Product owners must ensure they meet the needs of their stakeholders as they can influence the outcomes of the projects they undertake. Understanding who the stakeholders are, their impact on projects, their changing needs and expectations, their relation to a project’s risk planning and response activities, and their technique to plan an appropriate communication strategy can enable product managers to align stakeholder expectations with the project’s expectations and objectives by doing a stakeholder analysis.
What is a Stakeholder?
Stakeholders are individuals, groups, or organizations with a vested interest in a company, business, or project and can affect or be affected by the company/business/project’s outcome.
Therefore, they have active involvement in a project or business and can positively or negatively affect its outcomes. Project stakeholders are people or groups that stand to gain something from the outcome of the project. They may include the project managers, customers, team members in a performing organization, and project sponsors.
Stakeholder Analysis – an Overview
This analysis is a systematic process of identifying and establishing appropriate communication with stakeholders according to their influence and impact on a project. Product owners must identify stakeholders, assess and arrange them by their level of input, support, influence, and interest, and establish appropriate communication and involvement for each individual or group stakeholder.
The analysis helps a product owner to structure project operations according to the specific roles of each team member, the financial requirements of each sponsor to ensure confidence in the project, and end-user requirements to ensure a functional product is produced upon project conclusion.
Free Templates
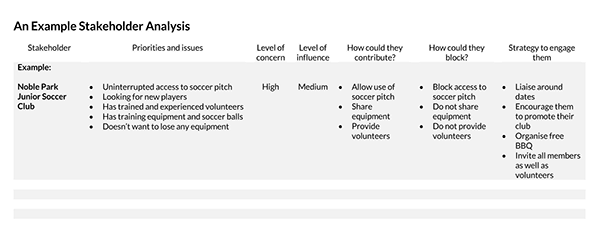
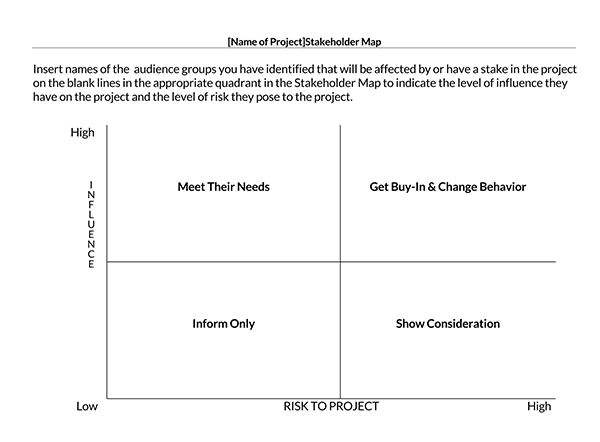
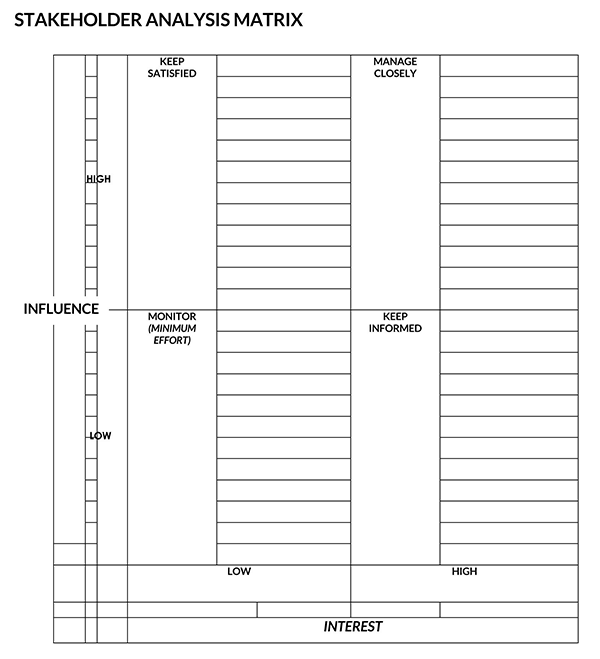
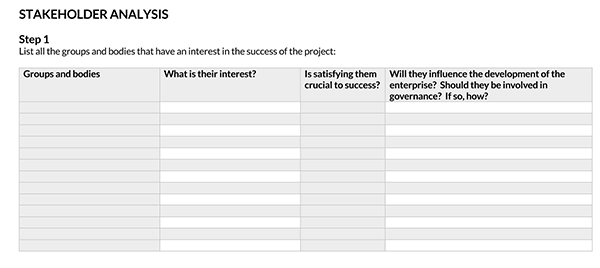
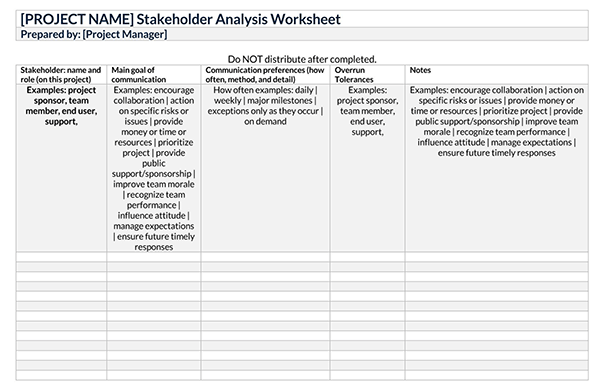
Purpose of a Stakeholder Analysis
Product owners must understand the purpose of carrying out the analysis to ensure the success of their projects. This will ensure that the analysis is carried out appropriately and efficiently.
The following are the purposes of undertaking a stakeholder analysis:
- To enlist the help of key players in the organization: It enables a product owner to quickly identify organizational players with the highest level of influence in a project. They may be executives, company influencers, project managers, etc. This will ensure that energy and resources are focused on stakeholders who benefit the project the most. In addition, the analysis should be conducted early on to ensure that these major stakeholders are involved throughout the length of the project.
- To gain early alignment among all stakeholders on objectives and plans: Product owners can also establish a clear, focused plan of action and goals among all stakeholders. This ensures that each stakeholder’s role in the project is aimed at one collective objective throughout the project. It will also help ensure each stakeholder provides meaningful input aimed at project success.
- To help address conflict/issues early on: It also help product owners identify conflicts that may arise early on or existing issues stakeholders may have. This will ensure product owners can resolve issues /conflicts early on or rest any concerns by vital organizational players. In addition, it helps in building stakeholder confidence in the project, which results in further resources allocated.
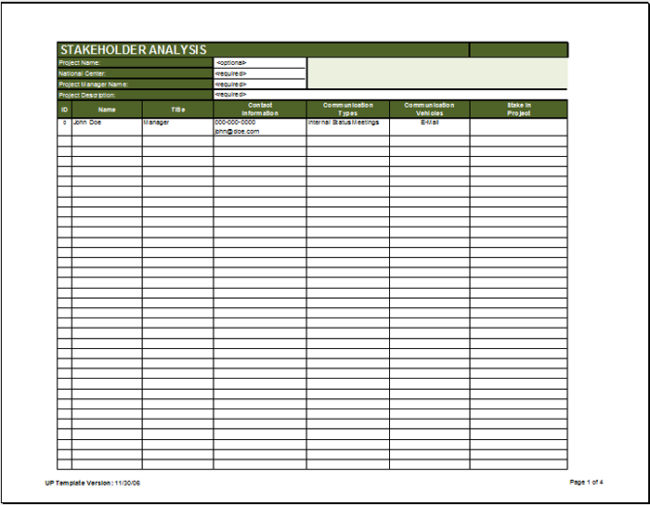
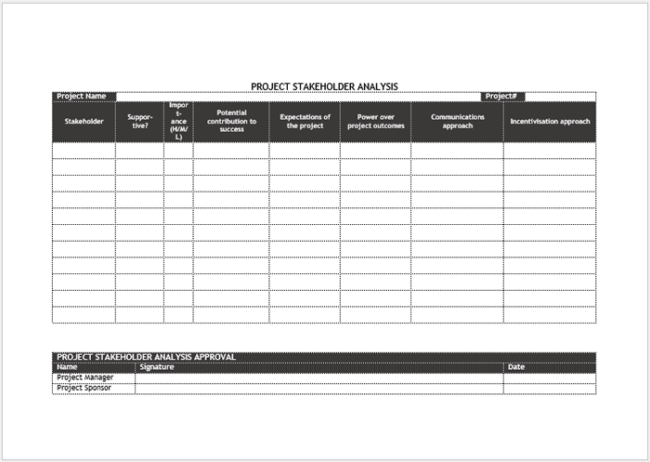
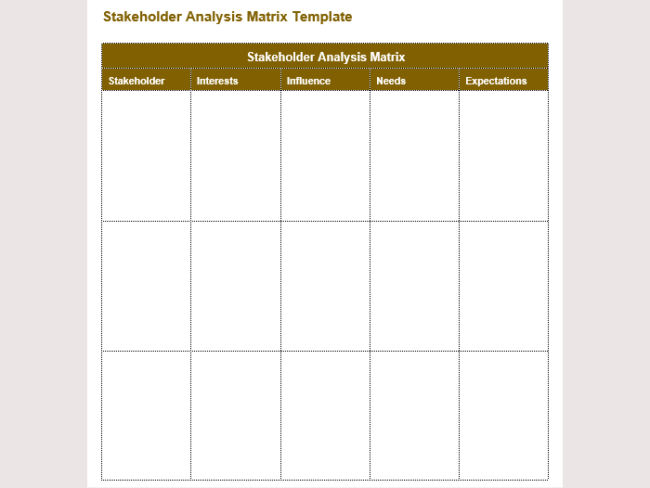
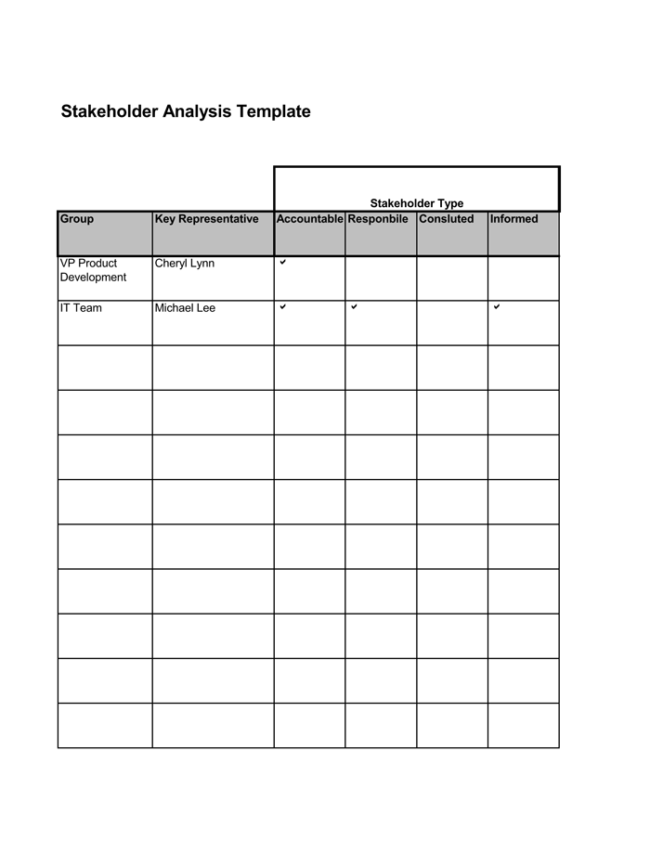
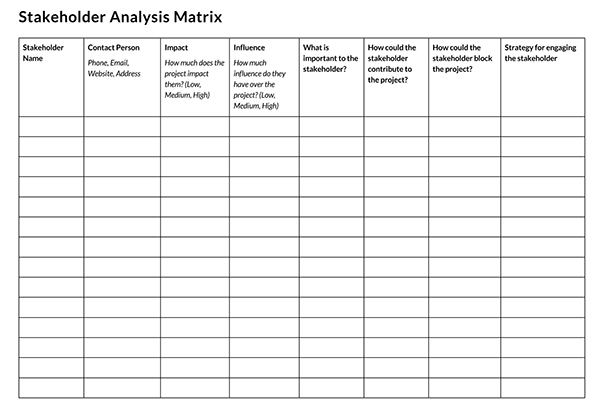
Stakeholder Analysis Samples
Following are a few samples for you:
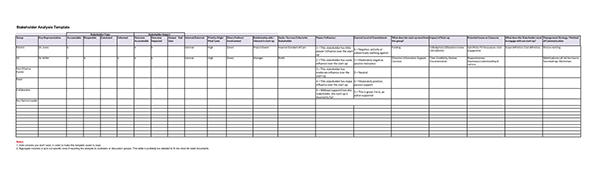
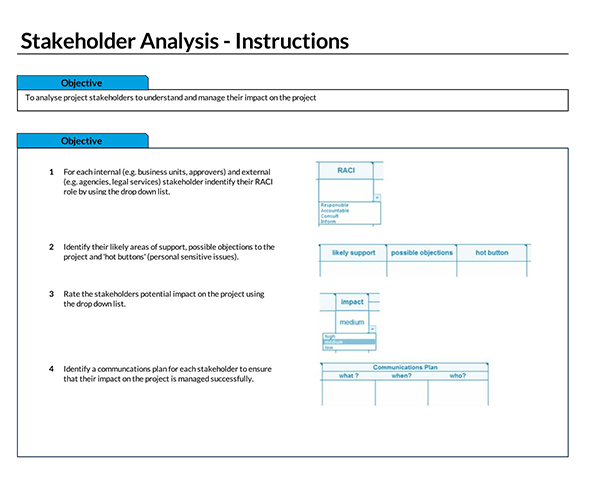
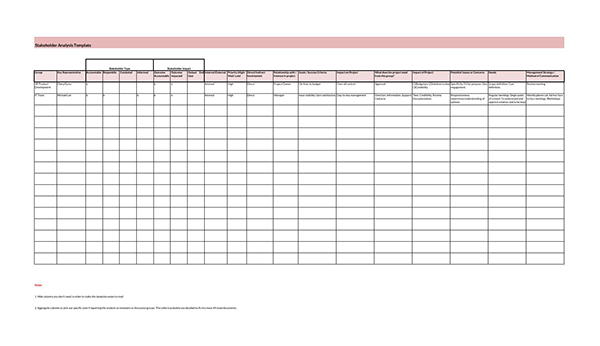
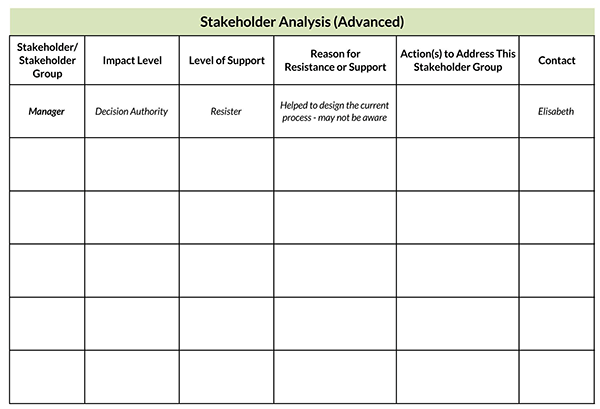
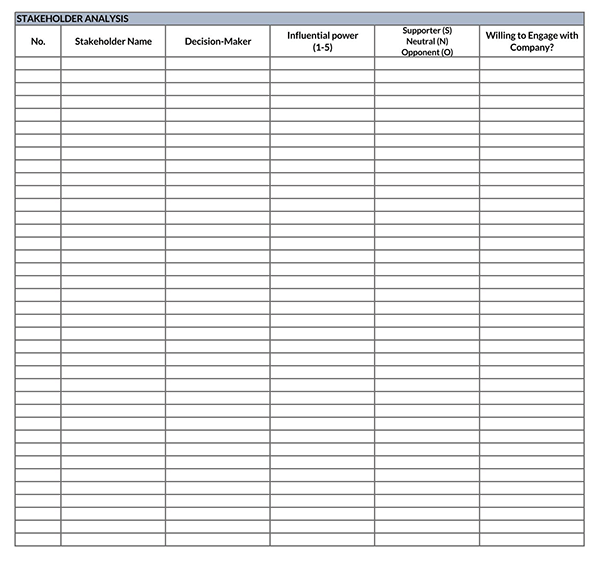
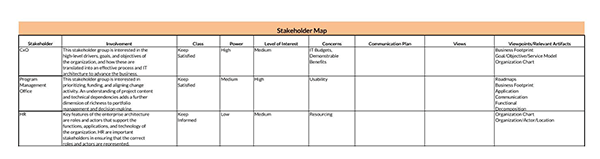
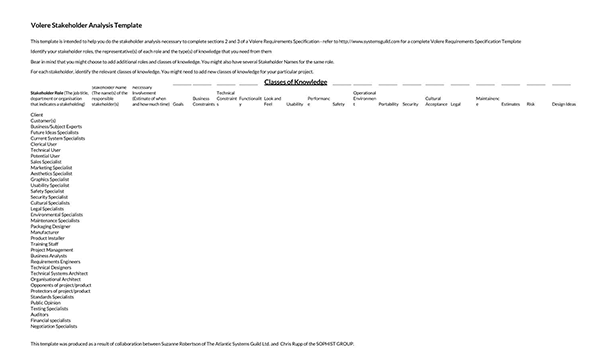
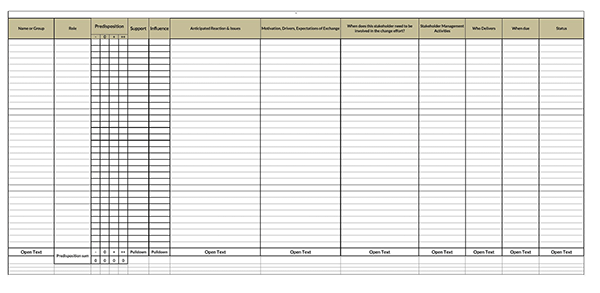
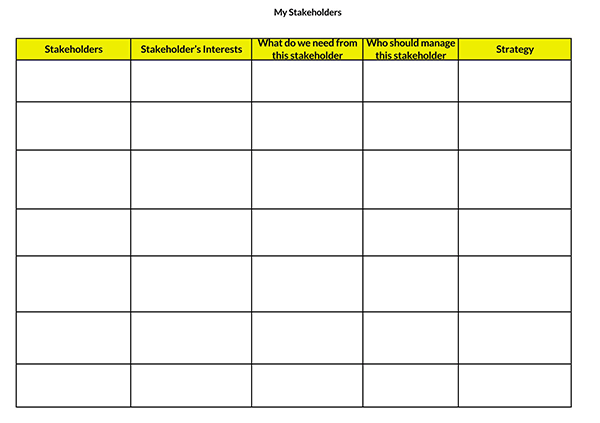
What is Stakeholder Interest?
Stakeholder interests can be defined as stakeholders’ concerns regarding a project, the product owner, team members, or the product/service.
A stakeholder’s interests can be positive or negative and categorized as either high or low interest. Product owners must be aware of stakeholders’ interests in the project to help them manage expectations and build sustainable, reliable, and effective relationships. It can also help product owners understand how to engage with stakeholders to help make informed decisions and ensure long-term sustainable support.
What is Stakeholder Influence?
Stakeholder influence is the ability of a stakeholder to resist or change a product manager’s recommendations.
It can be classified as either formal or informal influence. Formal influence is a power that stakeholders can enact with formal authority within the business, company, or organization. This type of influence can be enacted directly on a project.
On the other hand, informal influence is the power that stakeholders can enact that is not part of the formal structure of the business, company, or organization. Informal influence may be enacted directly or indirectly on a project.
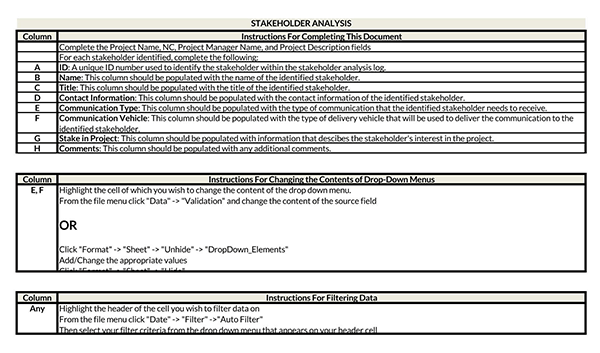
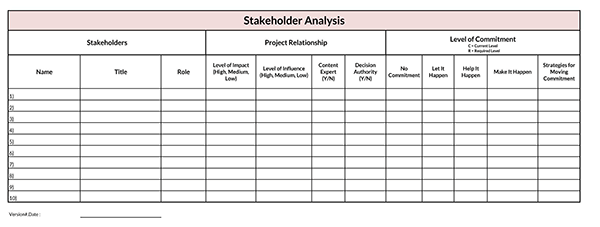
Professional Examples
Here are professionally crafted examples to understand the working of the analysis:
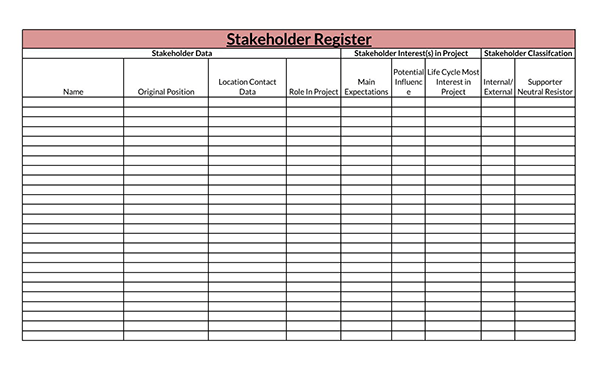
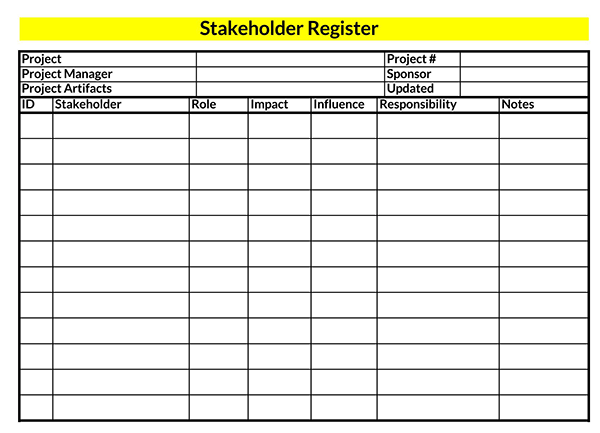
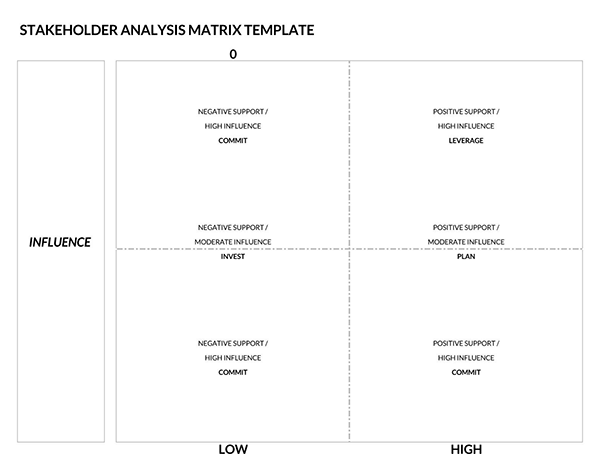
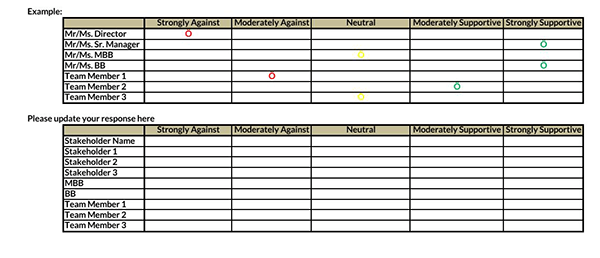
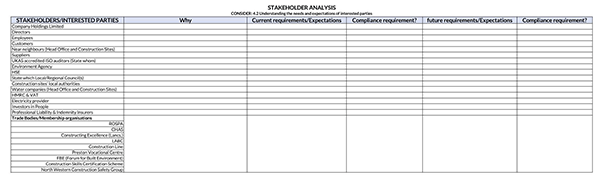
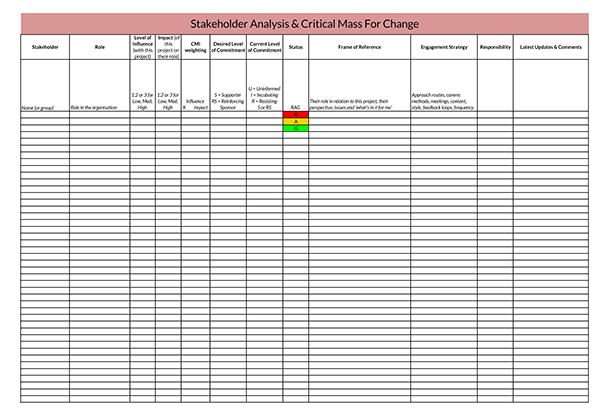
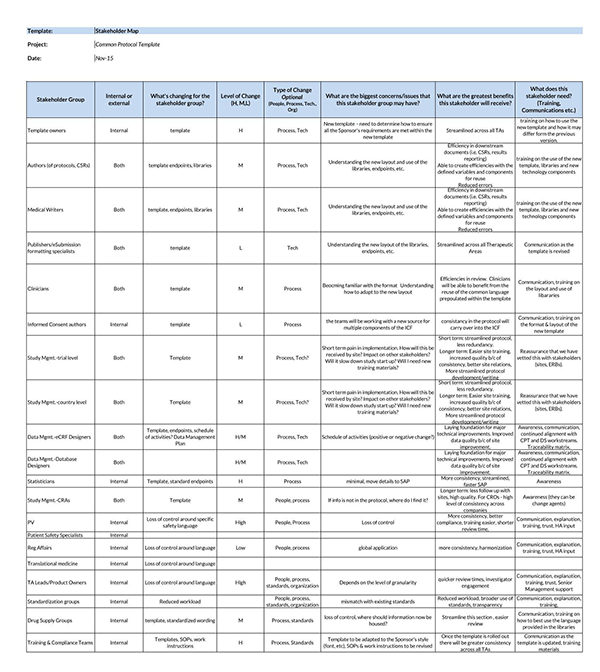
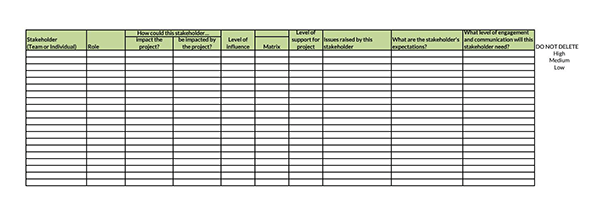
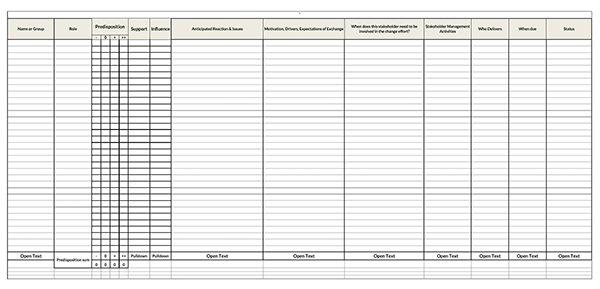
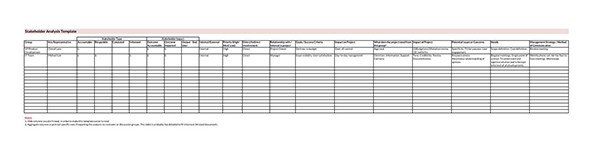
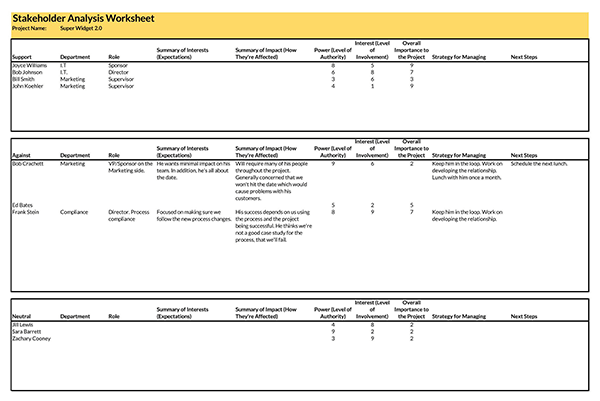
Benefits of a Stakeholder Analysis
There are several benefits of conducting the analysis for the product owner and the project. Understanding these benefits will ensure that product owners can fully utilize a template.
The following are the benefits/importance of the analysis:
Getting your projects into shape
Conducting an early analysis enables a product owner to gather input from each stakeholder on what objectives should be set. Stakeholders’ viewpoints help in identifying requirements and risks. It also helps to ease schedule management.
In addition, it eases project planning and workload allocation among team members and helps the product owner set up appropriate communication measures among the stakeholders.
Winning resources
A stockholder analysis will help the product owner acquire more resources, primarily from stakeholders interested in the project. This increases the chances of project success by ensuring areas of product development such as design, procurement, marketing, and financing, among others project aspects, are adequately resourced.
Building understanding
A product owner can also communicate and build understanding about the value of the project among stakeholders. Stakeholder analysis enables key organizational players to lay out their expectations and concerns about the project. Building understanding ensures trust is established and results in more enthusiastic participation in project development by stockholders.
Getting ahead of the game
It enables project owners to anticipate stakeholder attitudes and expectations towards a new project. This intern enables the product owner to stay ahead of the competition by presenting stakeholders with winning results of new projects. This is important because a stakeholder’s attitude has a significant impact on project success.
Formulation and outlining of policies
It enables the early formation of policies on predicted risks identified by the stakeholders. The formation and outlining of policies will ensure that the project owner can inform stakeholders on implementable solutions that can be applied to anticipated sources of conflict and cooperation. The policies are also able to ease intervention and negotiations over pressing issues.
Eases ventures into complex projects
Conducting the analysis also helps project owners to start their venture into complex projects. A project owner can achieve this by identifying stakeholders with vested interests in the projects. The project owner can then tailor communication about the project to stakeholders depending on their influence and understanding of its complexities. The tailoring of communication on complex projects ensures that stakeholders are aware of the intricacy related to the venture. This understanding increases the chances of the project’s success.
Steps to Conduct a Stakeholder Analysis
Understanding how to conduct the analysis will help ease the process of using a template. It will ensure that the product owner carries out an efficient process and will help ease project management.
The following is a step-by-step process on how to conduct the analysis:
Identify your stakeholders
A product owner must start by identifying who the stakeholders are. Brainstorming with team members can help ease and speed up the process of identification. Creating a list of all the people affected by the project or having a vested interest in its success or failure can help the identification process. The stakeholders identified could be teammates, investors, consultants, and procurement officers.
Other stakeholders may include executive staff, marketing, finance, product, heads of all business units, operations/IT, and development/engineering/manufacturing. They can also be grouped as either internal or external stakeholders.
External stakeholders are individuals or groups working outside the business or project that can affect the project outcome, while internal stockholders are those working in the project or business.
Identify stakeholders’ interest, impact level, and relative prioritize
Next, the product owner should identify the stakeholders’ interests, impact level, and relative participation. The product owner can use a chart to represent stakeholders’ viewpoints. This will help them a place to ensure each stakeholder’s viewpoints are represented and written. It will also help in identifying similar stakeholder sentiments.
Group and prioritize these stakeholders
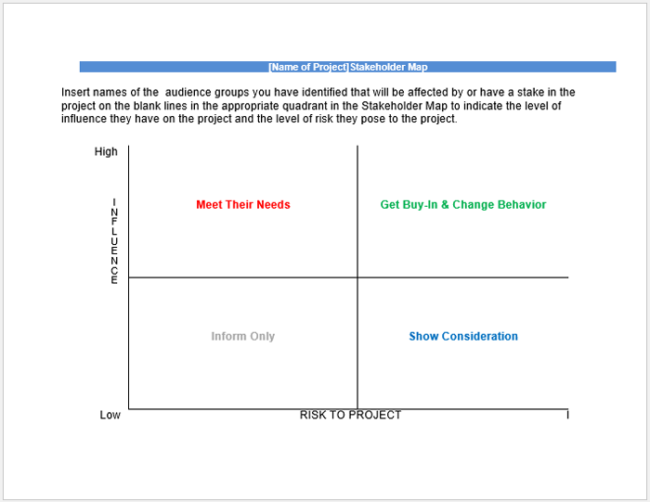
Now the product owner can group and prioritize stakeholders according to their level of influence and interest. A product owner can utilize visual tools like a Stakeholder Power Interest Grid to help assess and position the stakeholders. A stakeholder’s position on the grid will help in determining the actions the product owner should take.
Stakeholders can be categorized into the following groups:
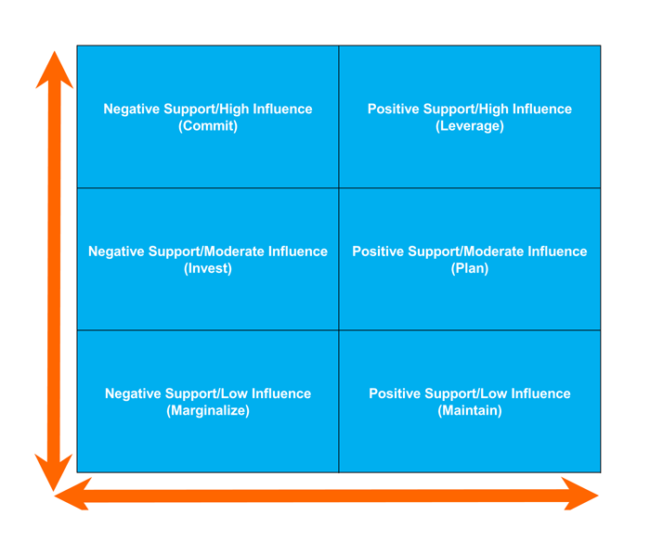
- Stakeholders with low interest and low influence: The product owner should monitor these stakeholders and provide them with information periodically. However, excessive communication with these stakeholders is unnecessary.
- Stakeholders with low interest and high influence: These people should be adequately informed and monitored to ensure no significant issues on the project arise. In addition, these stakeholders can play a supportive role in the project helping in detailing relevant project aspects.
- Stakeholders with high interest and low influence: The product owner should keep these stakeholders satisfied and informed because of their influence on the company. However, they should avoid doing too much to prevent them from being bored by messaging or over-communication.
- Stakeholders with high interest and high influence: These people should be closely managed. The product owner should fully engage and make great efforts to satisfy them because they are crucial for success.
Another approach to categorize stakeholders
The product owner can also utilize another approach to categorize stockholders. Strategies of engagement should be tailored according to the group a stockholder is placed.
The groups include the following:
- Players: Stockholders in this group should be collaborated and engaged with on a reasonably frequent basis. They have high influence and interest in the project, making them crucial for the product owner.
- Subject: Stockholders in this group should be engaged with and enabled to provide insights and ideas for the project; however, the product owner does not have to satisfy them; therefore, they can disagree or refuse to take their viewpoints if they deem it appropriate. This is because these stakeholders have a high interest in the project, but their influence is low.
- Context-setters: Stockholders in this group should be regularly consulted and updated on the project’s progress without involving them in its details. This is because they have low interest in the project but a high influence on it.
- Crowd: Stockholders in this category should be kept informed, but periodically. However, they have low interest and influence on the project; therefore, they are the least prior group of the product owner.
Understanding your stakeholders
The product owner should then focus on understanding how best they can communicate to each group/category of stakeholder. The product owner can do this by finding out the stakeholder’s motives, identifying the project information that is relevant to a stakeholder and how best information can be relayed, and finally what their current opinion on the project is or how they can help the stakeholder to form one if there is none.
Outline assumptions and risks
The product owner can follow up by outlining assumptions and risks related to the stakeholders. Making informed assumptions will ensure that stakeholders’ objectives align with those of the project. This will ensure that all stockholders work and aim for a singular objective.
Outlining risks enables the product owner and stakeholders to be prepared for any future problems that may arise. It also helps the product owner allocate roles and responsibilities appropriately according to a stakeholder’s skill set to deal with risks in a particular project area.
Define stakeholders’ participation
Finally, a product owner should define the duties of the stakeholders according to the needs of the project. This ensures that a stakeholder’s participation in the project is well outlined, enabling proper utilization of the resources. The product owner is also able to ensure that stakeholders not meant to be involved in the project throughout its lifecycle do not affect its outcome gravely.
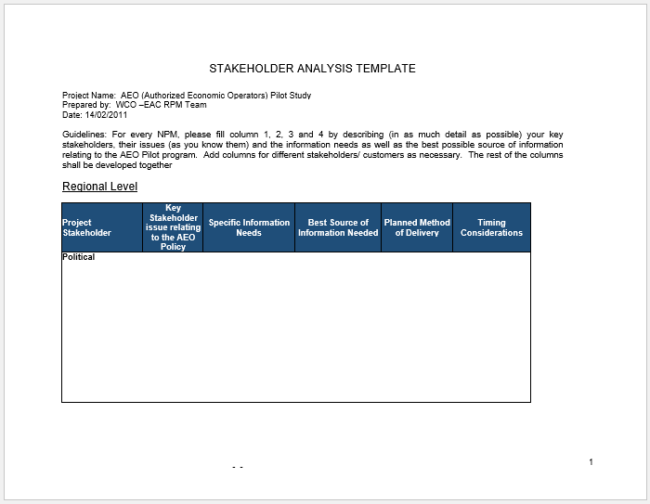
Stakeholder Analysis Templates
Conclusion
A stakeholder analysis enables a product owner to identify stakeholders in a project and assess their interest, influence, and participation. It should be conducted early to ensure that a product owner acquires adequate resources and increases project success. It also helps ensure that the project is well structured.
The stockholders of a project should be appropriately categorized according to their level of interest and influence in it. This will enable the product owner to determine how to engage and communicate with the stakeholders. In addition, understanding how to communicate with stakeholders will help product owners ensure that both project and stakeholder objectives are aligned.