A balance sheet is a financial document that indicates the financial health of a company or business. It provides a detailed picture of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder capital. In addition to this, the document further describes how each asset is financed either through debt or equity.
Put in simple terms; the sheet summarizes everything that a company owns and owes and the amount invested by shareholders. These are very vital for any business. They help troubleshoot any potential problem hence avoiding losses. Plus, they provide useful information that can help you make sound investment decisions.
Free Balance Sheet Templates
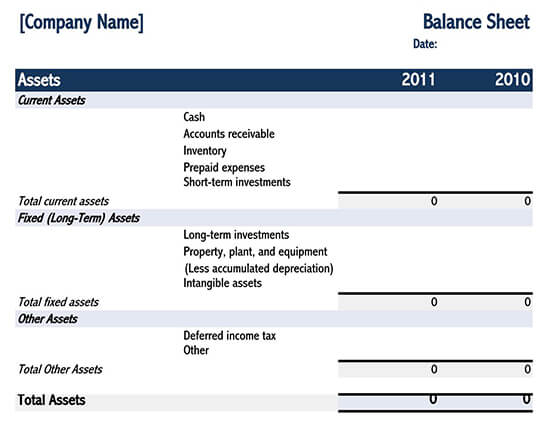
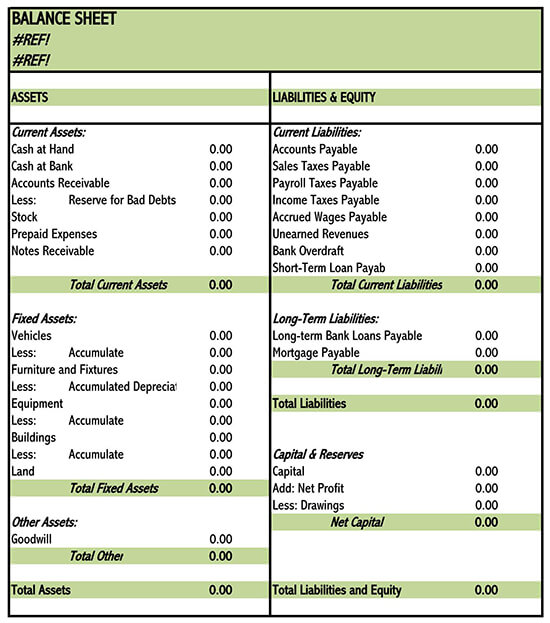
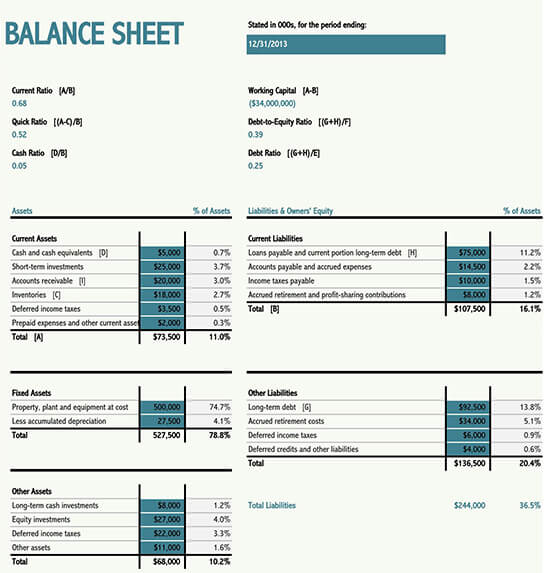
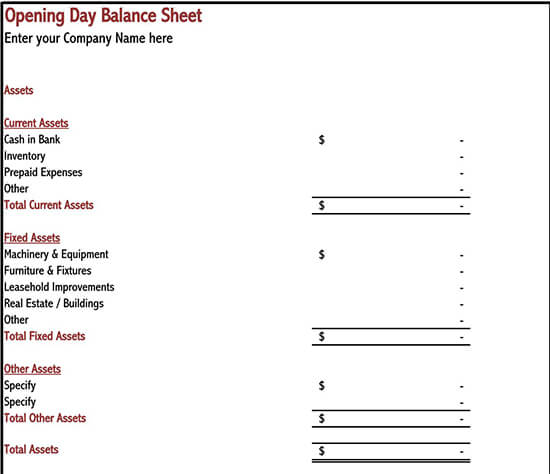


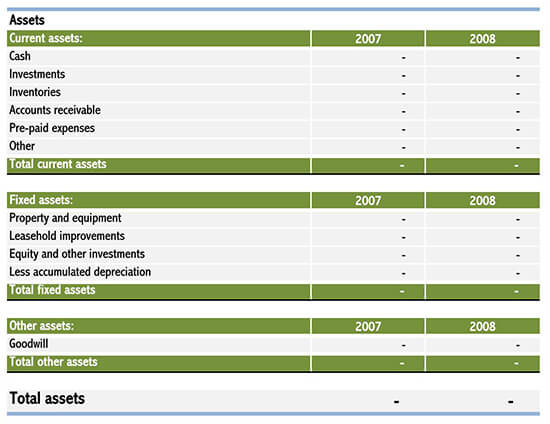
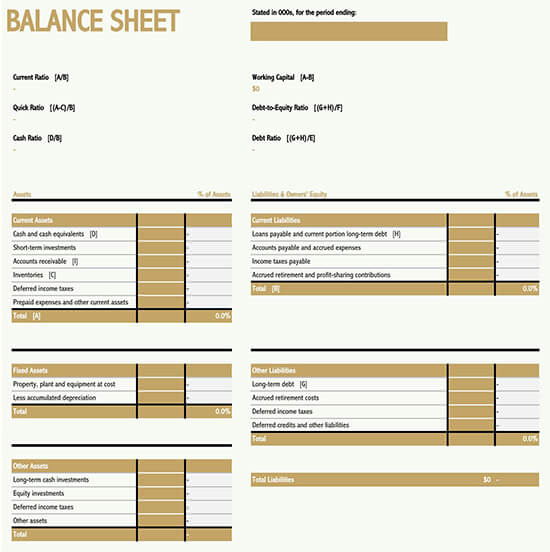
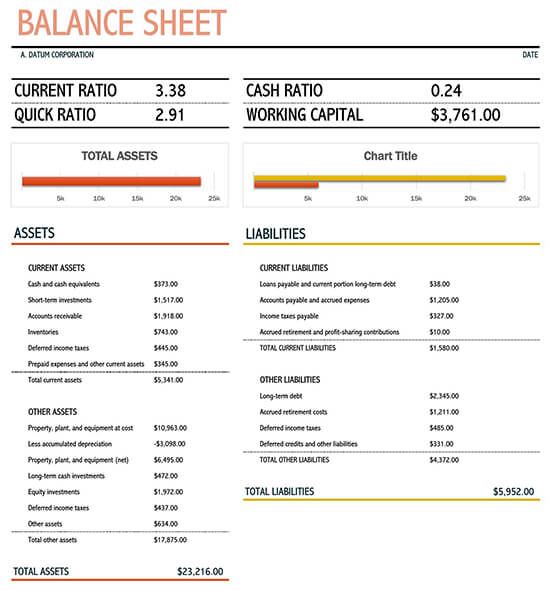
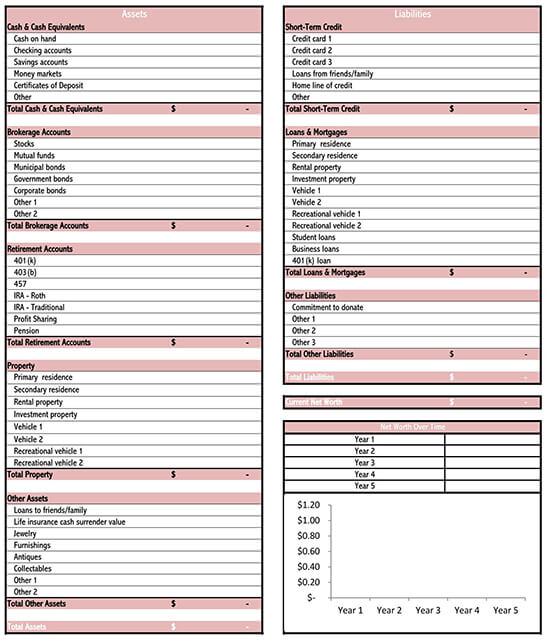
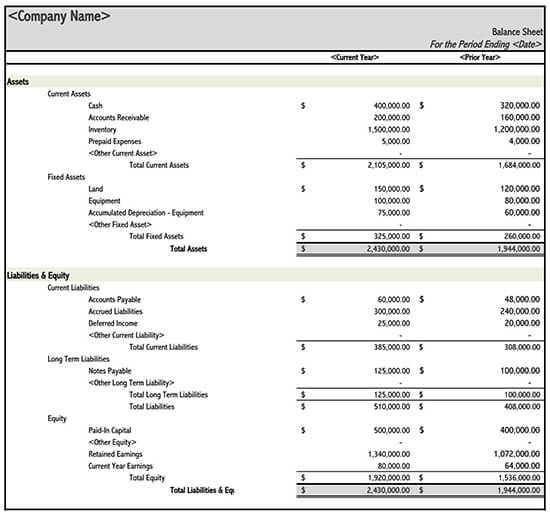

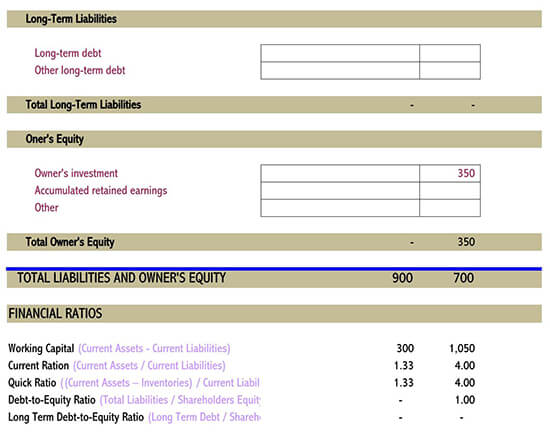
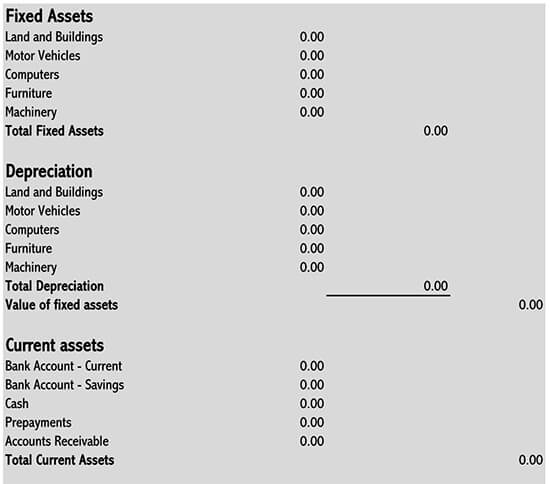
How to Read Your Balance Sheet
Understanding the operations of the sheet can be demanding, especially if you are new in the financial sector. However, by knowing specific elements, you’ll find it not only easy but more interesting.
Therefore, the following is a guide on how to read your sheet.
1. Understand current assets
In financial terms, current assists include every item that a company owns and can be converted into liquid cash within a period of one year. These items include accounts receivables, inventories and cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, and prepaid expenses, among others.
Accounts receivables
These refer to payments that your customers owe you and are due within a short duration. They may include an allowance, to mention a few.
Inventory
Inventory refers to goods that your business/company is ready to sell at market price or lower cost.
Marketable securities
These involve all the debt securities in which a liquid market exists.
Cash and its equivalents
These include money at hand, also known as liquid cash. They may either be hard cash, treasury, checks, or unrestricted bank accounts.
2. Analyze non-current assets
Contrary to the current assets, the non-current assets are those assets that can’t be converted into cash within a period of one year. In other words, they take long before being changed into cash. They are categorized into two, i.e., tangible and intangible assets.
Tangible assets
Tangible assets are physical assets such as machinery, buildings, computers, vehicles, to mention a few.
Intangible assets
They are non-physical assets owned by a company.
EXAMPLE
Goodwill, copyrights, and intellectual property.
Remember, the majority of non-current assets are calculated at a decreasing rate due to depreciation.
3. Examine liabilities
Once you’ve read the assets, it’s important that you focus on the liabilities. Liabilities, in its simplest definition, refers to everything that a company owes other parties. Usually, they are categorized into two, i.e., current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
- Current liabilities – these are liabilities that are due within a period of one year.
- Long-term liabilities– these are liabilities that are due more than one year after the reported date on the sheet. They often include loans, debts, deferred tax liability, the principal on bonds, and pension fund liability, among others.
4. Understand the shareholder’s equity
The next thing on the list after liabilities is the shareholder’s equity. Also referred to as net worth or net asset, a shareholder’s equity refers to the total amount of money attributable to the company’s owner. Put in simple terms, is the amount that the shareholder invested in the company during its formation.
EXAMPLE
An investor can start a company and fund it with $5 million. In addition to that, there is a retainer income. This also falls under the shareholder’s equity. Retainer income is the amount of net income a company decides to keep and pay it out as dividends.
Significance of Balance Sheet
The sheets play a vital role in the financial stability of your business. Therefore, having a professional sheets helps in the following.
- It helps you understand how quickly your customers are paying their bills.
- It helps you determine the amount of debt your business has in relation to its equity.
- It helps you determine whether or not your short term cash is increasing or decreasing.
- It helps you identify the number of tangible assets as well as the amount generated from accounting transactions.
- With a well-balanced sheet, you can determine the average number of days taken to completely sell your inventories.
- Through the b/sheet, you can also know whether or not the interest coverage ratio on bonds is decreasing.
Standard Formula
Usually, the sheet is divided into two parts, i.e., the debit side and the credit side. Each time, both sides must stay equal in order to balance with each other. To ensure this balance, there is a standard formula, as mentioned below:
EXAMPLE
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder equity
Whether you are a small-scale business person or an elite entrepreneur, a balance sheet is a mandatory financial document for your business. Much better, we have provided you with a free template to ease your financial balancing. The templates are straightforward and easy to read hence making you build a strong foundation for building your company/business financial statement.












