A risk register is defined as a management tool used to list the risks that have been identified and are being managed by an organization, together with their individual severity and likelihood.
The document can also be used to classify risks associated with the different aspects of your project and document the responses that have been implemented and their effectiveness in minimizing risks.
Every project organization is prone to certain risks at one point or another. It is, therefore, up to a project manager to anticipate these risks and plan on how to address them should they take place through a process known as risk management. A risk register is one of the key tools in conducting its assessment and management.
It features a simple display of the defined risks with an associated probability and impact ranking. It facilitates prioritization by sorting them according to their total calculated score. It can be filtered by project or date range or sorted according to various options such as risk type, probability, or impact. With such information, you can use the register to track risks throughout the project lifecycle. Other than being a project planning tool, it is used as a regulatory compliance document.
This article will discuss how these registers work, what they entail, different types of registers that project managers should be aware of when conducting risk management, and provide templates that you can easily edit and use instead of creating one.
When You Should Use This Register
They are used in multiple instances. Firstly, it is used when you, as the project manager, plan for risks associated with a project. The register records the forecasted or identified ones before the project begins. They affect projects greatly as they might lead to accidents, losses, or even non-achievement of the project goals.
It can also be used for managing and controlling different types of risks, such as financial, time, or technology-related risks. Such a register is not limited to certain types of risks. It can be used when you want to resolve risks as they occur. Once a predicted risk happens, the register can be consulted to determine the proposed mitigation measure or resolution.
You can use templates to record risks as soon as they occur and track the progress in a register in corrective measures when addressing them. The template allows you to add information to the register. You can add new risks, update existing ones and delete any of them.
It also lets you assign your register to a specific project or date range. This aspect is extremely useful in many situations, such as reporting, awareness training, or even internal management meetings where senior managers can view what they are currently affecting their projects.
Also, using a template ensures you have ample time to develop effective and well-planned responses to project risks. This can be essential in ensuring deadlines are met even with the impacts of existing ones being observed throughout the project cycle.
Register Templates





How does It Work?
Below is a series of steps involved in carrying out the management process:
Step 1: Identify potential risk(s)
The process begins with identifying all the projects associated with the particular project or organization. Each project will have its unique risks. However, similar projects and organizations can have similar potential ones. Predicting risks can often involve extensive research and experience. This step can involve cooperation with team members and stakeholders so as to ensure each party’s concerns are addressed.
Step 2: Describe project risks
Next, each one identified above should be described fully. A proper description should indicate the type, impact, and the owner. The description can also include any other additional details that provide further insight into the nature of the risk.
Step 3: Estimate risk impact and probability
To determine the severity, it should assess the impact and the probability or likelihood to occur. This step involves looking into the different aspects of the project which the risk is most likely to influence. Involving the owner is an effective way of determining these two properties of risks.
Step 4: Document all risks and response plans
Next, you should outline all of them and the associated responses in the template. The response plans should be direct to the point and must indicate the specific actions that need to be taken if the mentioned risk occurs. You can add an attachment to the template if the response plans have to be lengthy and covered in a long document.
Step 5: Prioritize project risks
Afterward, you can rank all these in order of priority. They vary in terms of impact and urgency. Therefore, some risks have to be prioritized over others. You can rank or categorize them as high, medium, or low risks. Low risks are the least significant risks that can be overlooked in favor of other, more important ones.
Step 6: Assign an owner
You should then assign a team member to each risk. Assigning them to team members helps in identifying them in good time before they cause significant damage that may be irreversible. It also helps with timely intervention since the assigned owner is expected to monitor the potential risk closely.
Step 7: Review and update
Lastly, you can progressively review and update the register as time passes. Any potential risk that had previously been identified and did not occur when expected can be noted, and any emerging ones can also be recorded in the document.
Templates with Types
It is a document that contains all risks that an organization is facing, for example, time, resources, and money. Risks can be anything from employee issues to legal problems or just plain bad luck. When identifying them, it is important to be as detailed as possible. As a result, multiple types templates are made to accommodate the different types of risk you can encounter as a project manager.
These include:
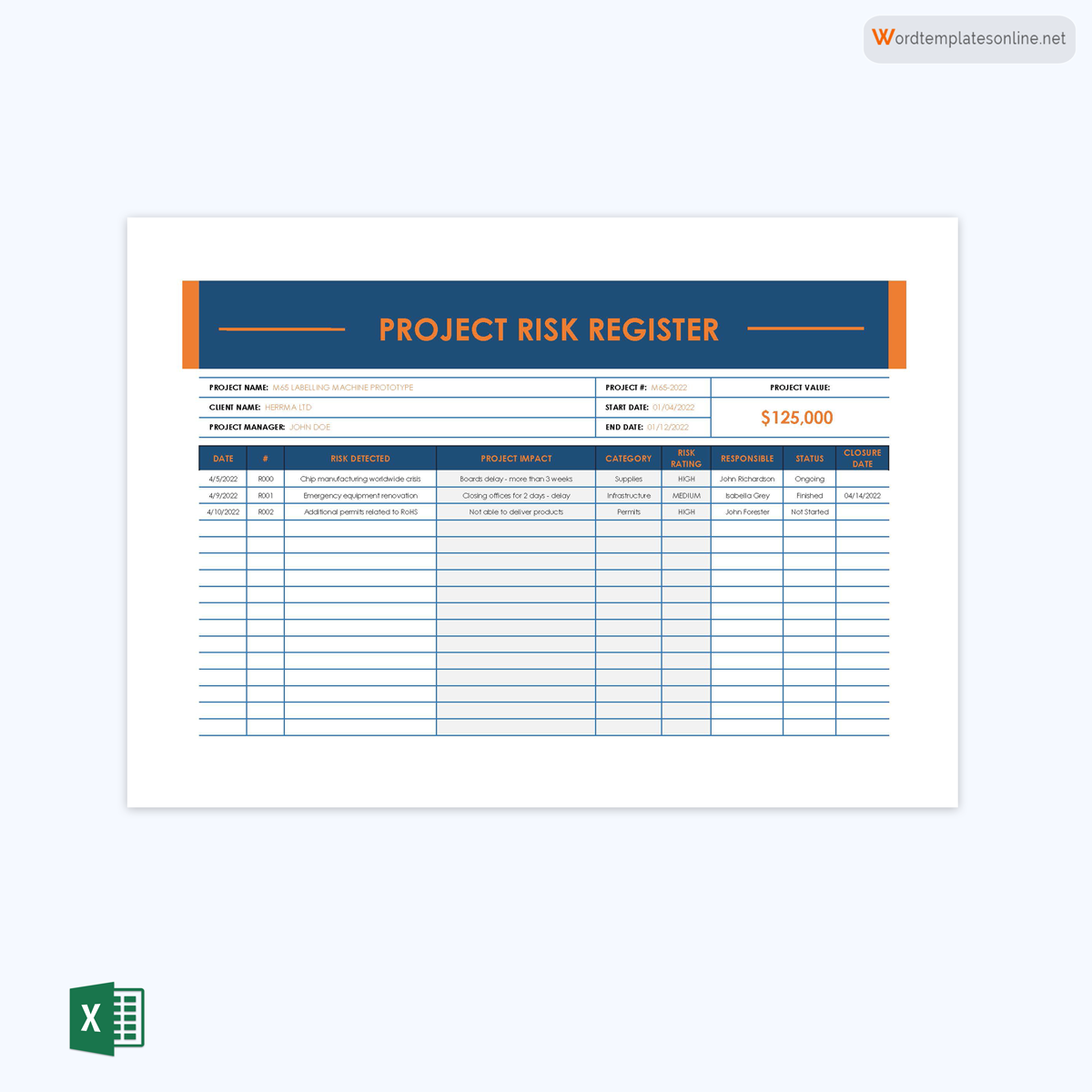
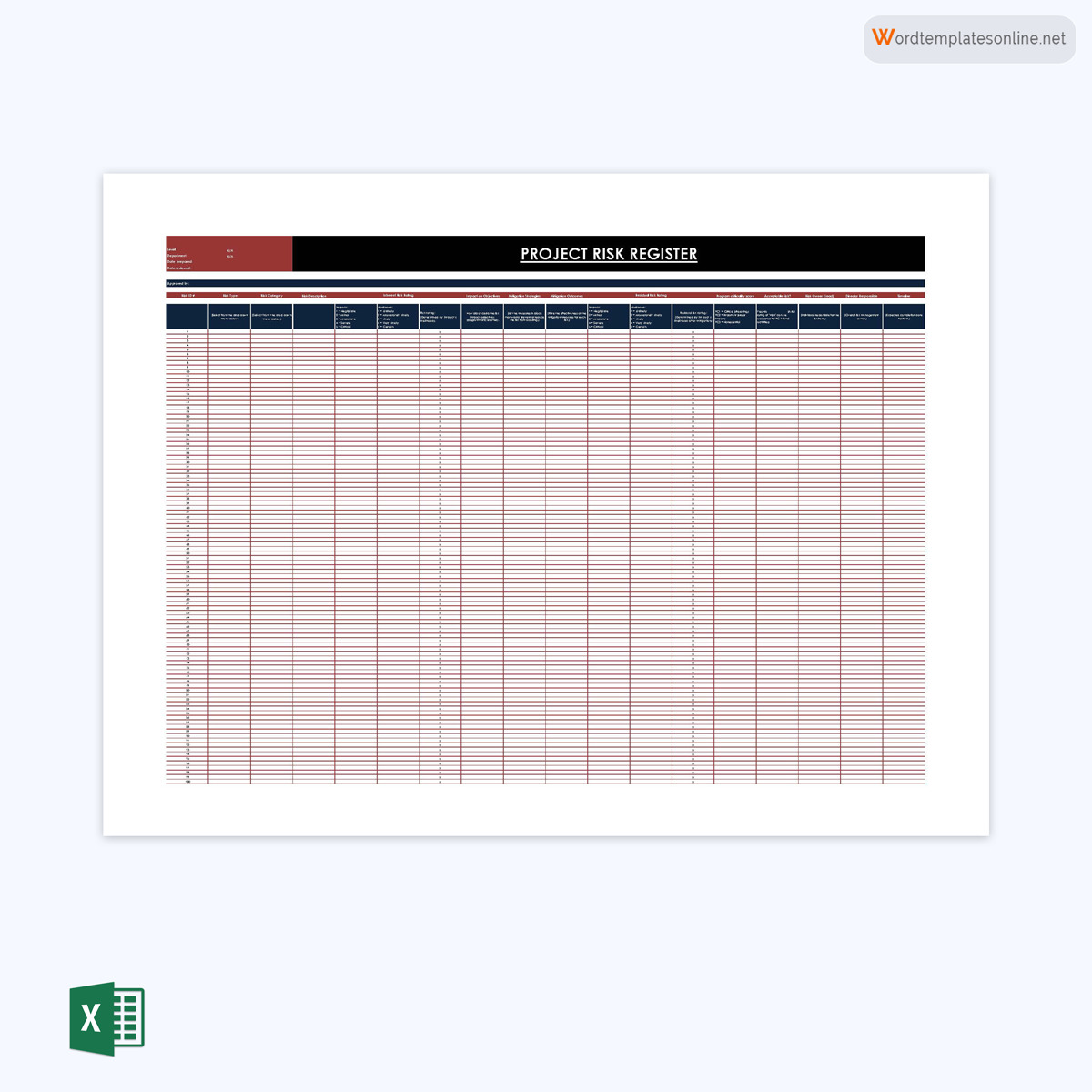
Project register template
These templates are used to list all the probable risks associated with a project. Such a template has sections to record the types, impacts, and risk response strategies.


Data register template
A data register is used to record risks associated with data within a project or organization. Some of them associated with data include data loss, access/privacy, data compliance, and corruption.


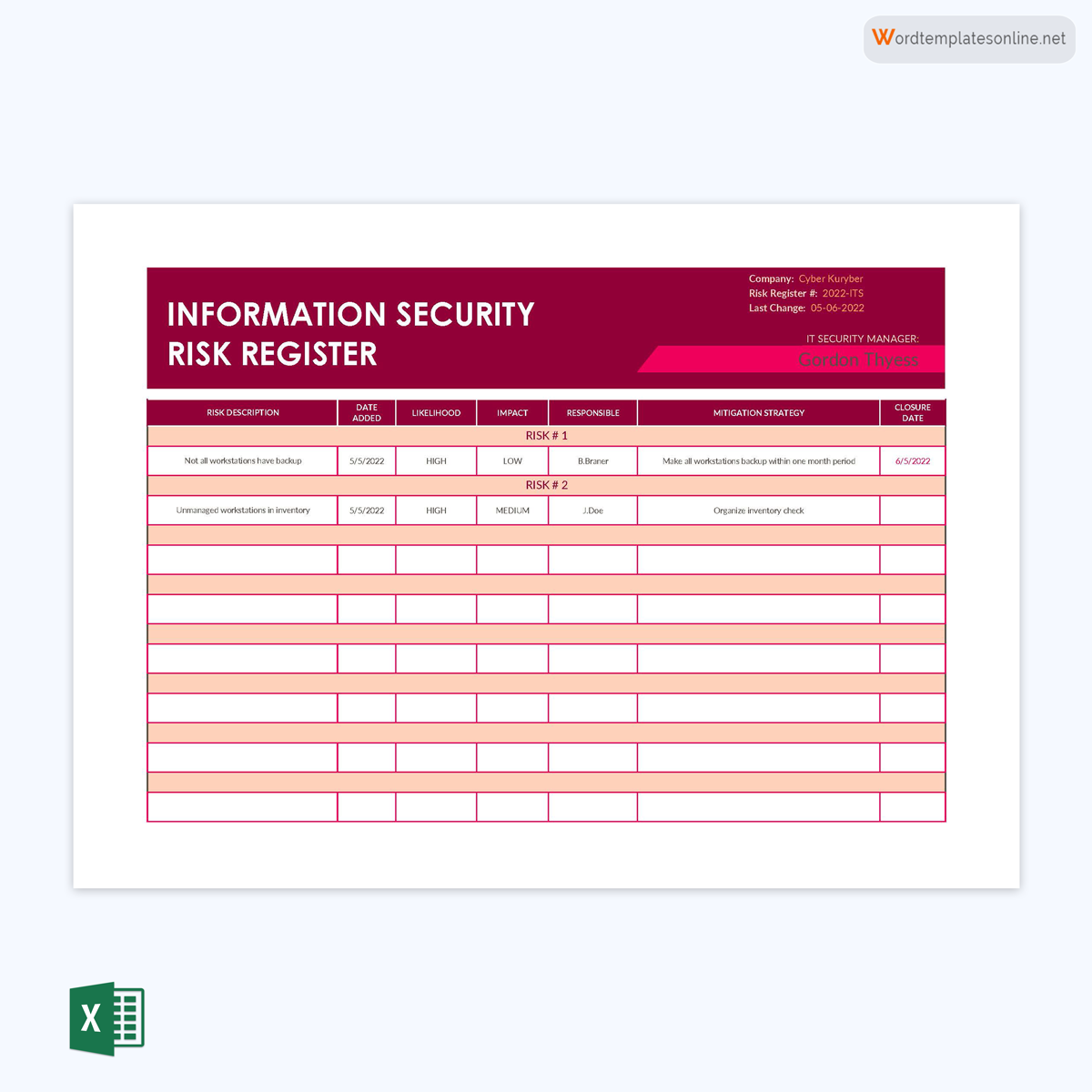
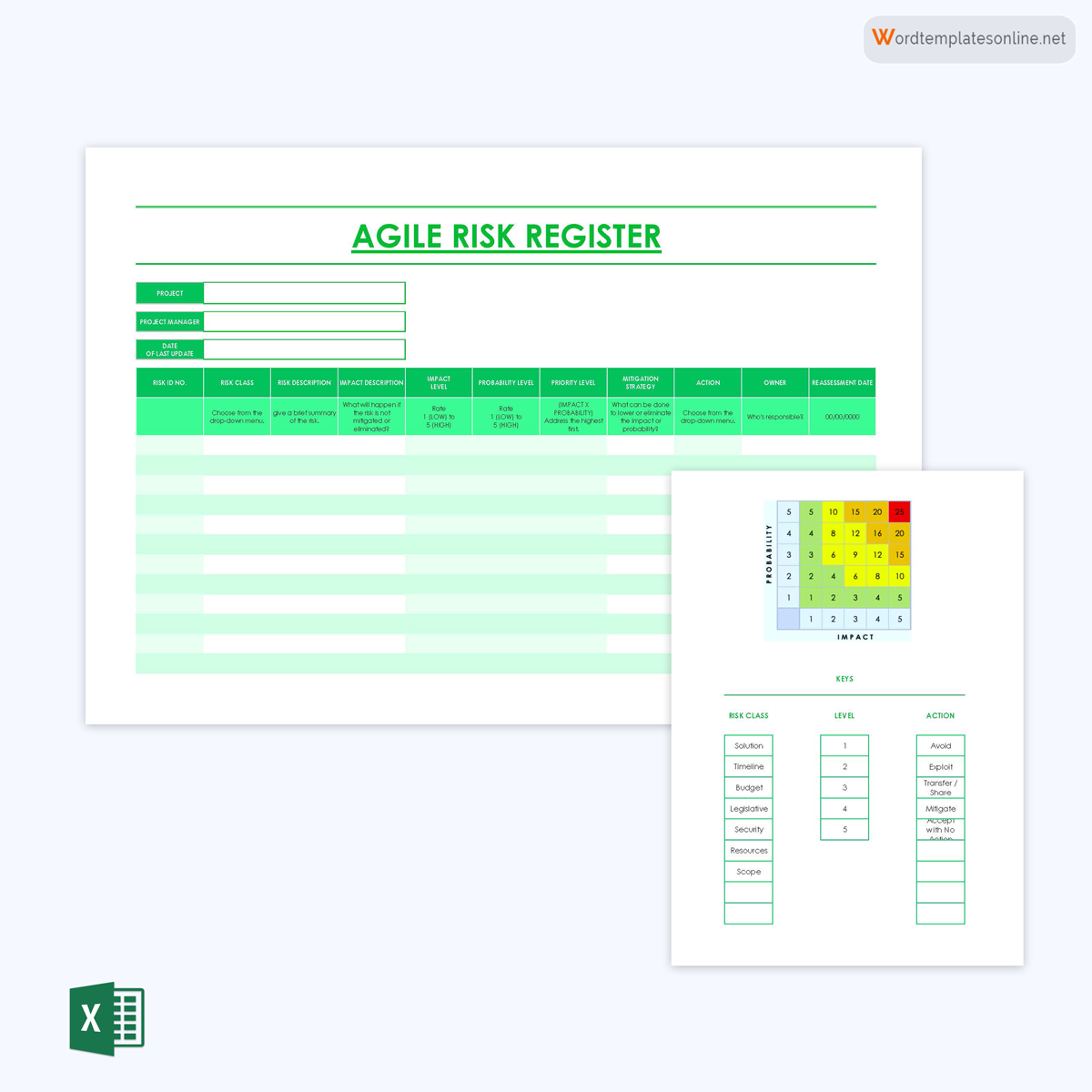
Agile register template for information technology
An agile register aims to outline the risks associated with the Agile methodology of project execution. This type of register is common in IT.

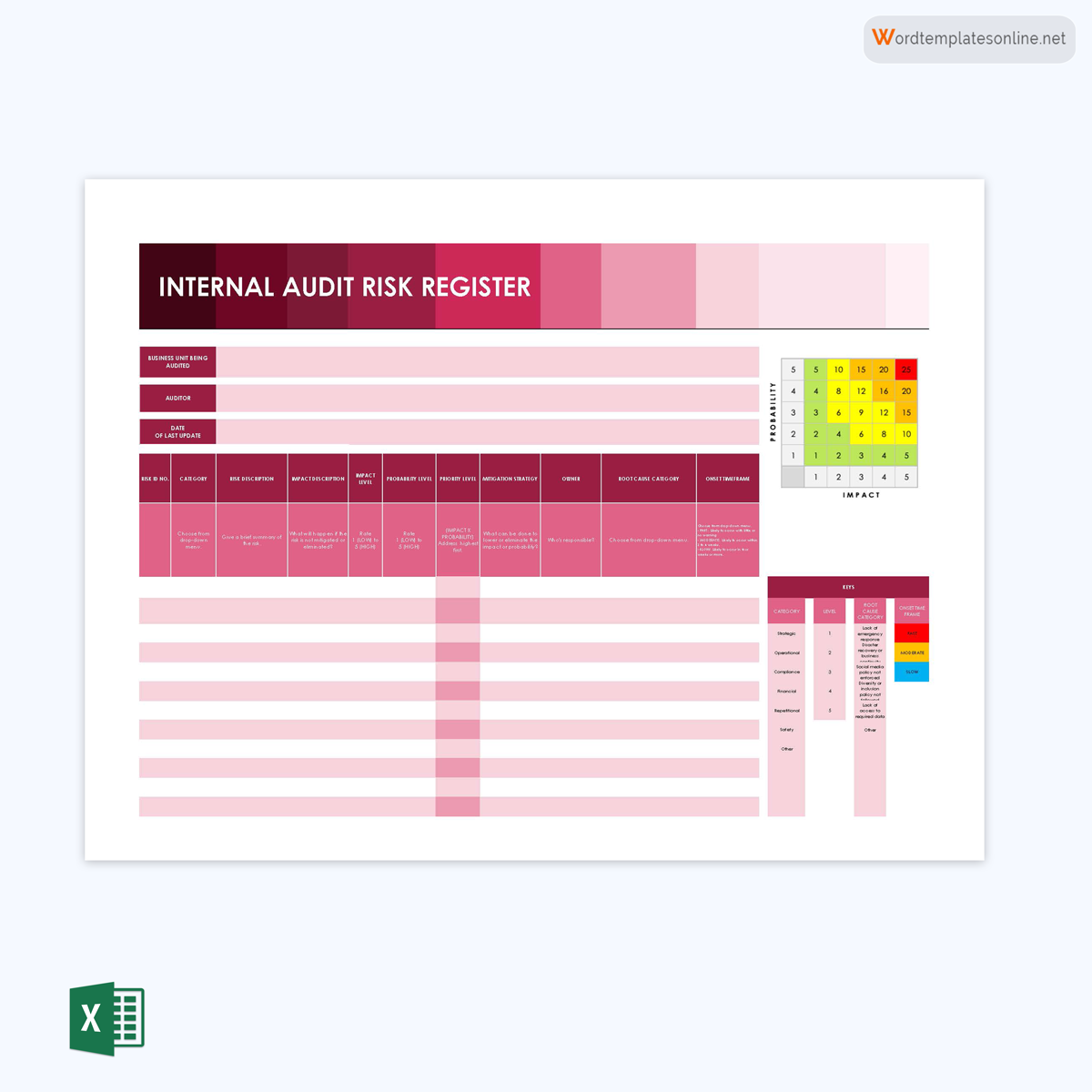
Internal audit register template
This template helps you identify all the risks that can cause a project to not meet its goals because of internal factors. It is often used by auditors to identify, categorize and track risks and develop mitigation strategies.

Corporate register template
It is used to record company-level risks and track them and their associated impacts. It can be included as part of the company’s strategic documentation.


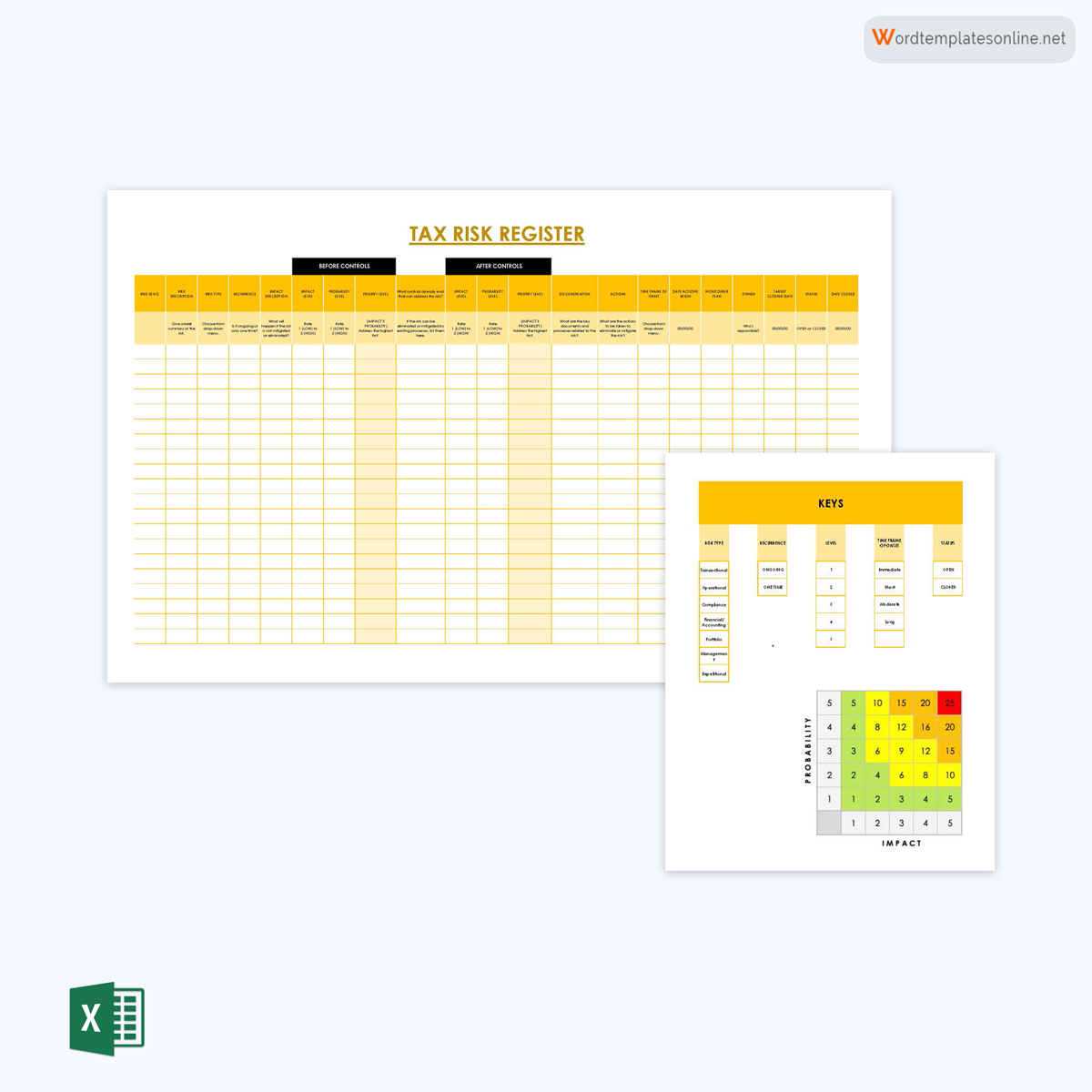
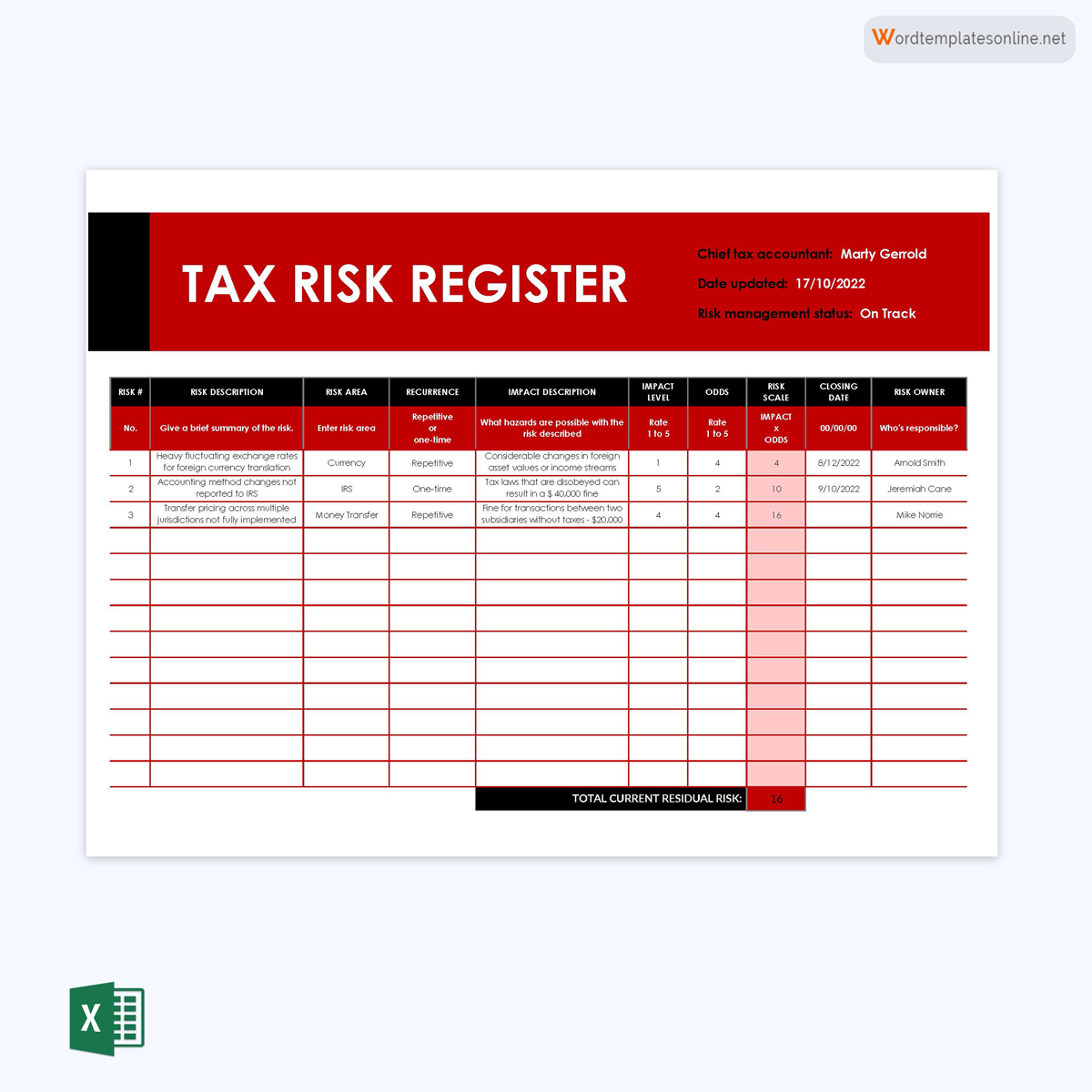
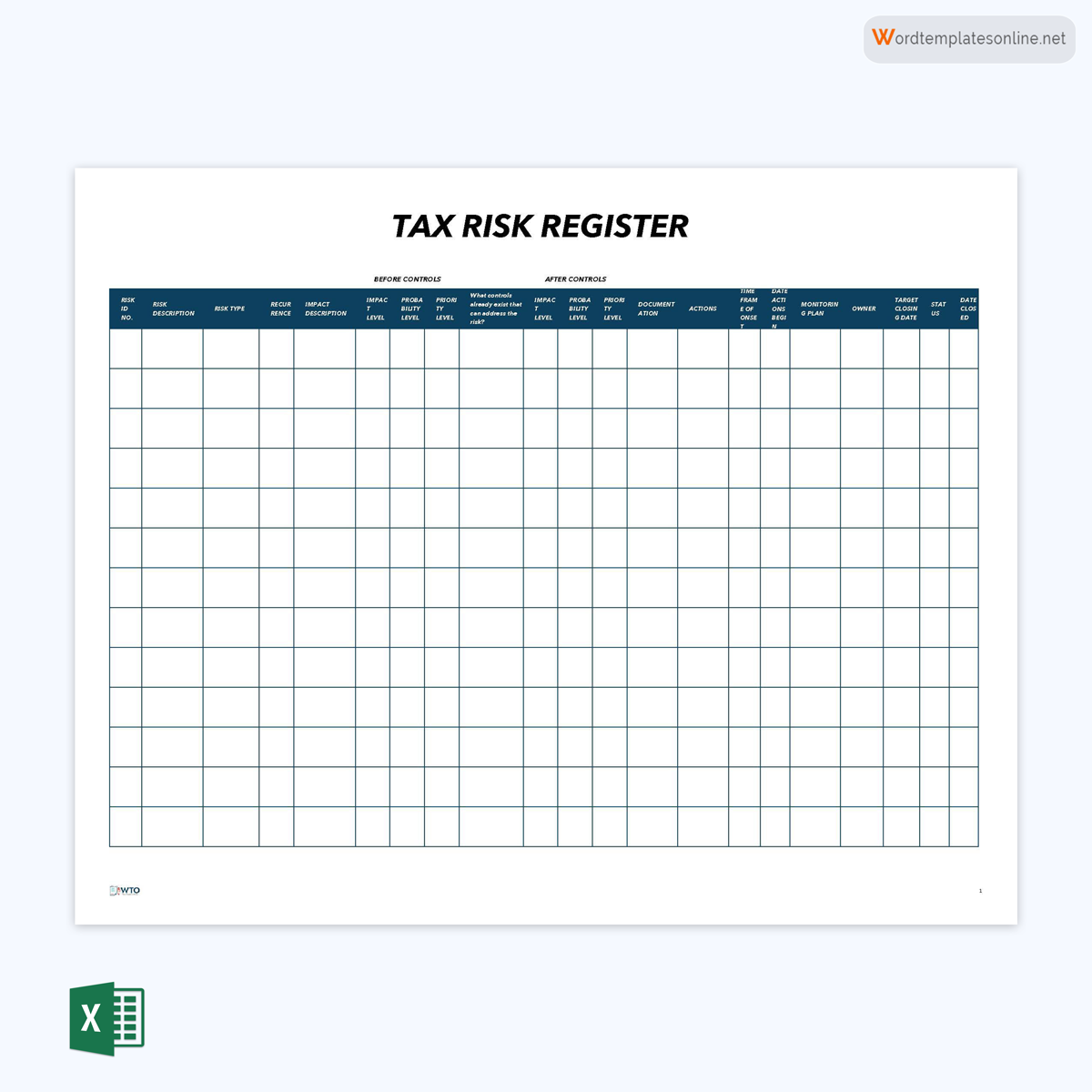
Tax register template
This register is used to manage risks associated with taxation. It can record the type, the onset, the response, and associated documents. It can be part of an organization’s or project’s compliance documents.
Strategic register for schools template
Education institutions also have to carry out periodic risk assessments and management. In such a case, a strategic register for schools can be used to ensure the school remains prepared for any probable ones.


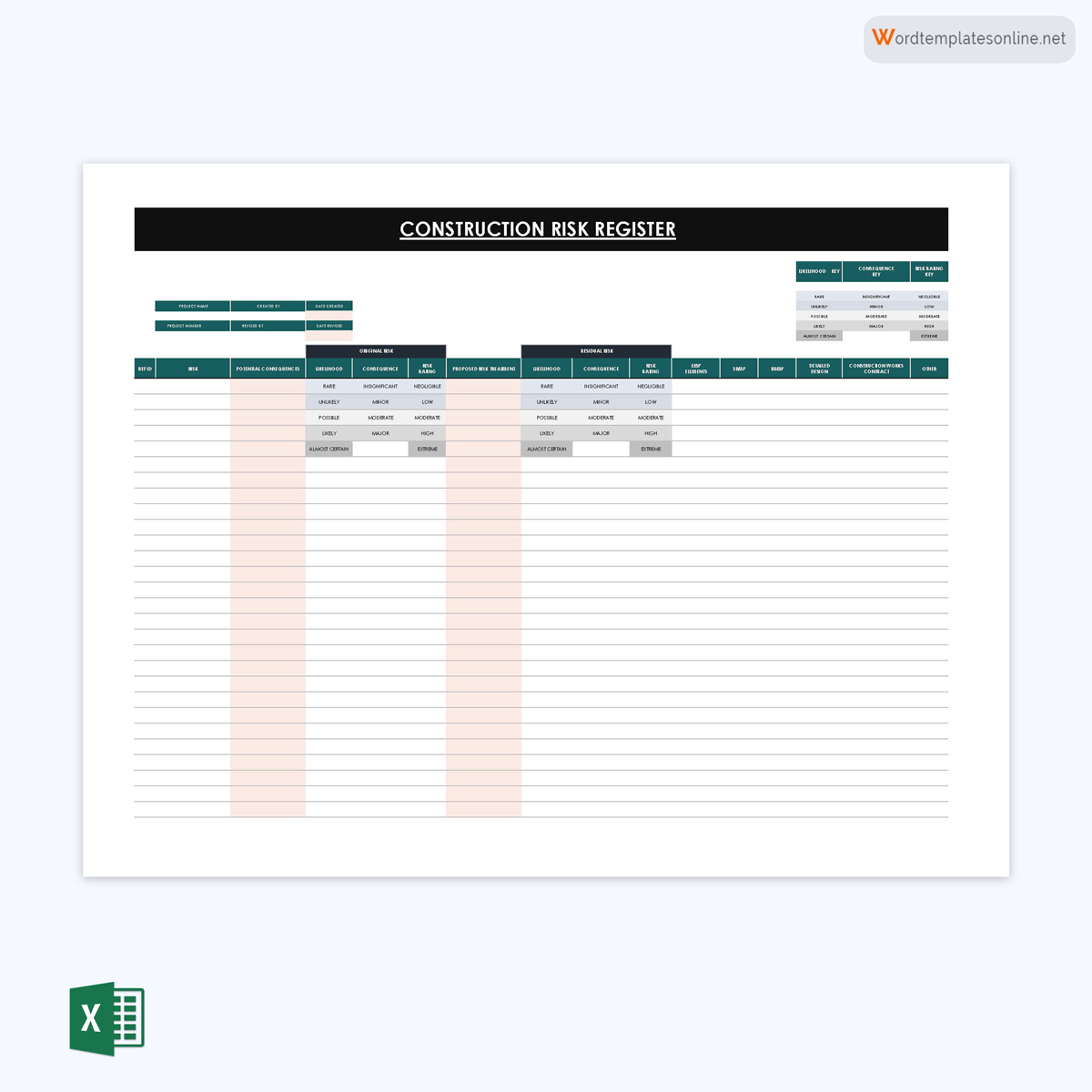
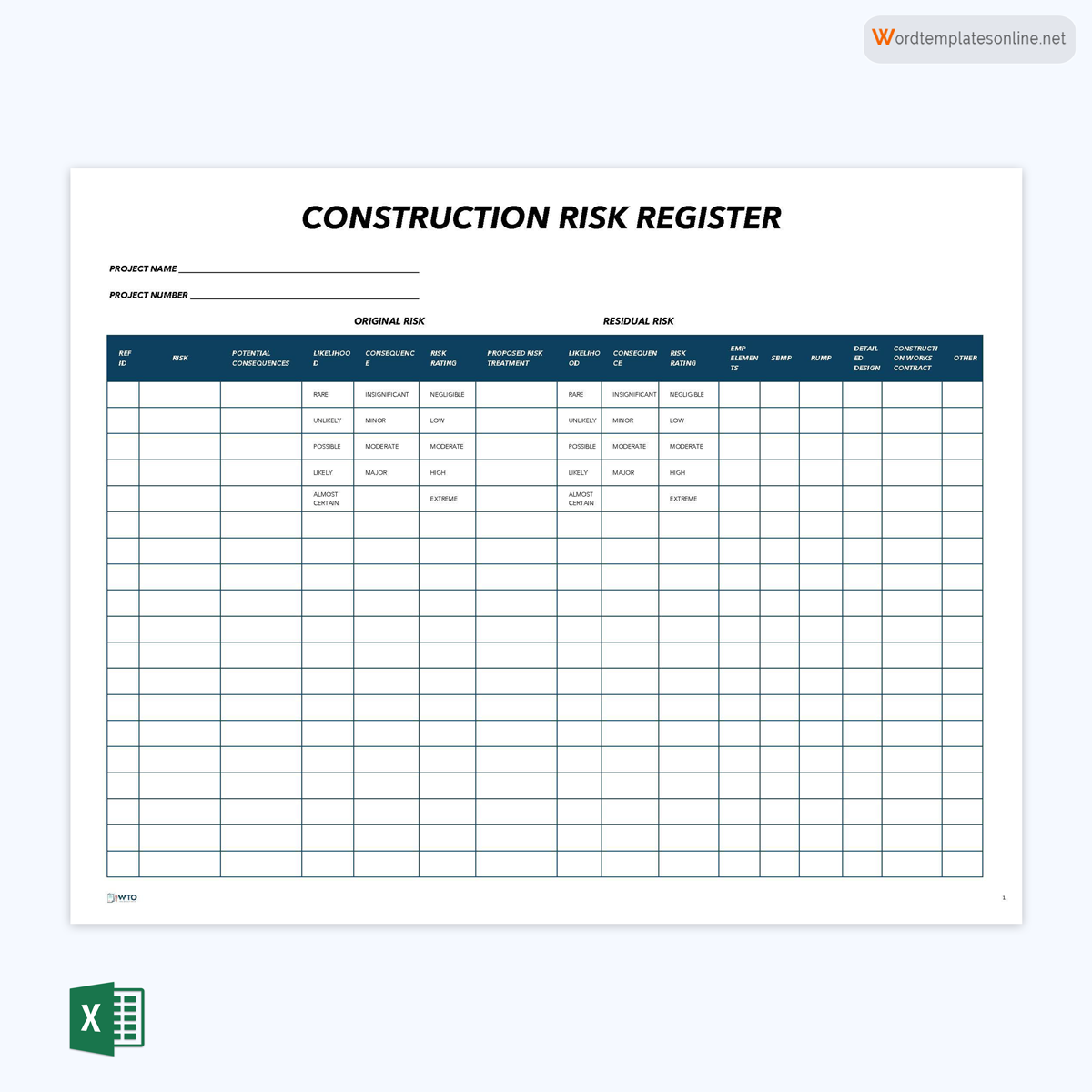
Construction register template
Construction projects are prone to risks throughout their lifecycle. Construction project managers can use this template to ensure they are effectively equipped and prepared for any risks that may arise from different parts and phases of the project.
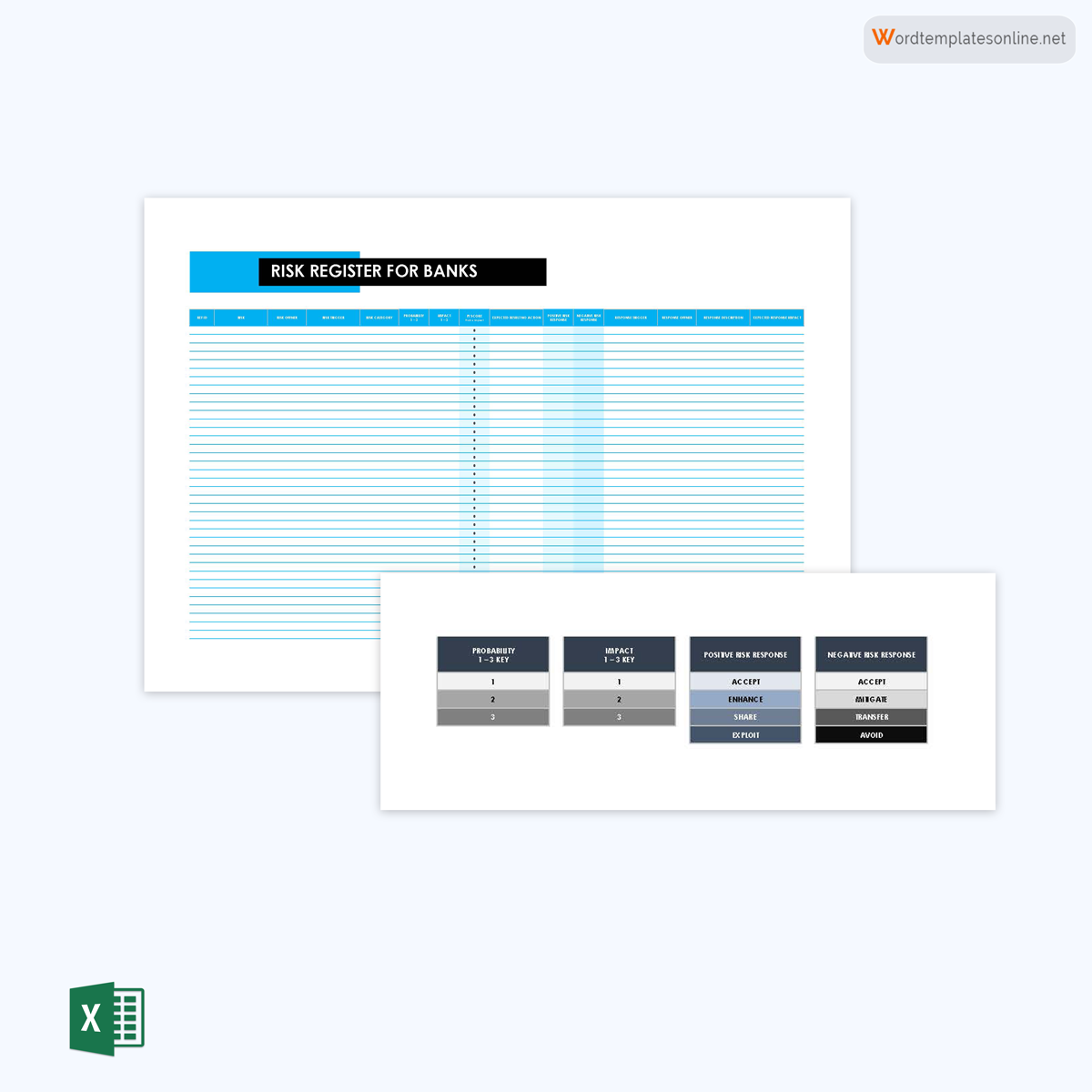
Template for banks
Banks can also carry out risk management through register templates. This register is meant to record risks associated with data security, safety, system failure, audit issues, etc. In addition, the register should record the expected impacts and proposed mitigation measures.


Operational register template
The operations of a project or an organization can face risks from time to time. It offers an effective way of recording these risks and keeping track of the effectiveness of implemented responses.

Data protection register template
Organizations involved with data handling can use a data protection register template to outline the probable risks of data protection. The register can be categorized into external and internal threats to the security of the data.

Human resources register template
Risks associated with human resources can be identified, defined, and tracked using this type of register. Humans are unpredictable, and this aspect poses some risks to a project or organization. This template allows the project manager to identify these risks before they happen.

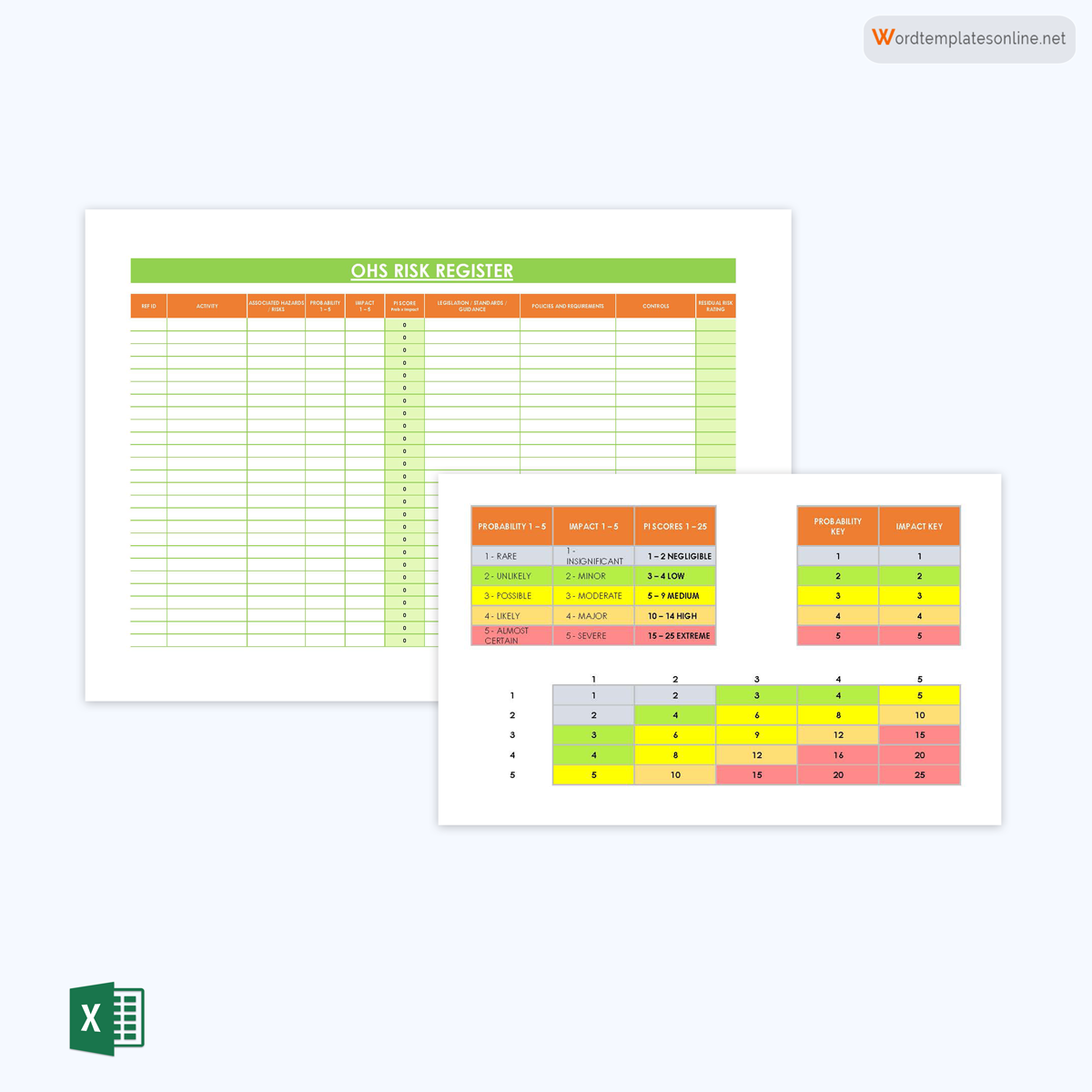
Occupational health and safety hazard register template
Each project has potential health and safety risks. This register helps management anticipate potential health and safety risks associated with a project and put measures in place to prevent these risks or address them should they occur. This register is mandatory and often created as a compliance document.

ISO register template
It is used to assess risks associated with a project to comply with ISO standards. Therefore, this type of template is more of a compliance document.


Clinical register template
This register is used in the healthcare industry to record and track associated risks. The register ensures a healthcare practitioner or institution complies with applicable laws and regulations.


What to Include in It?
Creating a register can be stressful, especially for complex projects and large organizations. As a result, project managers often practice using templates to create it. Templates are beneficial in reducing the time and effort used in creating this register. They are also reusable, and thus users don’t have to always create a register from scratch whenever they need one.
While its templates will vary from one project to the next, most will often have the following components:
Risk identification ID
Each probable one identified in the template should be assigned a unique identifier. The identifier can be a name or an ID number. The template should thus have a section to record the respective identifiers. This is typically the first item that appears in it.
Description
A section that records a brief description should be provided. The description should include the following information: main risk (sub-risk), type of risk (financial, time, etc.), project or date range that the risk applies to, and impact ranking.
Breakdown structure
It should be included in the template. A breakdown structure breaks them down into stand-alone risks and identifies the dependencies between the risks.
Categories
There must be a breakdown into categories that help organize and facilitate their management. Categories can be major, medium/minor, and critical risks or based on the aspect of the project affected, such as budget, schedule, weather, external, etc. It is important to note that not all projects will have the same number of risks. A breakdown can help you better understand what they are.
Analysis
After categorizing, it is time to analyze them. The probability and impact can be assessed using qualitative and/or quantitative data. This helps in determining the severity of each risk.
Probability
The next step is to calculate probability and assign a quantitative or qualitative value. The rating should be done carefully, considering factors such as the project experience level, resources available, and the time available to mitigate the risks. Finally, this can be scored and ranked from the most probable to the least probable under each category.
Priority
Probability and impact can then be factored in to determine overall priority ranking. This is usually done by multiplying probability and impact to give a score that ranks it from highest to lowest. Based on this ranking, the template then presents its information in order, with the highest-ranking risks first indicating the highest priority.
Response
Once the ranking is done, it is time to get it down to action items. This will be done by listing out actions that need to be taken to mitigate the identified risks. This helps in planning and taking action on getting rid of them before they are too big once they occur. Each one will typically have its response.
Ownership
It is a very good practice to identify the person or group who has ownership in the template. This person is responsible for monitoring and eliminating the identified ones before they become a problem.
Notes
The register template should usually have a section for storing relevant and important information about the risks. As it is reviewed and updated, this section will help maintain consistency in the information.
Advantages of the Register
Having a register helps you identify what, when, where, who, how, and why of risk management – which aspects need to be considered to reduce a project’s risk level. It also helps both management and staff know where to focus their attention to minimize these that could cost the business money or impede its growth. Using the register, a project manager can identify, forecast, grade, develop response strategies/mitigation actions and track risks associated with a project or organization.
It helps you to stay on top of things and appoint the owners who will assist in monitoring potential risks, thus reducing the workload of solely overseeing all projects. It can be used as a compliance document as it shows awareness of potential ones and efforts put in place to avoid or mitigate the risks. It is also a strategic planning document that helps management identify which ones are worth taking and which should be avoided.
Final Thoughts
A register helps management and staff be aware of the possible risks that may affect their project or organization. It helps them understand their nature and thus better prepare if they occur. This will reduce the management’s stress, and at the same time, it enables them to identify every possible source beforehand. Having a register also helps management coordinate action plans to address risks. Its main purpose is to assist you in managing risks associated with your project or organization. It will help you pinpoint the real source of risks and understand the nature of each type of risk. Additionally, having a template at your disposal will most likely save you time and money when you decide to undertake a project. Different types of templates suit different project needs, and it is thus advisable to ensure the most befitting template is used.




