Obtaining a loan can be a significant financial decision that requires careful consideration and understanding of the loan agreement. Loan agreements are legally binding contracts that outline the terms and conditions of a loan, including repayment terms, interest rates, and other crucial details. For borrowers, it’s crucial to fully comprehend the complexities of loan agreements to make informed decisions and ensure successful borrowing.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to explain loan agreements, covering key elements such as loan terms, interest rates, collateral, repayment schedules, and more. Whether you are a first-time borrower or seeking to refine your understanding of loan agreements, this article aims to provide valuable insights and practical tips to navigate the loan agreement process with confidence and clarity.
What is Loan Agreement?
A loan agreement is a legally binding contract between a lender and a borrower that outlines the terms and conditions of a loan.
It serves as a written agreement that establishes the rights and responsibilities of both parties in relation to the loan transaction.
The agreement typically includes the following key elements:
- Loan Amount: It specifies the amount of money that is being borrowed by the borrower from the lender.
- Interest Rate: It outlines the interest rate that will be charged on the loan, which is the cost of borrowing the money.
- Repayment Terms: It includes the repayment terms, such as the installment amounts, due dates, and duration of the loan, which specify how and when the borrower is required to repay the loan.
- Security or collateral: If the loan is secured, the agreement will specify the collateral or security that the borrower is providing to the lender to secure the loan. This can be a property, a vehicle, or any other valuable asset that the lender can seize in the event of default.
- Default and Remedies: It may include provisions related to events of default, such as failure to repay the loan or breach of other terms, and the remedies available to the lender in case of default, such as late fees, penalties, or the right to accelerate the loan and demand immediate repayment.
- Governing Law and Jurisdiction: It may specify the governing law and jurisdiction that will govern the interpretation and enforcement of the agreement, which can be important in the event of disputes between the parties.
- Representations and Warranties: It may include representations and warranties made by the borrower to the lender, such as statements about the borrower’s financial condition, creditworthiness, and the purpose of the loan.
- Covenants: It may include covenants or promises made by the borrower to the lender, such as maintaining certain financial ratios, providing financial statements, or obtaining the lender’s consent for certain actions during the term of the loan.
- Other Terms: Depending on the nature of the loan, the agreement may include other terms and conditions, such as prepayment penalties, loan fees, dispute resolution mechanisms, and other provisions that are negotiated and agreed upon by the parties.
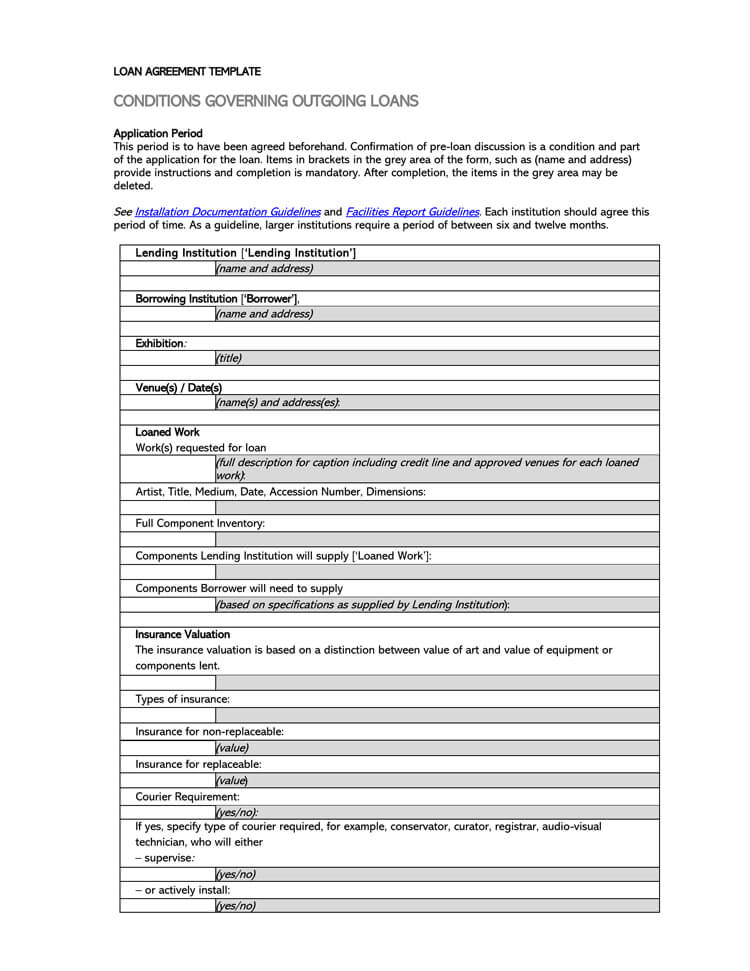
Loan Agreement Templates
Types of Loan Agreements
There are several different types of loan agreements, each with its own unique features and purposes.
Some common types of these agreements include:
Personal loan agreement
A personal loan agreement is a contract between an individual borrower and a lender for a loan used for personal purposes, such as funding education, home improvements, or other personal expenses.
Business loan agreement
It is a contract between a business borrower and a lender for a loan used for business purposes, such as financing working capital, purchasing equipment, or expanding operations.
Mortgage loan agreement
It is a contract between a borrower and a lender for a loan used to finance the purchase of a property, with the property itself serving as collateral for the loan.
Auto loan agreement
It is a contract between a borrower and a lender for a loan used to finance the purchase of a vehicle, with the vehicle serving as collateral for the loan.
Student loan agreement
It is a contract between a borrower and a lender for a loan used to finance education expenses, such as tuition, books, and living expenses, and is typically offered by financial institutions or government entities.
Payday loan agreement
It is a short-term loan agreement typically used for small amounts of money with high interest rates and fees and intended to be repaid by the borrower’s next paycheck.
Revolving credit agreement
A revolving credit agreement is a type of loan agreement that provides the borrower with a pre-approved credit limit that can be used repeatedly, with the borrower repaying and borrowing against the credit line as needed, similar to a credit card.
Bridge loan agreement
It is a short-term loan agreement that provides temporary financing to bridge the gap between two transactions, such as the purchase of a new property before the sale of an existing property.
Construction loan agreement
It is a type of the agreement used to finance the construction or renovation of a property, with the loan typically dispersed in stages, or “draws,” as the construction progresses.
These are just a few examples of the various types of loan agreements that exist. Each type of the agreement may have its own unique terms, conditions, and requirements, and it is important to carefully review and understand the specific terms and conditions of any contract before entering into it and to seek legal or financial advice if needed.
When is a Loan Agreement Necessary?
The agreements are signed for the purposes of clarifying the terms and conditions of the loan.
Here are some of the reasons why they are written:
Legal protection
An agreement serves as a legally binding contract that outlines the terms and conditions of the loan, including repayment terms, interest rate (if applicable), security or collateral (if any), late payment or default provisions, and other important provisions. Having a written contract helps protect the rights and interests of both the borrower and the lender and provides a legal framework for resolving any disputes that may arise during the loan term.
Clarity and understanding
An agreement helps ensure that both the borrower and the lender have a clear understanding of the terms and conditions of the loan. It outlines the loan amount, repayment schedule, interest rate (if applicable), and other relevant terms, which helps prevent misunderstandings or miscommunications between the parties. This can help foster a healthy borrower-lender relationship based on transparency and trust.
Compliance with applicable laws
The agreements are subject to various laws and regulations, depending on the jurisdiction and type. Writing an agreement helps ensure that the transaction complies with applicable laws, such as usury laws, consumer protection laws, and other relevant regulations.
Customization and flexibility
The agreement can be customized to suit the specific needs and requirements of the parties involved. This allows for flexibility in negotiating and documenting the terms of the loan, including repayment terms, interest rate, security or collateral, and other provisions. A written agreement provides a clear record of the agreed-upon terms, which helps avoid confusion or disagreements in the future.
Record keeping and documentation
A written agreement serves as an important piece of documentation that can be used for record keeping and evidence purposes. It provides a written record of the loan transaction, including the terms and conditions agreed upon, which can be referred to in case of any disputes or legal proceedings.
Lender’s requirements
In some cases, a lender may require a written agreement as a condition for providing a loan. Lenders may have their own internal policies or requirements for documenting loan transactions, and a written agreement may be necessary to comply with these requirements.
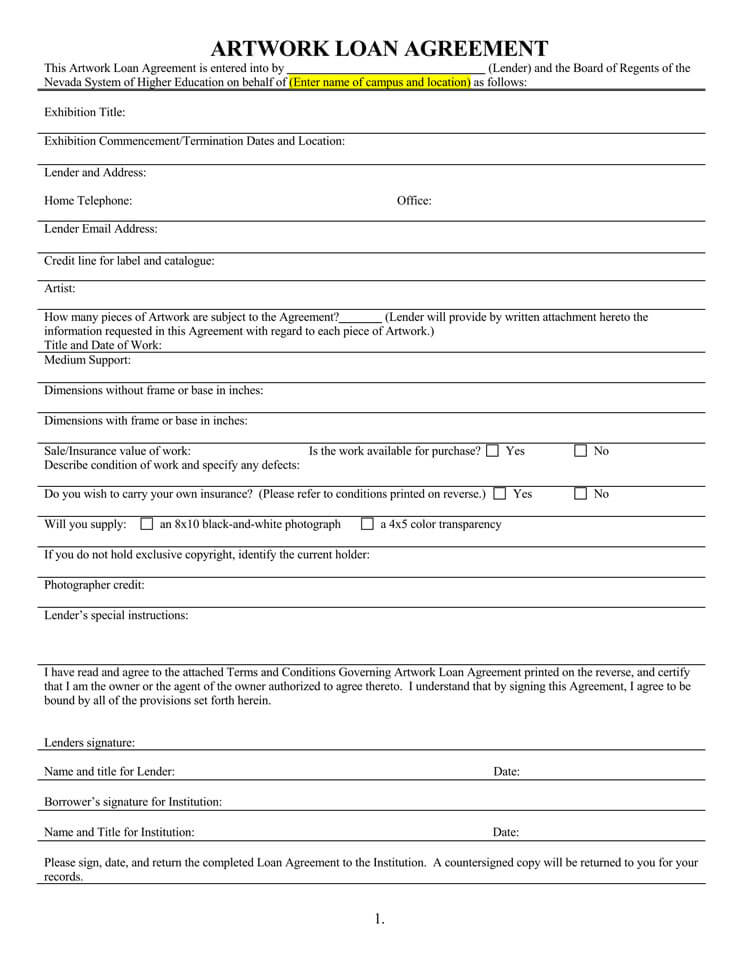
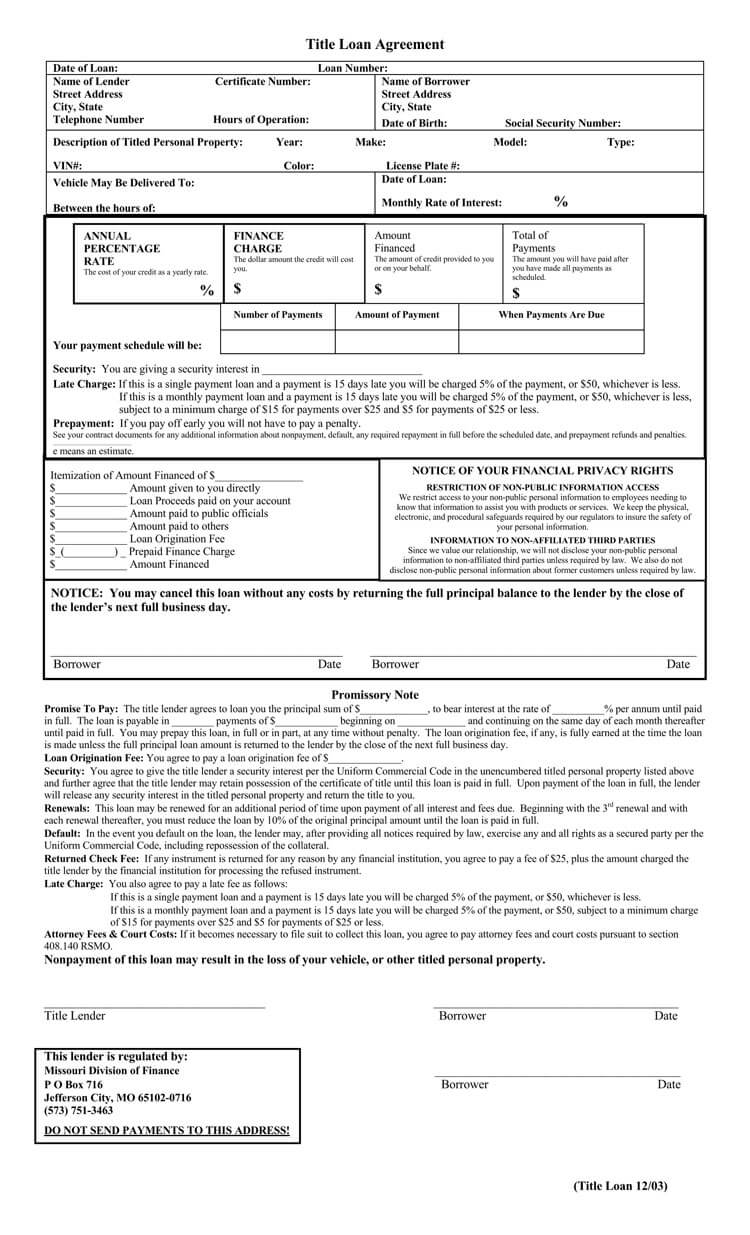
Components of Standard Loan Agreement
The elements of a loan agreement are as follows:
- Detailed contact information: The details of the borrower, the lender, the guarantors, if any, and referees and witnesses are required. The information is given on their official names, nationalities, physical postal addresses, gender, ages, and dependents.
- Maturity date: The maturity date in the agreement refers to the date on which the loan is due and payable in full. It is the date by which the borrower is obligated to repay the loan amount, including any accrued interest, fees, and other applicable charges, to the lender according to the terms and conditions of the agreement.
- Acceleration: These are details that give the lender protection from defaulting. Here the details of the payment mode, the interest, and the principal amounts are indicated.
- The principal amount: This is the money that the borrower receives. It does not include the interest or any other charges that the loans might attract.
- The interest: Lenders make their profits through interest. This is the amount added to the principal amount as payback for the loan given. Interest is always a percentage of the given amount spread across the paying period.
- Collateral: Loan security is important. Collateral is usually an asset that the borrower commits to using to recover the loan should they fail to repay it.
- Amendments: Amendments occur when, in the future, there are changes in the form of payment. Sometimes the lending institution might change localities or management, and the new information must be updated in the agreement to ensure the accuracy of the details.
- Default: Information on what constitutes defaulting, as well as associated fines, is provided here. These details are important, especially when legal action is needed later.
- The repayment schedule: If there is a possibility to pay back in installments, a repayment schedule is also indicated. The information about what happens in case of default is also mentioned. There are two types of schedules: even total and even principal payments. The lender chooses the schedule.
- Late repayment: In cases of prepayment or late payments, the agreement outlines exactly what is expected by both parties. There might be charges in some cases.
- The applicable laws: Every country has its own laws on lending money. Companies and firms also have their own that are tailored to meet legal requirements. These details are also included in some agreements as legal references.
- Loan transfer: Loan transfer, also known as loan assignment or loan assumption, refers to the transfer of an existing loan from one party (the original borrower) to another party (the new borrower). In other words, it involves changing the borrower on an existing loan without changing the terms and conditions of the loan itself.
- Joint Liability: In cases of joint and several liability, every involved party is given the details of their roles and the terms and conditions of participating.
- Security Details: The details about any collateral must be mentioned. Both parties should approve the security specifics.
- Dates and signatures: Accurate dates are given, and spaces for signatures and names are provided.
Frequently Asked Questions
In some cases, a loan agreement may contain provisions for early termination, such as prepayment options or acceleration clauses. However, such provisions, if any, should be clearly stated in the agreement. It typically requires mutual agreement and compliance with the terms and conditions of the contract.
Interest rates for loans are determined based on various factors, including the lender’s assessment of the borrower’s creditworthiness, prevailing market rates, and the type of loan being offered.
Defaulting on a loan agreement typically triggers consequences outlined in the agreement, such as late fees, penalties, acceleration of repayment, or other remedies available to the lender. Understanding the default provisions in the agreement and being aware of the potential consequences of default are important.
Loaning money to someone with bad credit is a risk that one should really think through before going ahead with it. If someone has a bad credit rating, they are likely to default on the loan if it is granted. However, there are people who have been badly rated for genuine reasons. Before lending, it is good to do background research on why the person was poorly rated. Here, an informed decision can be made.
It may be possible to obtain a loan even with a bad credit rating, but it can be more challenging. Lenders typically consider credit ratings as an indicator of a borrower’s creditworthiness, and a low credit score can affect the terms and conditions of a loan. Borrowers with a bad credit rating may face higher interest rates, stricter loan terms, or may need to provide additional collateral or guarantors to secure a loan.
However, some lenders specialize in offering loans to borrowers with poor credit ratings, often referred to as “bad credit loans” or “subprime loans.” These loans may have higher interest rates or fees, but they can provide an option for borrowers who have difficulty obtaining loans from traditional lenders due to their credit histories.
A subsidized loan is a type of federal student loan available to undergraduate students with financial need. It is offered by the U.S. Department of Education and is designed to help students cover the cost of their education. Unlike unsubsidized loans, which accrue interest while the borrower is in school, a subsidized loan does not accrue interest during certain periods, making it a more cost-effective borrowing option for eligible students.
Sharking occurs when money is given to individuals or companies to manage a business or work on income and profit-generating ideas. The sharks give money and expect returns after investments. The sharks additionally hold full or partial ownership of the company until the amount agreed on is fully paid, along with the estimated profits.
When one consolidates a loan, all of their outstanding debts are combined and paid off together under new loan terms and conditions. Loan consolidations are considered for their low interest rates and the ability to focus on one loan rather than many. Larger loans are used to pay small ones in this case.
A Parent PLUS loan is a type of federal student loan available to parents of dependent undergraduate students who are enrolled in eligible colleges or universities. It is designed to help parents cover the cost of their child’s education. The Parent PLUS loan is offered by the U.S. Department of Education and requires a separate application process from other federal student loans.