A project proposal is a document that states the purpose of a project and describes how it will be executed.
A proposal is meant to ask decision-makers or external parties such as sponsors to buy in and support the implementation of a project. It has not been deemed a contract as it doesn’t outline legal terms and obligations. Senior management or sponsors do not have to sign the document to approve the project for execution.
Why is a project proposal needed? It initiates a professional working relationship between an organization and outside contributors or senior management (decision-makers) employees. The proposal should outline all the aspects of a project; objectives, purpose, activities, costs, and any other relevant information. By giving stakeholders a clear understanding of what it entails, approval and funding can be allocated and awarded to the project.
A proposal is essential in several ways, such as proving the viability and need for a project. It also helps identify the requirements and define the roadmap toward the success of a project. Since most sponsors and senior managers won’t approve the budgets with a proposal, it is essential to secure funding and support.
A proposal also helps define the structure and organization of its execution plan beforehand, facilitating accountability within an organization and among project stakeholders. In addition, proposals increase an organization’s credibility and exposure when they reach out to external partners, fostering organizational growth. Lastly, a proposal gives a broad overview of the project and clarifies the associated deliverables.
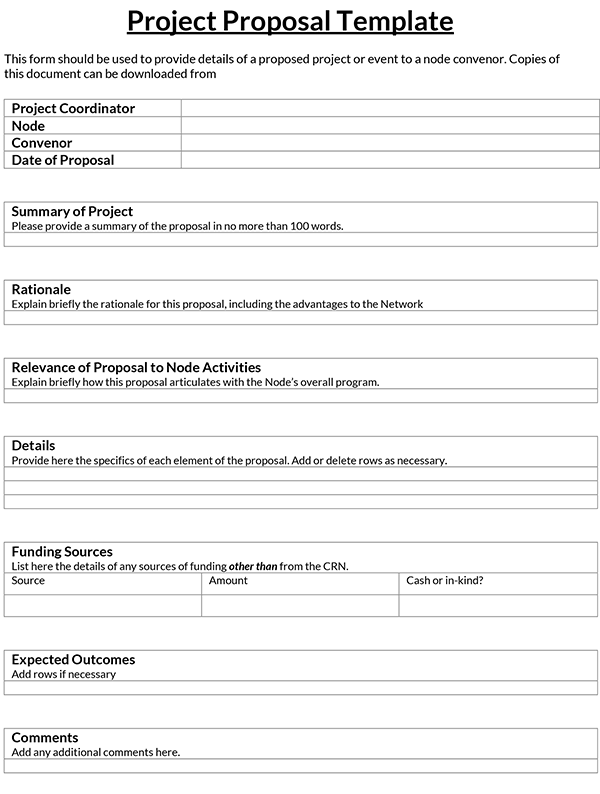
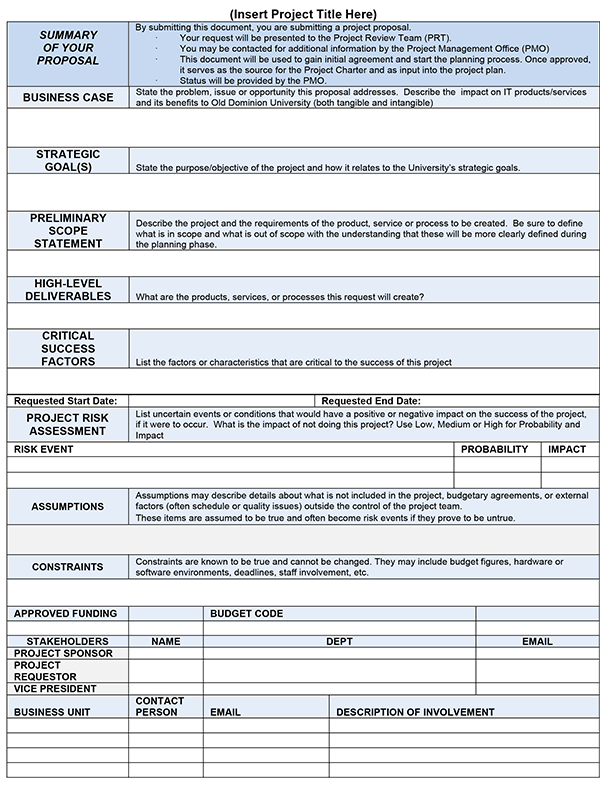
Proposal Templates


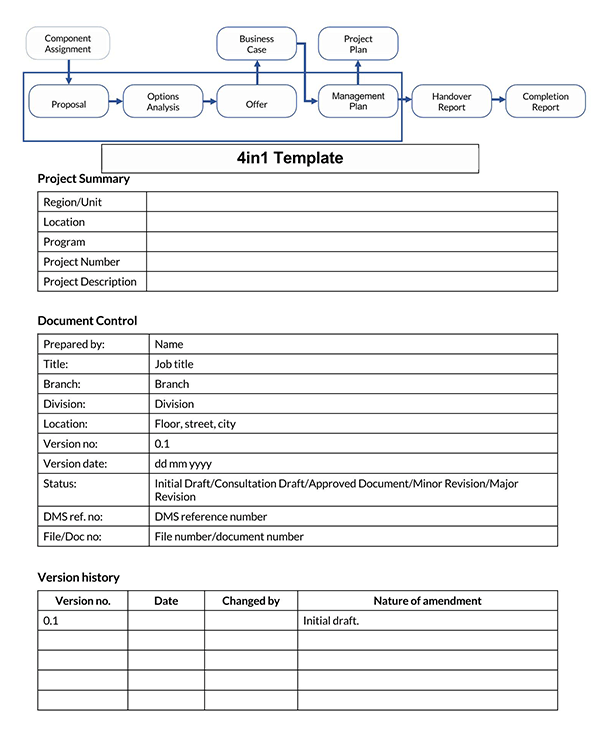

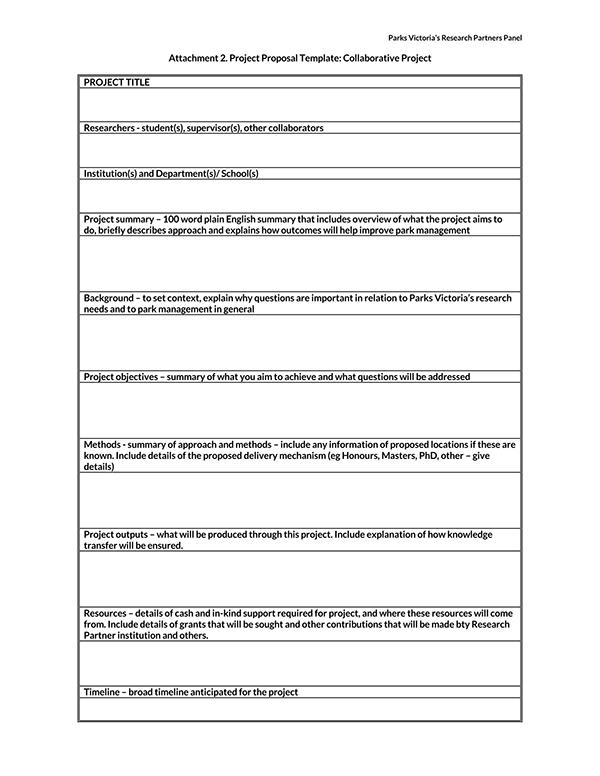

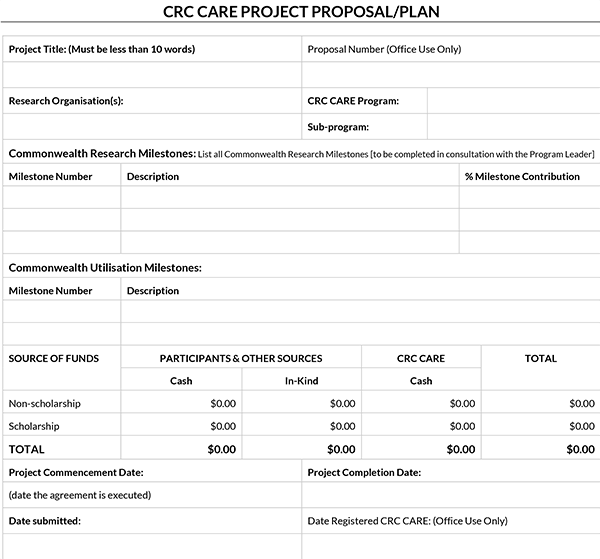

Different Kinds of Proposals
Different types of project proposals can be used under different circumstances. These types of proposals include:
Formally solicited proposal
A formally solicited proposal is prepared to respond to an official Request for Proposal (RFP). An RFP outlines the stakeholder or client requirements and needs and, in some cases, instructions on how the proposal should be structured. A formally solicited proposal is written by the specifics of the RFP and is, therefore, more constricted.
Informally solicited proposal
A proposal prepared without an official RFP is known as an informally solicited project proposal. This implies there are no project specifics or demands by which the proposal is expected to abide. Therefore, this type of proposal is the initial step and acts as a proposal request outlining rough details about the project that simply prove its viability.
Unsolicited proposals
An unsolicited proposal is presented when the sponsor or manager has not requested one or doesn’t expect it. The proposal must be detailed to prove the project’s viability and value to the audience.
Continuation proposals
A continuation proposal is written to update ongoing projects or a reminder of already approved ones. A continuation proposal will usually be submitted as a report on progress and changes within project execution or check-in after a milestone to secure funding for the next phase.
Renewal proposal
Sometimes projects can be terminated for varied reasons, such as outliving their usefulness or halted due to a lack of resources and support. A proposal can be written to prove the project is still viable and valuable by highlighting its ROI (Return on Investment). Such a proposal is known as a renewal proposal.
Supplemental proposal
Supplemental projects are drafted when more resources than allocated initially have to be added to it. This type of proposal highlights the need for the additional resources and value they bring to it. A supplemental proposal continues the original proposal and will usually be required when the project scope outgrows the initial scope.
Some other types of templates include:
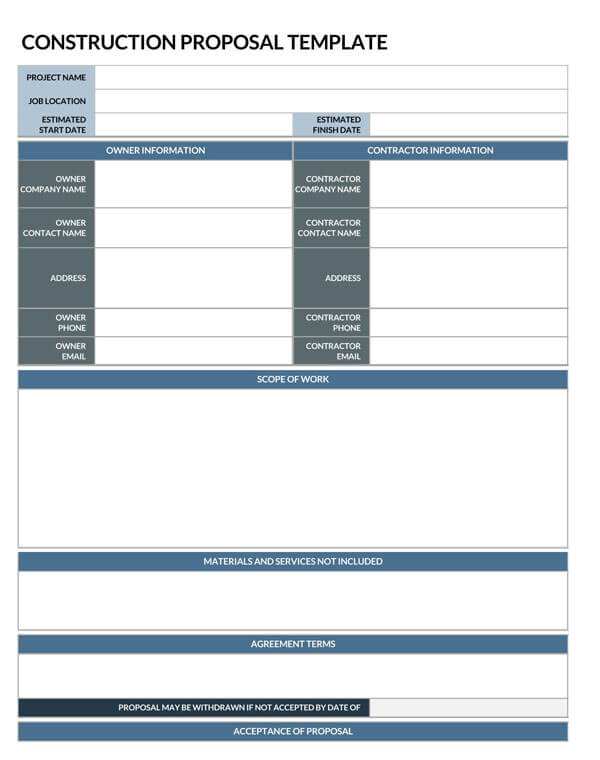
Construction Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)
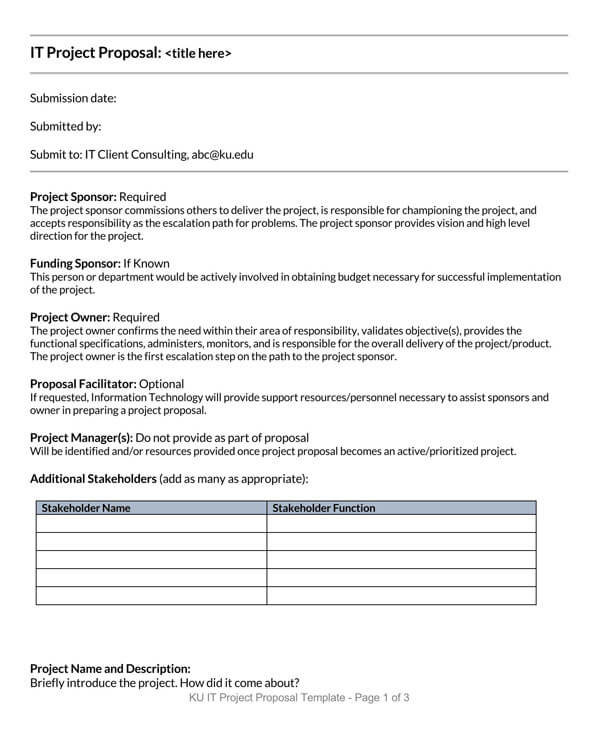
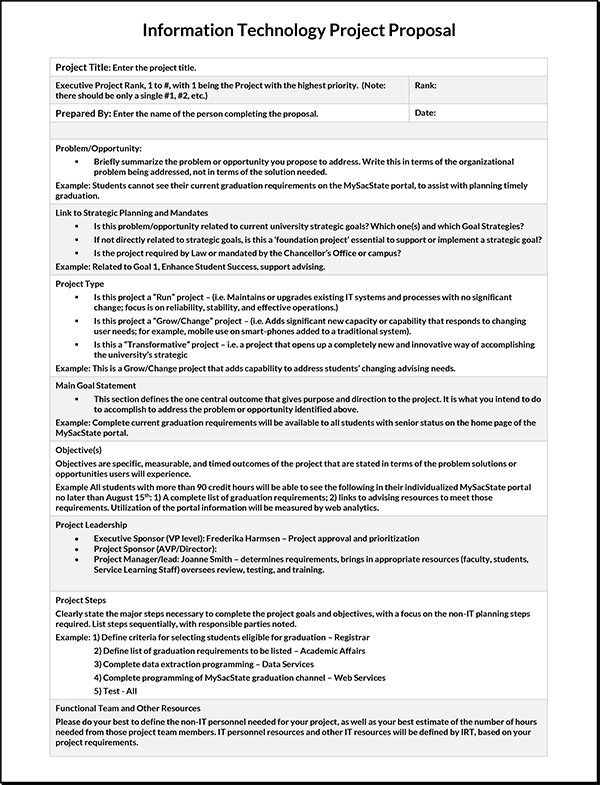
IT Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)
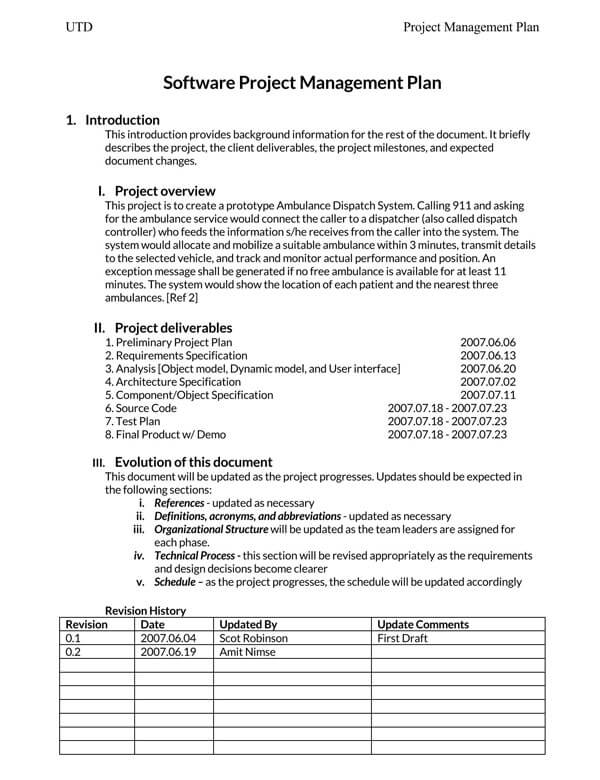
Software Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Marketing Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Engineering Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Business Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Freelance Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Mobile app Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Web Design Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)
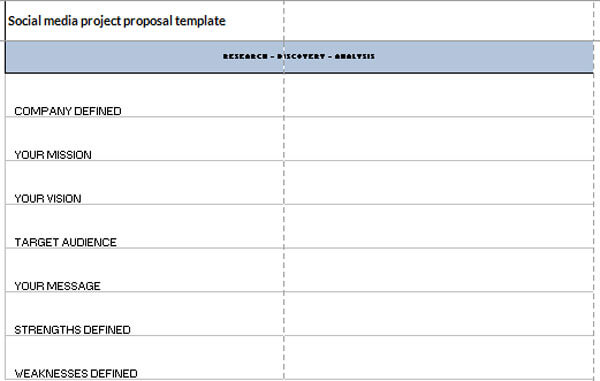
Social Media Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Accounting Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

Consulting Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)

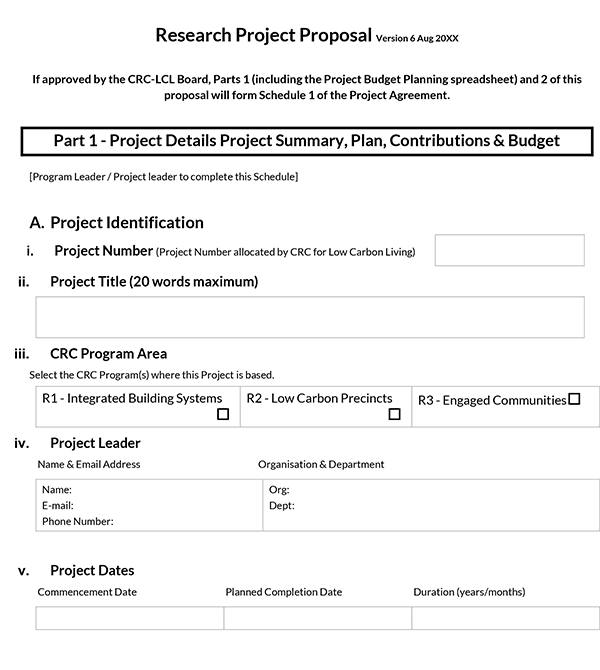
Research Project Proposal Template
Download: Microsoft Word (.docx)
How to Write a Proposal
Once it is clear what type of project needs to be prepared, the writing process can be initiated. Writing can be done from scratch or with a template. Regardless of the approach, essential components need to appear in the proposal.
They include:
Write proposal outline
The first item to be prepared is the proposal outline. The outline takes up the cover page and sometimes the document’s first page. This introduces the proponent to the audience and gives other relevant introductory details such as:
- Name of the organization: The name of the proponent organization should be written to let the sponsor or manager know who is proposing.
- Project title: Each project will have a title or name that it is referred to. The title can be based on the project’s purpose or the proponent.
- Project timeframe: The time frame needs to be indicated at the beginning of the proposal so that the sponsor or manager knows what level of commitment is being asked of them. These have varying time frames from daily, weekly, quarterly, yearly, two years, etc.
- Prepared by: The proposal should highlight the participants involved in preparing the proposal. Where the proponent is an organization, the proposal could be written by the manager or any other appointed organization representative.
You can take help from our pre-formed documents:
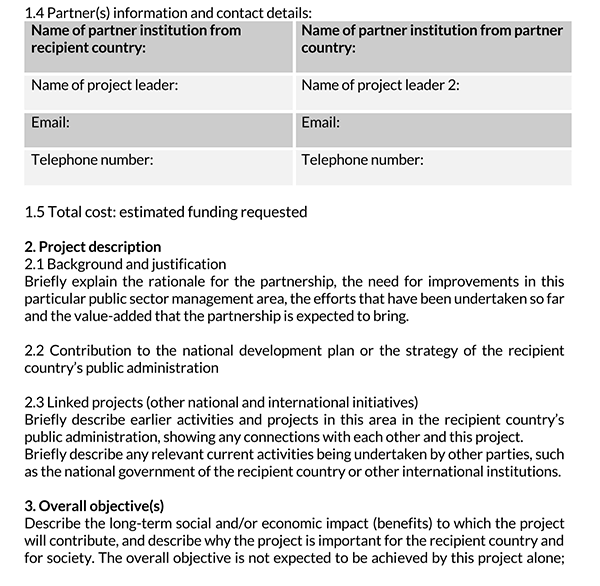


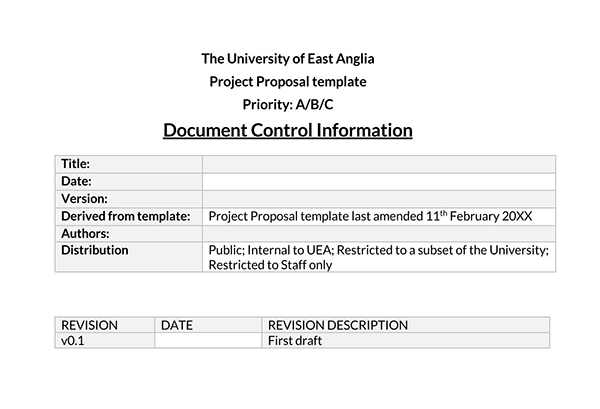
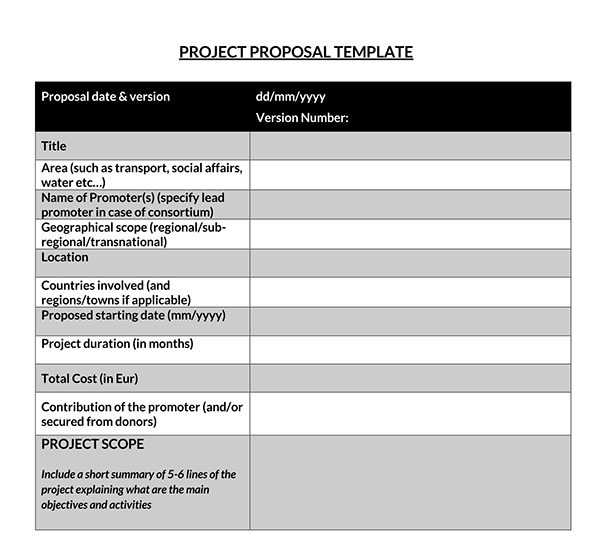



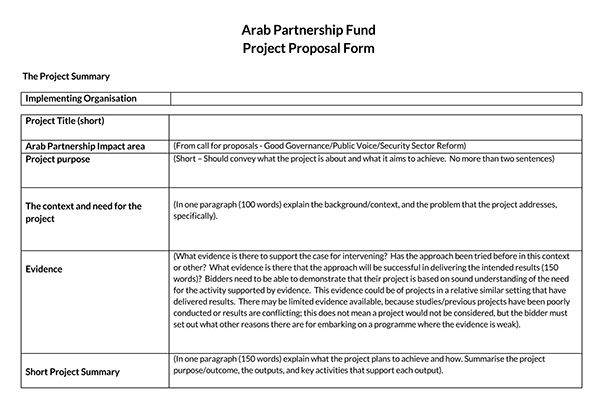
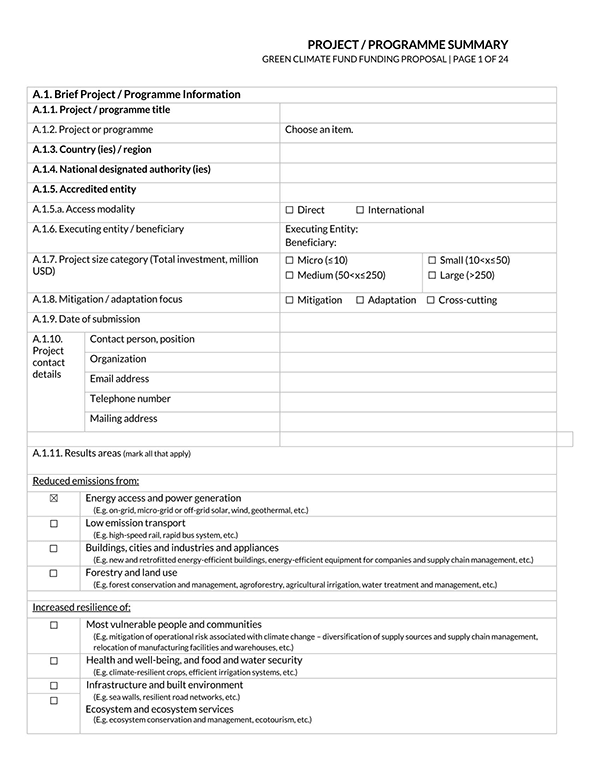


Attached documentation
Any attached documentation should be indicated. This can be achieved by supplying a list of the documentation.
Contacts and authorization
Communication is an essential factor in the success of a project. Therefore, contact details and individuals required for various authorizations should be provided to streamline the flow of information should the project be approved.
Write an executive summary
The next component of a proposal needs to be included in the executive summary. The executive summary can capture two items: background information and objectives.
Give background
Several things should be highlighted to give the audience a background of the project. A proposal summary needs to address the following:
- History: There should be a detailed summary of the subject matter or topic associated with the project and the problem being addressed by it. It should identify the problem and why the sponsor or manager should aim to resolve it.
- Requirement: A summary of the resources that will implement the project should be provided. It can have recurring or one-time requirements. Requirements can be defined by description and quantity.
- Success criteria: Once the problem is defined and the requirements, the metrics to measure the project’s success can be indicated. Most projects will use KPIs (key performance indicators) to measure success. These with measurable outcomes have a higher approval rate.
- Solution and implementation: The proposed solution and process of implementation should also be introduced in the summary.
Objectives
To conclude the summary, the objectives of the project should be clarified. Objectives are the measurable goals that will be achieved after it has been successfully implemented. Therefore, proponents are urged to have at least a specific objective (specific to the project) and a general objective (supports other sponsors or business objectives).
Methodology
The third item that ought to appear on the proposal is the project methodology. The methodology can be characterized by the following:
- Project approach summary: A summary of the techniques, processes, and methods to fulfill critical activities, such as milestones, should be given. The overall plan of the proponent can be provided at this point.
- Deliverables: The deliverables expected at the end of the project should then be listed. Examples deliverables are products, services, information, etc
- Task breakdown: A breakdown of all major activities should be given. A list of tasks involved at every stage effectively breaks down tasks.
- Time estimates: The timeframes associated with each step required to achieve the set objectives should be provided. These can be indicated in the form of a project schedule. The time estimates must add up to the estimated project timeline. Ordinarily, a Gantt chart that shows the tasks, timeline, and resources needed to complete each task is used.
Management techniques
When undertaking a project, risks are generally inevitable. Any probable changes from the predetermined workflow can be deemed as risks. Sponsors and managers will ordinarily want to see a proponent’s preparedness for such risks. This section should have the following information:
- Risk management plan: A risk management plan indicates the necessary actions to be undertaken if a risk or change occurs. The plan should be detailed to show the contribution of the mitigation action to the objectives.
- Risk register: All the foreseeable risks associated with the project matched with proposed counter efforts should be provided.
Cost
The next step is to identify and define the project requirements. Every project requires money to implement. This section of a proposal is essential to a sponsor or manager in that it influences its viability.
This section should describe the following:
- Project budget: A detailed budget of all expected costs at different phases should be included. The costs should be divided into different categories such as salary, construction, miscellaneous, etc. A well-written budget should incorporate overhead and indirect costs.
- Budget narrative: A brief budget narrative can be provided to clarify or justify items in the budget – for example, why a 5% miscellaneous cost is needed etc.
- Resources: All the resources needed at different phases are necessary. Resources cover a wide range of items needed to execute the project, such as tools and equipment, time, labor, etc.
- Additional costs (travel and expenses): Any additional costs incurred before, during, or after the completion should be indicated. Additional costs will typically not be directly utilized by the project. Additional costs include permits, licenses, industry-related fees, travel fees, etc.
- Additional financial statements: The proposal should then state any additional financial documents required to make decisions for the project—for example, tax return files, profit and loss statements, receipts, invoices, etc.
- Measurement and reporting: Monitoring, measuring, and reporting results are crucial in determining success and should be defined next. The procedure for these three processes should be clearly defined. The frequency of monitoring and aspects to be monitored should be stated. The metrics for measuring results should be defined, and the reporting procedures. It should be clear how and when sponsors should be expecting status reports.
- Implications for the project: Next, the proposal should have an overview of all the essential details that illustrate the value of the project and why the sponsor or manager should approve it. Should it fail to be approved, the implications that would ensue should also be highlighted. Note that sponsors and managers want a project whose benefits outweigh the costs.
- Milestones: Milestones are phases that need to be completed between the project timeline for the overall project to be completed. Milestones are more of a measure of success than tasks. Each one must have several milestones so that any issue can be identified and attended to earlier in the project.
Appendix
Lastly, the document appendix should outline all the separate documents or accompaniments attached to the proposal as supporting material. For example, attachments can include study reports, letters supporting the proposal, site maps, charts, graphs, images, etc.
Tips to Make Your Proposal Professional
Every proponent hopes that their proposal will be approved. However, approval may not always be guaranteed due to various factors such as impracticality, poorly scoped project, affordability factors, or poorly written/drafted templates.
The latter can be remedied in the following ways:
Write an outstanding executive summary
Get the reader’s attention from the start; executive summary. Note that most sponsors or managers will go through the summary before reading the entire document. Therefore, aim to win them over with the executive summary.
Do your research
Research what each stakeholder expects from the project and demonstrate your familiarity with the topic throughout the document. Use factual information. If any misleading information is identified, this can harm the proposal’s chances of being approved.
Proofread
Always review the proposal before submitting it. Carry out several reviews and edit any mistakes in the template. Have someone else read the proposal and give feedback before submitting the final draft.
Keep it simple and concise
An excellent proposal should convince the audience that a project is worth undertaking in simple, clear terms. Also, it should be kept brief by going directly to the point.
Make a positive hypothesis
The sponsor or manager will always be interested in the outcome and whether it solves or identifies a problem. It is, therefore, wise to develop a positive theoretical outcome to represent what the sponsor or manager should expect.
Set realistic expectations
When setting deadlines and schedules, allocating funds/resources, determining requirements, etc., be realistic. Exaggerated expectations in the template can lead to false expectations if the proposal is approved.
Tailor it to who you’re writing for
A proposal should be personalized to meet the person’s requirements being proposed. For example, a CEO will require different information than an MD within the same organization.
Make a realistic estimation
IT is best to develop the best and worst-case scenarios outcomes for the project, which is a realistic estimation of the success. If the worst-case outcome is better than the current status of things, then the probability of approval rises significantly.
Use emotive language
As much as a proposal is a formal document, it is okay to evoke emotions from the reader as long as it is not overdone. Long boring proposals take away the reader’s interest in the proposal.
Be confident with your decision
It is hard to sell an idea you don’t believe. Therefore, own your proposal and let it show in the document. Use case studies where possible to support the information given in the proposal.



Final Thoughts
Project proposals are essential tools for communicating ideas in a bottom-up organization system. The proposal introduces the project to the sponsor or manager and outlines requirements and processes, timeline, and expected outcome. Depending on how the proposal is initiated, there are different proposals; formally solicited, informally solicited, unsolicited, continuation, renewal, and supplemental.
These proposals can be written using templates designed to satisfy different user requirements based on the type of project. Lastly, a proposal should not be too long but should be detailed enough to communicate what the proponent is proposing.




