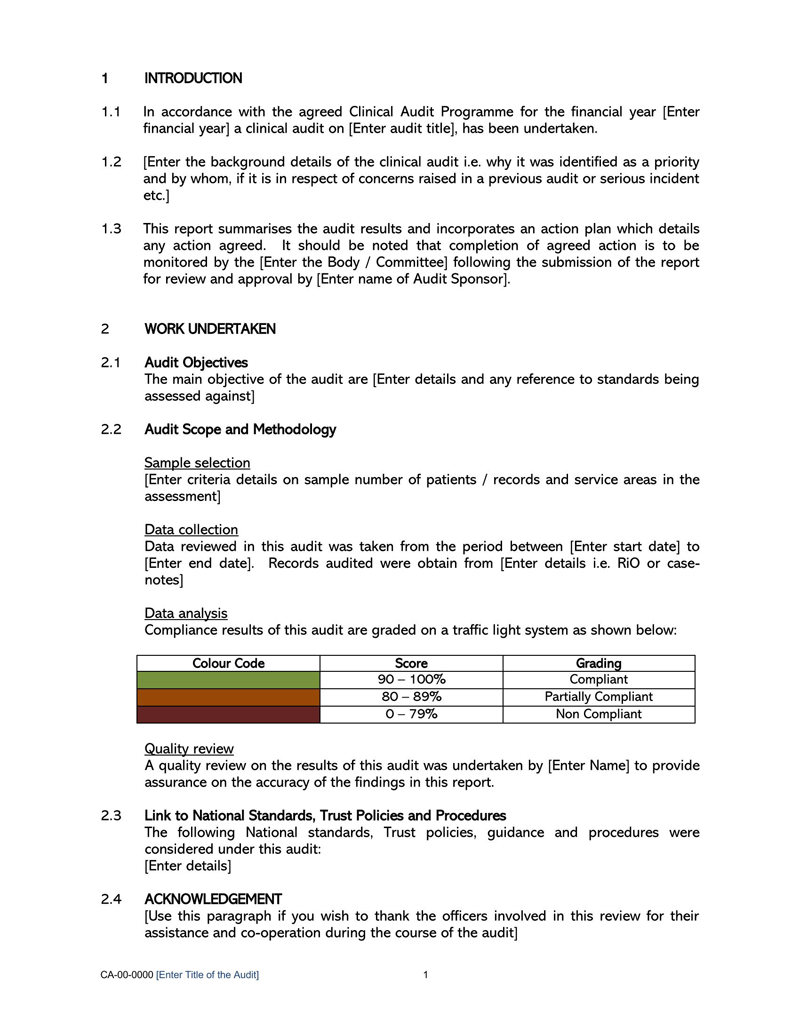
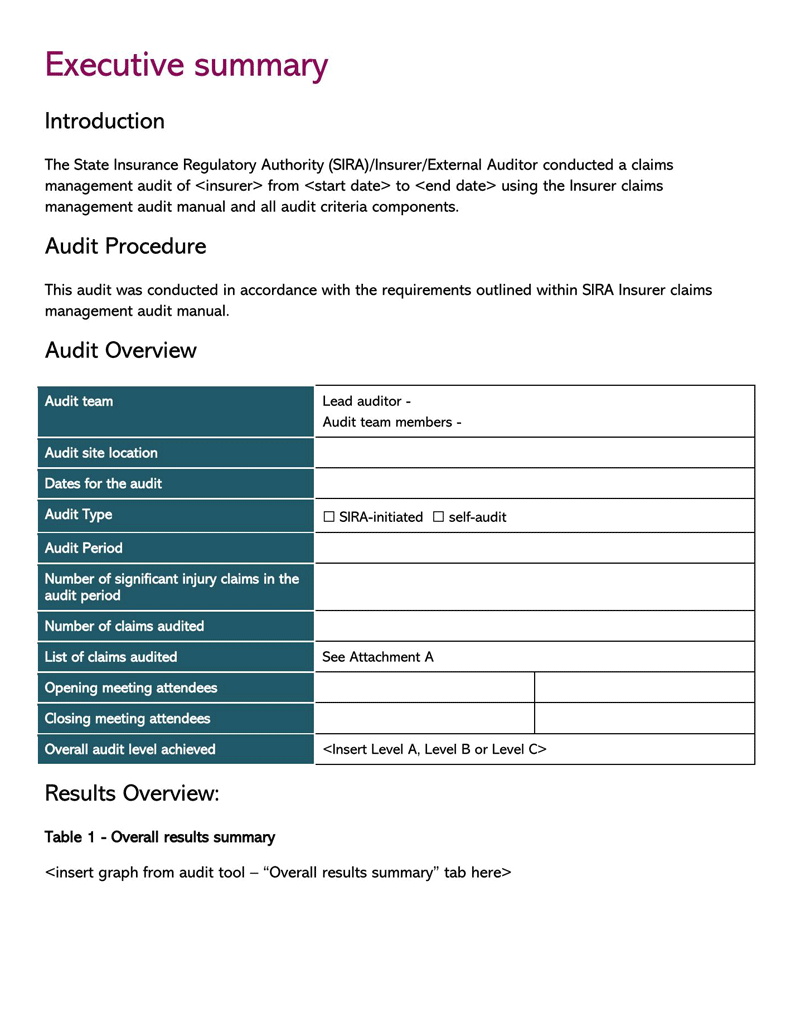

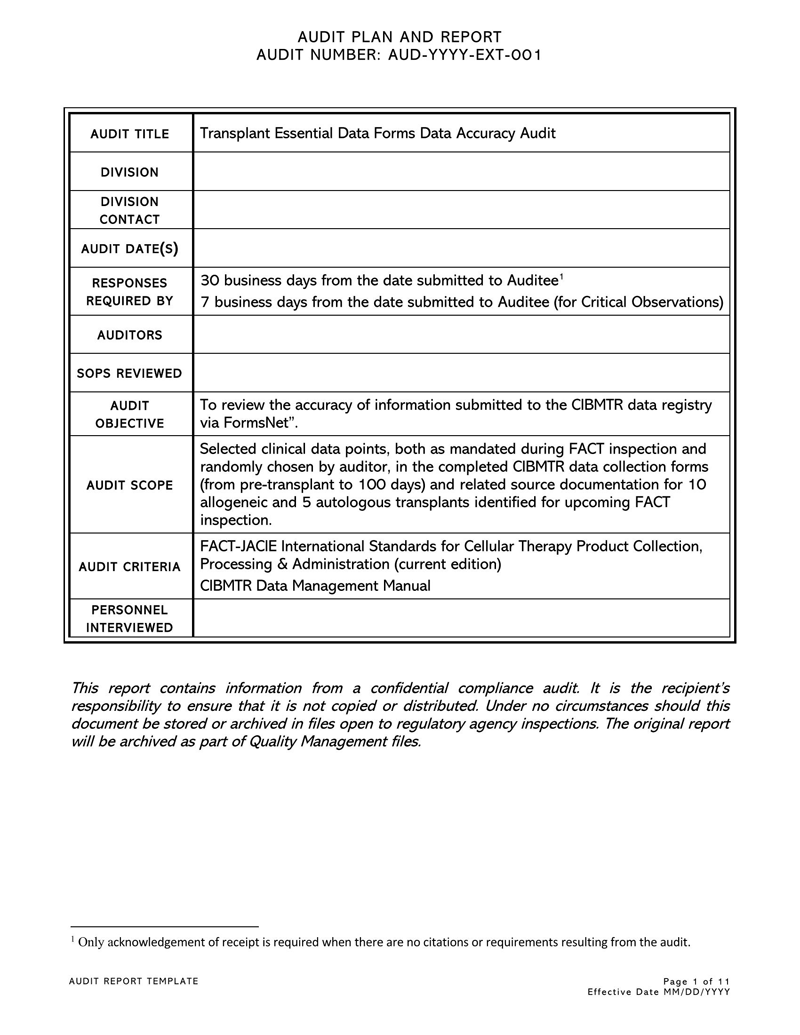


Types of Audit Reports
As earlier stated, the variations in audit reports form grounds for the different types of the same. Different auditor’s reports will have different opinions depending on the misstatements found in an entity’s financial statements. Consequently, different types provide different levels of assurance.
These types are:
Unqualified audit reports (clean audit reports)
An unqualified or clean report is the best type of report an entity can receive from an auditor. It implies that the auditor found the financial statements free of any misrepresentations/misstatements after the audit. Additionally, it states that its financial records have been prepared and presented following Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) regulations. It is also interpreted as reflecting the management’s integrity as up to standard. However, most stakeholders will consider whether the report is from an independent auditor before accepting this derivation.
Qualified audit report
it is received when there are limitations or the GAAP has not sustained any misstatements or misrepresentations in the financial statements; therefore, the auditor has a qualified opinion in that regard. A qualified report is prepared similarly to an unqualified report but with an additional paragraph that outlines why it is not unqualified. This means any other information not highlighted in the paragraph is considered true and fair based on the auditor’s examination.
Adverse audit report
It indicates, through a sufficient examination of the company’s records, that there are pervasive misrepresentations in the company’s financial records. It states that the auditor found material misstatements that impact other accounts and the financial statements in general. Consequently, the integrity of all the other information presented in the financial records cannot be ascertained, as they do not meet the GAAP threshold in terms of compliance. This report outlines all the misstatements identified and how they impacted the entity’s financial statements and decision-making. This is the worst variation/type of audit report a company receive as it harms the trust of investors, lenders, and other users of the report.
Disclaimer audit report
it is obtained when the auditor cannot make a definite and accurate opinion on the entity’s financial status due to infringement of the auditor’s independence. Common infringements that cause auditors not to have an accurate opinion are limited access to crucial information, absence/omission of significant financial records, etc.
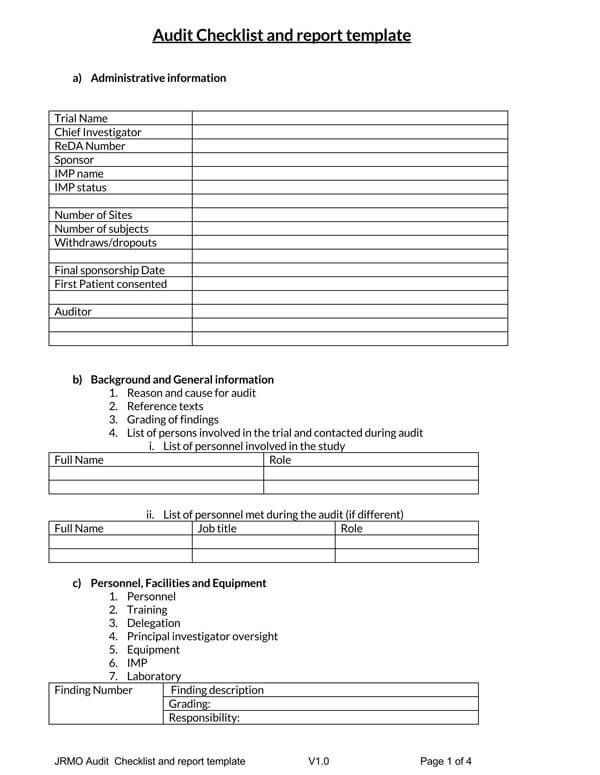
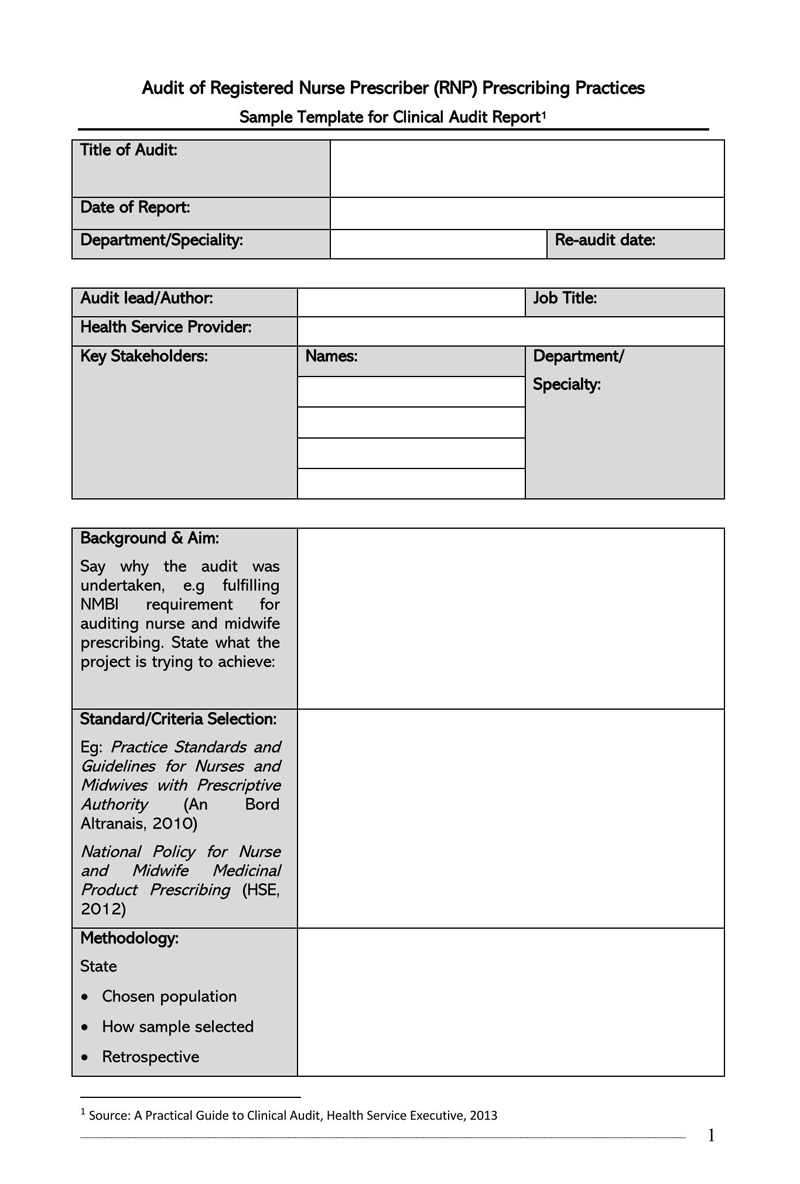
Free Internal Audit Report Templates
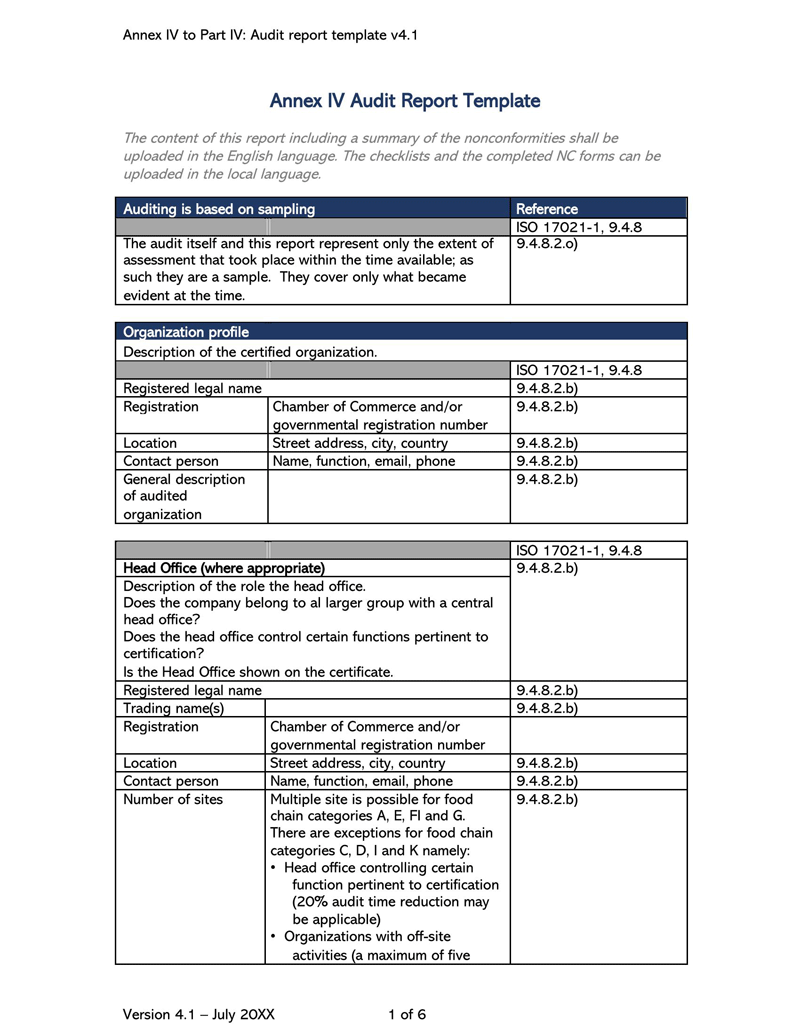
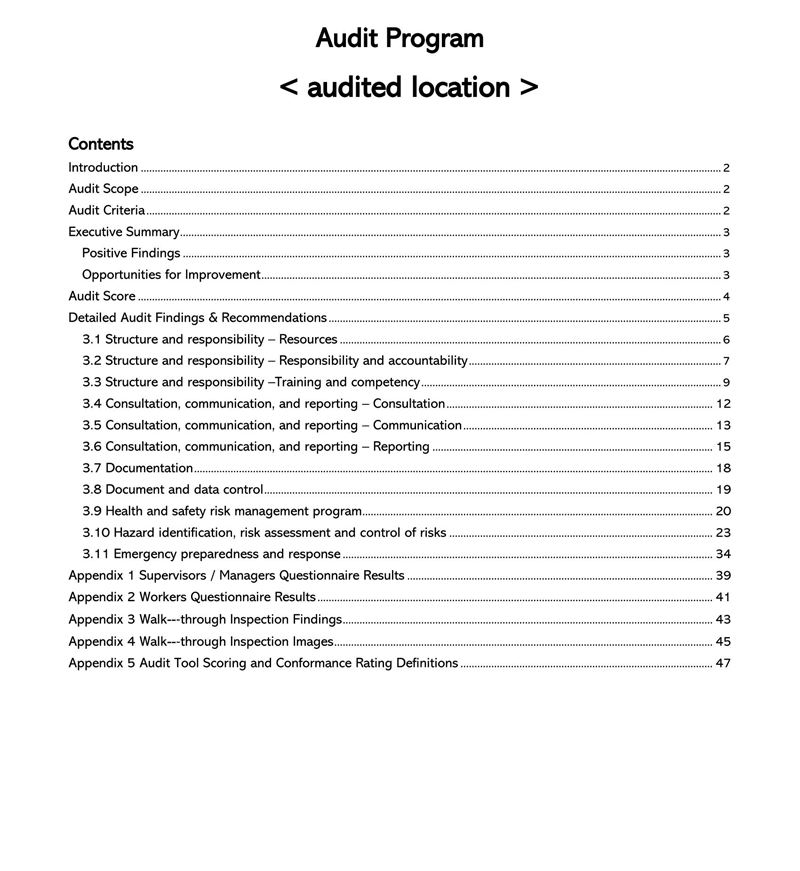




Components of an Audit Report template
An auditor’s report should illustrate the auditor’s detailed observations and opinions related to the financial position based on the provided financial records. It should point out weaknesses, errors/frauds, and lapses observed in the records. Therefore, the template should have the necessary components to communicate this information.
The fundamental components are:
Responsibilities of the auditor and addressee
The report should state that it represents the auditor’s opinion based on their professional examination of company records. It is the management’s responsibility to provide and grant access to all financial records of the entity. The information must be accurate to the best of their knowledge. The auditor’s responsibility is to review all the financial documentation presented to them and form an entity’s opinion. It should also identify the person or entity that appointed the auditor, referred to as the addressee–the stakeholders, board of directors, etc. It should also specify the period covered by the financial records used to form the opinion.
The scope
Shows the extent of documentation examined in the process. The scope can be defined by stating the records examined. Common areas covered by the scope are company accounts, balance sheets, profit and loss accounts, budgets, and cash flow statements. This section represents all the processes and resources the auditor used to base their opinion.
Auditor’s opinion
Lastly, the auditor’s opinion, observations, and comments on the entity’s financial and operational position should be presented. The opinions and comments should be free from bias.
The report should show the auditor’s opinion on the following:
- Arithmetic accuracy of financial statements and whether the figures correspond to books of accounts
- In a qualified report, the auditor should give the reasons why financial statements do not represent a free and fair view of the entity’s financial position
- In an unqualified report, the auditor should state if the records give an accurate and free representation of the entity’s compliance.






Advantages of Audit Reports
Audit reports have a wide range of advantages when it comes to running a company.
Below are common advantages that companies have been observed to benefit from audits;
- They help assure third-party users of the credibility of an entity’s financial statements.They are prepared by independent auditors who are unlikely to misrepresent the financial status of an entity.
- A good, desirable report indicates the integrity of management, which is a desirable trait in the eyes of stakeholders.
- Periodic auditing is a legal requirement in many countries. Auditing financial records is thus one way of ensuring an entity is compliant with the rule of law.
- Shareholders require them to determine if the company’s records can be trusted. The report communicates this in layman’s language, meaning each shareholder can understand the financial position even with a background in accounting.
- Audits help parent companies manage their subsidiaries by examining their financial records and providing status updates.
- It helps an entity determine if there are any concerns (both financial and non-financial) associated with its books. This can help in mitigating financial problems such as bankruptcy and any foreseeable issues.
Limitations
The following limitations are applicable regarding the auditing process;
- The scope might be limited due to access restrictions on documentation by management, which might hinder the shareholders from getting an accurate opinion from the auditors.
- Time is often a constraint on the auditing process. This will consequently result in a hurried report, which might prevent the entity from obtaining a wholesome report from the auditor.
- They will often not take into consideration factors besides the financial records presented. Therefore, some inherent fraud risks might not be accounted for, which exposes the company to continued fraudulent behaviors without detection.
- Some might carry out mediocre audits to finish and move on to the next job, resulting in poorly done reports that are not beneficial to the company.
- bias in opinion. To avoid this, auditors are expected to observe the code of ethics, which directs them to work independently.
Key Takeaways
- An auditor’s report outlines the responsibilities of the auditor and management in the process, the scope of a company’s audit, and the auditor’s opinion and comments regarding the financial status of a company. Individual auditors or firms conduct audits.
- An independent auditor should prepare the report to ensure there is no bias in stating the company’s financial status. It is used by third parties like lenders, shareholders, and government agencies to determine if the company’s financial statements are compliant with GAAP.
- They are essential in establishing whether a company’s financial documents can be relied on to make decisions and illustrate management’s integrity in producing factual and accurate financial information to directors and stakeholders.
- However, the credibility of audit reports is limited due to the scope, time constraints, and ethics, among others.




