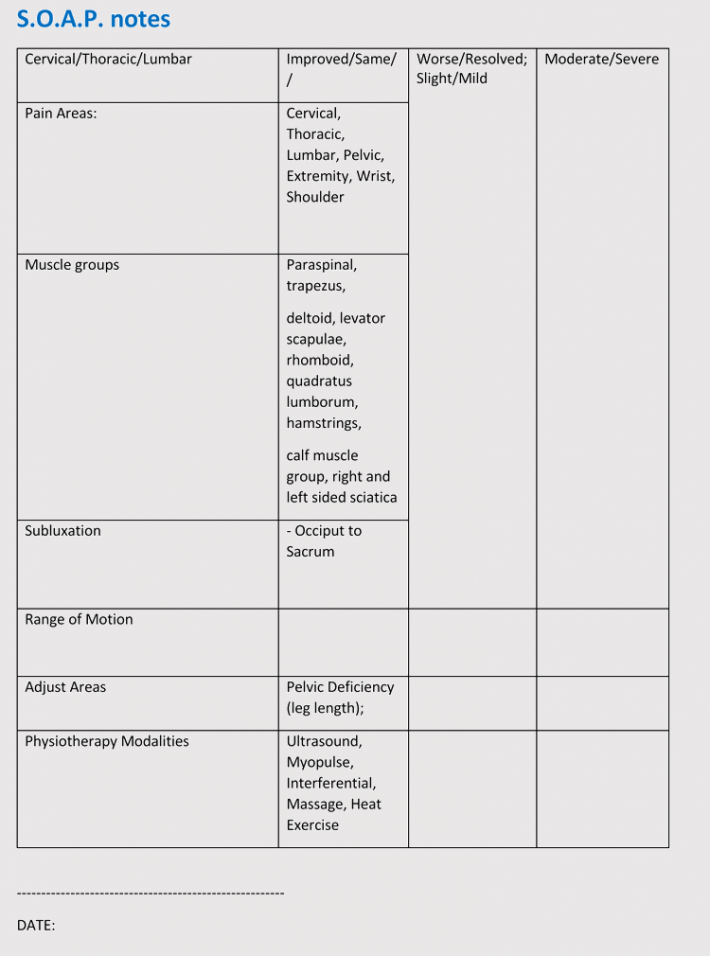
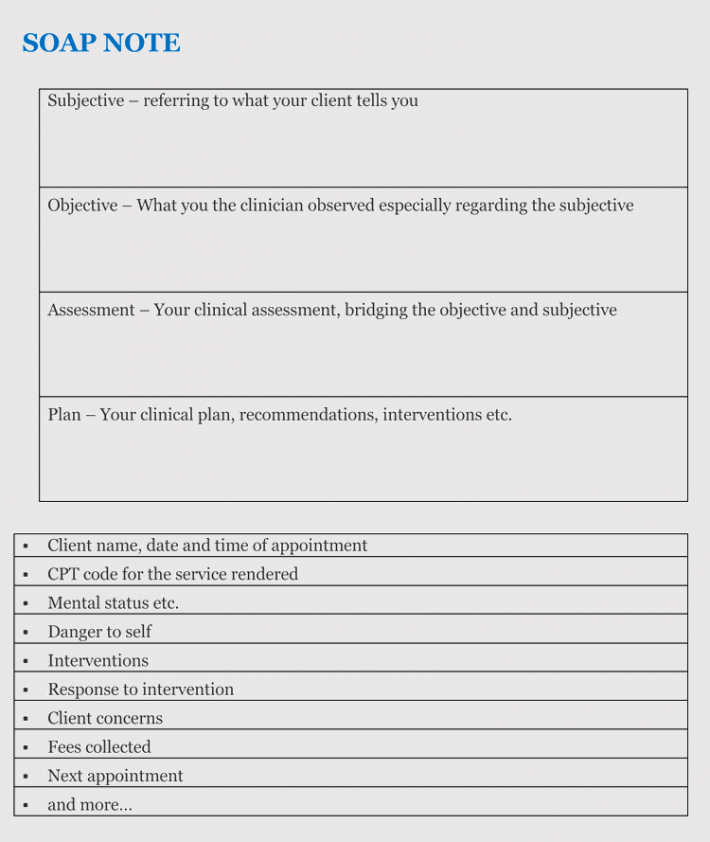
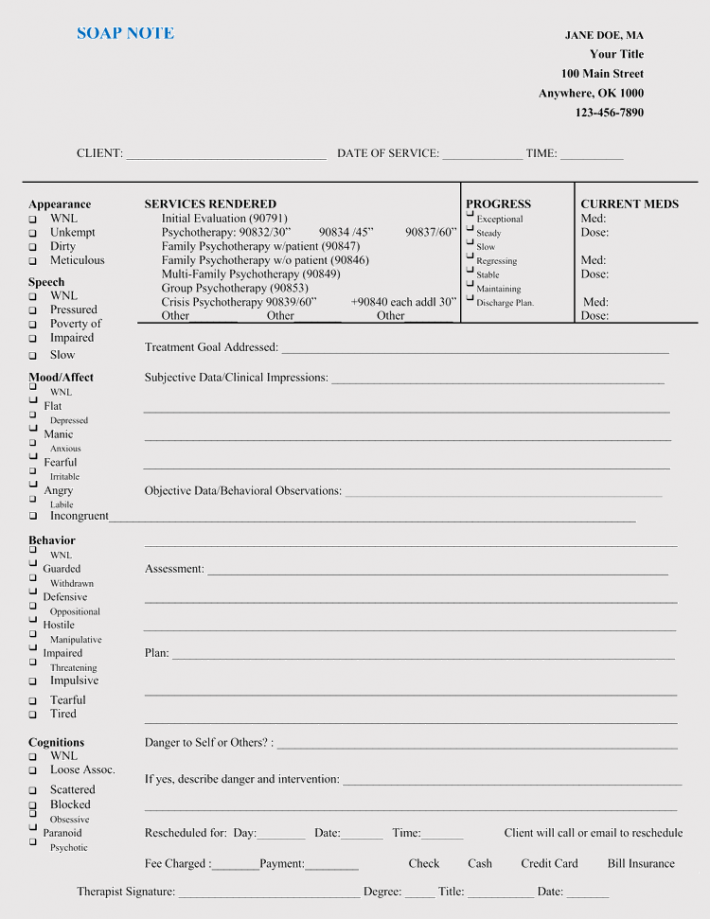
A SOAP note is a note-taking system or documentation used by doctors and medical practitioners to track the progress of a patient from one visit to the next and communicate the same to other medical practitioners attending to the patient.
SOAP notes provide a clear, accurate, informed, and organized record of the patient’s medical information by outlining pertinent need-to-know details about a patient’s visit to a doctor. They streamline the sharing of information between different doctors who attend to a particular patient. Having information recorded ensures medical practitioners keep accurate information, unlike in situations where they were to rely on their memory in between their involving schedules.
SOAP Note Templates
Goals and Benefits of SOAP Notes
What was the aim of developing the SOAP note documentation system? Before it, communication between medical practitioners working with the same client was complex, as they had to rely on the patient remembering all and any information regarding their medical sessions:
- SOAP notes created a simpler method to achieve effective communication between medical practitioners.
- Also, they helped medical practitioners track patients’ progress in an orderly fashion. They are structured to accommodate all vital aspects of a patient’s session, that is, assessment, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Another objective of introducing SOAP notes into medical practice was to have consistent and progressive medical records. When medical professionals share medical history, it means they do not have to start from scratch when treating a patient; information relayed in the note should form grounds for their assessment and diagnosis and should give specific details about the patient and various aspects of the session.
Benefit to doctors
- The main benefit for doctors is that they allow a standard and organized way of documenting the patient’s information for easy reference.
- It makes it easy for health providers to know the status of a patient and administer the medications as required.
- The SOAP notes have a history of the patient. This is important as it helps the practitioners when it comes to an objective to determine and narrow down the list of potential injuries.
Benefit to patients
- Patients get much-needed attention as SOAP notes allow them to describe every detail of their condition as the medical practitioner jots them down.
- The history of the patient is noted down and if the patient has seen other providers for the same symptom, he/she will get a different and better treatment plan that will work.
Components of a SOAP Note
What does one include in a SOAP note? The following components of a medical evaluation should be reflected it:
S-Subjective
The first section should address the “subjective” experiences, personal perspectives, or feelings of the patient or someone who is close to them. Subjective information gives details about the client/patient’s status and behavior.
The patient should be allowed to explain their CC. A CC can be a symptom, previous diagnosis, condition, or other examples, including headache, shortness of breath, lack of sleep, etc. Since the patient might be having more than one issue, it is the medical practitioner to ask questions that clarify details of the CC.
tip
Words that can characterize the CC include sharp, dull, aching, stabbing, cramping, shooting, or any other.
Content to be included
The objective is to identify the main problem, and thus attention must be paid to detail.
EXAMPLE
The patient claimed to….
The patient expressed his concern over….
Mr. Doe expressed he has been having severe pain in his lower back for the last two months. He claims it started when he started taking medication X.
Procedures employed at this stage include; a statement of the history of present illness (HPI), patient’s history, review of systems (ROS), and listing of current medications and allergies. An HPI can be conducted using the OLD CARTS, as illustrated earlier. The patient’s history is inclusive of the medical history, surgical history, significant family history, and social history. A ROS assesses symptoms not mentioned by the patient.
Content to avoid
Statements that cannot be supported with facts should be avoided. Thus, one’s personal opinions should be avoided. However, statements made by the client’s loved ones, colleagues, teachers, etc., and are relevant can be included. For example, “Ms. Doe was a willing participant in the session.” This statement is a personal opinion of the medical practitioner.
Avoid going overboard with irrelevant details.
EXAMPLE
- The client sat on the office sofa.
- The patient was wearing a suit.
As much as details are necessary if a particular detail does not contribute to the patient’s assessment and diagnosis, it does not need to be included. Such minor details are recommended where the patient is mistrustful of the medical practitioner.
Medical professionals can also adopt another approach of recording subjective information about their patient’s medical sessions, referred to as OLDCARTS. It is primarily meant to focus on the patient’s chief complaint, formally referred to as CC.
note
A CC is regarded as the principal reason for the patient to seek medical care.
OLDCARTS is used to organize information of an HPI (history of present illness) and typically falls under the subjective portion of a patient session or interview. OLDCARTS is an acronym for the following:
- Onset – One should find out when the CC began, that is, symptoms.
- Location – Record where the pain or concern is located. Medical practitioners should localize the issues as specific as possible.
- Duration – How long the patient has had the CC should be documented. Specificity is desired, and therefore it can state the number of hours, days, weeks, or months.
- Characterization – A description of the CC in the patient’s words is included.
- Alleviating and aggravating factors – The document should state what helps or makes the CC worse. The medical practitioner can ask how different positions such as lying down, sitting, standing, and moving influence the severity of the CC. The effect of consuming various foods and drinks should also be enquired.
- Radiation – The movement of the CC should also be stated. Ask if, say, pain, moves from the neck to the back or any other body part.
- Temporal factor – The document indicates if the CC has a particular pattern of recurrence, for example, at specific times of the day.
- Severity – The medical practitioner should also assess how severe the CC is on a scale of 1 to 10, 10 being the most severe.
note
These questions are necessary as they lay the blueprint for diagnosis and treatment.
O-Objective
The objective section addresses the observable, quantifiable, and measurable information. The objective section is typically the longest and presents the objective measurements, observations (behavioral, symptoms, mood, and appearance), and test results.
Basically, the objective section is factual documentation or record of the physical examination of the patient’s condition.
Content to include
The aim is to give the medical practitioner’s observation and interpretation of the client’s condition. Some of the aspects to consider include:
- Laboratory results
- Vital signs
- Imaging results
- Physical, interpersonal, and psychological exam findings
- Patient’s mental status
- Affect and behavior
- Vital signs
- Documentation of other clinicians such as reports and psychological tests.
- The client’s ability to participate in the session
Examples of data found under the objective section includes:
- Manual muscle tests (MMTs)
- Range of motion measurements (AAROM, AROM, PROM, etc.)
- Level of independence (CGA, MIN A, etc.)
- Functional reporting measures (DASH screen, etc.)
- Wound healing details (for post-op patients)
- Objective measures from assessments related to the diagnosis
EXAMPLE
As a statement, one would say – Doe’s response to stimuli (light and touch) is delayed by a few seconds, or Kel is emaciated and struggles to lift relatively light objects (office desk chair in this case), or the vital signs included a temperature of 40⁰, BP of 131/89 and have swollen lymph nodes.
For a life coach, what to include will depend on why the subject is seeking assistance from the coach. It is advisable to take diagnostic details (signs) before, during, and after exercise. For example, if the patient’s CC is “Inability to focus and achieve goals,” a life coach and doctor will take two distinct approaches. A life coach might observe that the client’s inability to stay focused is because they do not plan their day in any structured way: they use sticky notes. A doctor, on the other hand, will test the client’s eyesight and determine if the client has ADHD (attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder), which might be contributing to their CC: inability to focus.
Content to avoid
Things to avoid in the objective section include:
- General statements that cannot be supported by data
- Assumptions and opinionated statements (avoid personal opinions but not professional opinions)
- Personal judgments, for example – the patient seemed to be drunk as he arrived.
- Labels
- Statements with negative references can be subjected to personal interpretations; for example, the patient was uncooperative, drunk, spoiled, etc.
A-Assessment
Assessment involves the analysis of data provided in the Subjective and Objective sections, basically how the patient’s story fits the objective measurements and observations taken by the medical professional.
It should state the doctor’s or therapist’s diagnosis of the existing condition. The outcome of the assessment could be the discovery of one primary issue or multiple issues. However, in other cases, it might not be possible to make a definitive diagnosis, and as a result, it becomes important to include multiple diagnoses. The assessment should incorporate professionally acquired and clinical knowledge and understanding to identify themes or patterns and interpret any data obtained during the session and in the SOAP note. Medical professionals should look out for DSM criteria exhibitions by the patient.
The “diagnosis” of a life coach is not the same as that of a doctor; life coaches primarily help the patient have more clarity or a novel perspective of things they already know.
Content to include
The elements of the assessment section include a declaration of the problem and the differential diagnosis.
- The problem – Indicate the problem (diagnosis), or if there are multiple diagnoses, list them in the order of importance—for example, diagnosis 1, diagnosis 2, and henceforth.
- Differential diagnosis – The medical professional should provide a list of all the different possible diagnoses determined. The differential diagnosis should list the conclusions of the decision-making process—for example, Diagnosis 1, differential diagnoses, discussion, and then the plan for diagnosis one.
EXAMPLE
Assessment: The 25-year-old male reported unusually frequent shortness of breath and a high heartbeat rate of 145/80. The patient has a medical history of shortness of breath and comes from a family with a history of asthma and HBP. Clinical suggestion suggests:
Diagnosis 1: Onset of asthma
Diagnosis 2: Low levels of fitness more inclined to the subject’s lifestyle
Content to avoid
Avoid repeating statements previously mentioned in the S and O sections. Also, avoid copying and pasting generic and ambiguous sentences.
EXAMPLE
The patient was in bad condition.
High levels of professionalism should be exhibited in the assessment.
P-Planning
Planning is the last component of the SOAP note. The plan should outline what is next for one’s patient. More often than not, the plan is to continue with the patient’s current PT POC. Additional information can be included in the frequency of visits, specific treatment options, and any changes to be made in the next session.
The plan represents the next plan of action that the medical practitioner, in their professional and medical opinion, recommends to the client. The plan revolves around things agreed on by both parties, and any nutritional, physical, and medical actions that will contribute to the patient’s positive progress should be considered.
Content to include
The contents of the plan should be feasible and strategic. Check-in points and deadlines can be included for smaller and larger goals, respectively to observe the patient’s progress.
The plan incorporates:
- The medication to be administered
- Therapies required going forward
- Suggested surgeries
- Recommended activities for the patient to take in, for example, yoga classes, group therapy, etc
- Suggested physicians the client should consult
EXAMPLE
- Medication X – to be taken twice every 24 hours for 4 days.
- Medication Y – to be taken once a day for 10 days.
Additional lab tests to be conducted. Patients to present themselves after 20 days or to a nutritional specialist if symptoms persist. A fiber-rich diet is recommended.
Content to avoid
Ambiguous plans that are not definitive should be avoided.
EXAMPLE
The patient shall proceed as they see fit.
Also, avoid regurgitating the overall treatment plan. Focus on goals to be achieved before the next session. To avoid this, unrealistic and immeasurable goals should be avoided.
A comprehensive SOAP note should take into account the relevant subjective and objective information; and provide an accurate assessment of the same to create a patient-specific assessment and plan.
Free Downloads
Documentation Requirements
Other than the S, O, A, and P, the document should include other important aspects. Documentation requirements will vary depending on the applicable legislation, necessitating legal consultations for medical practitioners to acquaint themselves with specific requirements.
However, fundamental requirements include:
- Date of session/visit
- The location where the session took place (office address provided to the insurance company). If it was conducted through video telehealth, a statement that declares that the medical practitioner was using video telehealth or telephone should be included.
- Patient’s personal information – Name, age, sex
- Duration of the session (start and end time)
- The date of the next visit
- Interventions made in the session
- Mental status
- People present during the session (typically for family sessions)
Tips for Completing SOAP Notes
A SOAP note being medical documentation should protect the medical practitioner. In this regard, they should be written in concrete and clear language; avoid using excessive professional jargon.
Below are tips for incorporating recorded information into it:
- Make it legible (remember it can be used by more than one practitioner).
- Caution should be taken in how the patient is being represented. Words like “good” or “bad” should be avoided as they might be interpreted as moral judgments.
- Focus on the patient; they are the heroes of the story; the medical practitioner is just a guide.
- Do not incorporate tentative language such as probably, might, seems, etc. Be decisive.
- One should write such that if they were asked to defend its contents, they could justify everything.
- Consider using a consultative style when conducting the session, such as that seen in mental health and family therapy.
- Be culturally sensitive when asking questions.
- Quotation marks must be used when quoting the exact words of the patient.
- Proofreading one’s notes is recommended.
- The SOAP note should use correct grammar and be spelling mistakes-free. Slang and odd abbreviations should be avoided.
- It should be short and to the point.
Frequently Asked Questions
They are used by medical care or consultation providers to document or note down a patient’s medical records. Examples of users include; doctors, pharmacists, nurses, therapists, and others.
Yes. They are still a widespread form of communication accepted between inter-disciplinary healthcare providers to record and monitor patient’s progress. Today, these can be found in EMR (electronic medical records).